TEP 2.6.11-00 Fourier optics – 2f Arrangement TEP 2.6.11
... assumption that a spherical wave emanates from each point (x,y,0) behind the diffracting structure (Huygens’ principle). This leads to Kirchhoff’s diffraction integral: ...
... assumption that a spherical wave emanates from each point (x,y,0) behind the diffracting structure (Huygens’ principle). This leads to Kirchhoff’s diffraction integral: ...
depending on the wave - Rowan County Schools
... Period (T): how long it takes for a single wave to pass a single point. seconds Frequency (f): number of waves that pass a given point in a time period of one second. Hertz (Hz) = 1/s Q. What is the period of a 60 Hz wave traveling at 3.0 x 108 m/s? ...
... Period (T): how long it takes for a single wave to pass a single point. seconds Frequency (f): number of waves that pass a given point in a time period of one second. Hertz (Hz) = 1/s Q. What is the period of a 60 Hz wave traveling at 3.0 x 108 m/s? ...
Interference
... • Use the following applet to help explore the different interference patterns produced by single, double and multiple slits... ...
... • Use the following applet to help explore the different interference patterns produced by single, double and multiple slits... ...
Document
... Fourier transform of the transparency times a spherical wavefront • The lens produces at its focal plane the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of the transparency • When the transparency is placed exactly one focal distance behind the lens (i.e., z=f ), the Fourier transform relationship is exact. ...
... Fourier transform of the transparency times a spherical wavefront • The lens produces at its focal plane the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of the transparency • When the transparency is placed exactly one focal distance behind the lens (i.e., z=f ), the Fourier transform relationship is exact. ...
Monochromatic plane waves ( ) Plane waves have straight wave fronts
... A homogeneous surface perpendicular to say the z direction can not change the transverse momentum. Since the propagation vector is proportional to the photon's momentum, the transverse propagation direction (kx,ky,0) must remain the same in both regions. Assuming without loss of generality a plane o ...
... A homogeneous surface perpendicular to say the z direction can not change the transverse momentum. Since the propagation vector is proportional to the photon's momentum, the transverse propagation direction (kx,ky,0) must remain the same in both regions. Assuming without loss of generality a plane o ...
Fourier Spectra for Non-Homogeneous Patterns
... using bands much smaller than t:.k (lop I) for any particular band centered on k. If there is reason to believe that the spectrum is relatively smooth, then one might be able to use bands much wider than this. In general, it turns out to be impossible to construct a mosaic from hands of constant t:. ...
... using bands much smaller than t:.k (lop I) for any particular band centered on k. If there is reason to believe that the spectrum is relatively smooth, then one might be able to use bands much wider than this. In general, it turns out to be impossible to construct a mosaic from hands of constant t:. ...
10NonlinearOptics.pdf
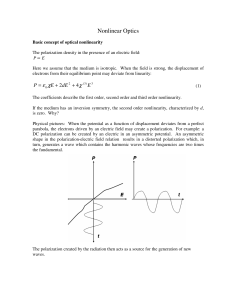
... If the medium has an inversion symmetry, the second order nonlinearity, characterized by d, is zero. Why? Physical pictures: When the potential as a function of displacement deviates from a perfect parabola, the electrons driven by an electric field may create a polarization. For example: a DC polar ...
... If the medium has an inversion symmetry, the second order nonlinearity, characterized by d, is zero. Why? Physical pictures: When the potential as a function of displacement deviates from a perfect parabola, the electrons driven by an electric field may create a polarization. For example: a DC polar ...
Surface waves
... Surface waves A semi-infinite, homogeneous medium fills the x > 0 region. The optical properties of the medium are described by a dielectric function ε = ε(ω) having real values in the frequency range of interest. A monochromatic EM wave propagates along the y-direction, parallel to the surface of t ...
... Surface waves A semi-infinite, homogeneous medium fills the x > 0 region. The optical properties of the medium are described by a dielectric function ε = ε(ω) having real values in the frequency range of interest. A monochromatic EM wave propagates along the y-direction, parallel to the surface of t ...
Optical Diffraction and Image Formation
... diffraction pattern from that slide, which corresponds to the intensities (= Amplitudes2) of the Fourier transformation of the slide image. If the slide, for example, shows some lines, then the distant wall will show the diffraction peaks from those lines. The Fraunhofer theory explains how that sha ...
... diffraction pattern from that slide, which corresponds to the intensities (= Amplitudes2) of the Fourier transformation of the slide image. If the slide, for example, shows some lines, then the distant wall will show the diffraction peaks from those lines. The Fraunhofer theory explains how that sha ...
doc - University of Rochester
... Ghost imaging with entangled photon pairs (biphotons) has been extensively discussed in the literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this ...
... Ghost imaging with entangled photon pairs (biphotons) has been extensively discussed in the literature [1,2]. Recently, the question of whether the resolution of ghost imaging is improved using non-degenerate biphotons (biphotons with pairs of photons of different frequency) has been raised. In this ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (a) Explain the action of a half wave plate when a plane polarized light is incident normally on it. (b) Calculate the thickness of a half wave plate for light of wavelength 6000Å. Given µe= 1.553 and µ0=1.533.(2.5). ...
... (a) Explain the action of a half wave plate when a plane polarized light is incident normally on it. (b) Calculate the thickness of a half wave plate for light of wavelength 6000Å. Given µe= 1.553 and µ0=1.533.(2.5). ...
Wave equation
... This is the differential equation that describes the propagation of dissipationless, dispersionless waves. This derivation will be inductive and general. For each specific case like tension waves on a string or sound waves in the air, it is also possible to give a detailed deductive derivation that ...
... This is the differential equation that describes the propagation of dissipationless, dispersionless waves. This derivation will be inductive and general. For each specific case like tension waves on a string or sound waves in the air, it is also possible to give a detailed deductive derivation that ...







![Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008906603_1-55857b6efe7c28604e1ff5a68faa71b2-300x300.png)