Last Year`s Midterm Solutions
... What questions would you pose in order to be able to properly answer question i) asked by your boss? List as many relevant questions you can think of. Marks will be given for consistent, relevant questions that would quickly resolve the issue. 1)Are the units for the Electric field not V/m? 2)Are th ...
... What questions would you pose in order to be able to properly answer question i) asked by your boss? List as many relevant questions you can think of. Marks will be given for consistent, relevant questions that would quickly resolve the issue. 1)Are the units for the Electric field not V/m? 2)Are th ...
lecture 36 - waves in 3 dimensions, optical devices
... No office hours tomorrow (neither TA nor I), even though we do have class. Exam 3 starts Tuesday after the break. Lab 10 (final lab) going on right now. Due the Tuesday after the break. ...
... No office hours tomorrow (neither TA nor I), even though we do have class. Exam 3 starts Tuesday after the break. Lab 10 (final lab) going on right now. Due the Tuesday after the break. ...
pupil function - UCT Digital Image Processing
... CCDs can be scanned at television rates (25 frames per second) or much more slowly. Since they can integrate for periods of seconds to hours to create low-light images, they are used in astronomy and florescence microscopy, for example. The long integration times require that the sensor be cooled to ...
... CCDs can be scanned at television rates (25 frames per second) or much more slowly. Since they can integrate for periods of seconds to hours to create low-light images, they are used in astronomy and florescence microscopy, for example. The long integration times require that the sensor be cooled to ...
A1982PU06800001
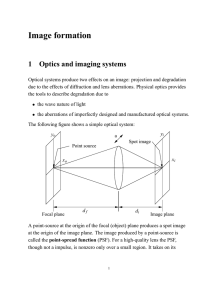
... Some time later it was shown that this extra term was equal to zero, and 4 that our solution was indeed correct. “One reason for this paper being cited many times may be that the three parts of the paper are separably useful in other problems in optics. For example, when the paper was written there ...
... Some time later it was shown that this extra term was equal to zero, and 4 that our solution was indeed correct. “One reason for this paper being cited many times may be that the three parts of the paper are separably useful in other problems in optics. For example, when the paper was written there ...
Topic 4 Waves - MrSimonPorter
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
... Wavelength is the shortest distance along a wave between two points that are in phase. Phase difference is the time difference or phase angle by which one wave leads or lags another. Wave speed is the speed at which wavefronts pass a stationary observer. Intensity - The average amount of energy tran ...
1051-733-20092 Homework #1 Due 12/09/2000 (W)
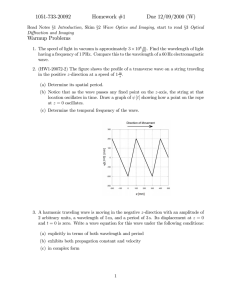
... (b) Show that the two-dimensional sinusoidal part of this function contributions ALL of the volume and that the cosine part contributes none. 6. Consider propagation over the distance z1 and then over the distance z2 , where both distances satisfy the conditions for Fresnel diffraction. Show that a s ...
... (b) Show that the two-dimensional sinusoidal part of this function contributions ALL of the volume and that the cosine part contributes none. 6. Consider propagation over the distance z1 and then over the distance z2 , where both distances satisfy the conditions for Fresnel diffraction. Show that a s ...
Week7-animations
... • The wave is INPUT at z=0 with an input wave f(x,y)=U(x,y,0). • The wave propagates through a distance d. • The output wave at z=d is given by g(x,y)=U(x,y,d). ...
... • The wave is INPUT at z=0 with an input wave f(x,y)=U(x,y,0). • The wave propagates through a distance d. • The output wave at z=d is given by g(x,y)=U(x,y,d). ...