6,
... High diffraction efficiency may be achieved, particulary when generating HOEs as thick phase holograms ; in this case, however, the image field and wavelength range are restricted by volume effects. Since thick holograms present these angular and wavelength selectivities, it is possible to realize a ...
... High diffraction efficiency may be achieved, particulary when generating HOEs as thick phase holograms ; in this case, however, the image field and wavelength range are restricted by volume effects. Since thick holograms present these angular and wavelength selectivities, it is possible to realize a ...
Reflection and Refraction of Plane Waves
... Reflectance and Transmittance • The Fresnel formulas give the ratios of the amplitude of the reflected wave and the transmitted wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. • The power flow parallel to the boundary surface is unaffected and is a constant throughout the medium. • As far as the reflec ...
... Reflectance and Transmittance • The Fresnel formulas give the ratios of the amplitude of the reflected wave and the transmitted wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. • The power flow parallel to the boundary surface is unaffected and is a constant throughout the medium. • As far as the reflec ...
optical/photonic bandwidth
... The term bandwidth is also often used for the data rate—that is, in Gigabytes per seconds achieved in an optical communication system. Precisely, the data rate is limited by the optical bandwidth, but is not really itself a bandwidth. The optical bandwidth of a light source is strongly related to th ...
... The term bandwidth is also often used for the data rate—that is, in Gigabytes per seconds achieved in an optical communication system. Precisely, the data rate is limited by the optical bandwidth, but is not really itself a bandwidth. The optical bandwidth of a light source is strongly related to th ...
4.6.2 Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction
... • Then, any reflected or refracted wave must also have frequency and a wave vector , ′ for any integer . ...
... • Then, any reflected or refracted wave must also have frequency and a wave vector , ′ for any integer . ...
On Classical Electromagnetic Fields (cont
... We are looking for a wave propagating in, say, the z-direction, so we write a particular component of the potential in the form [ III-2 ] In Equation [ III-2 ], the function represents a spatial modulation or "masking" of a plane wave propagating in the z-direction. The z-direction is obviously spec ...
... We are looking for a wave propagating in, say, the z-direction, so we write a particular component of the potential in the form [ III-2 ] In Equation [ III-2 ], the function represents a spatial modulation or "masking" of a plane wave propagating in the z-direction. The z-direction is obviously spec ...
An Introduction to Propagation, Time Reversal and Imaging in
... governed by the scalar wave equation while the electromagnetic wave in dielectric media is governed by the vector wave equation for its vector potential. In media such as the earth’s turbulent atmosphere there is negligible depolarization. Thus, by restricting the source to be linearly polarized or ...
... governed by the scalar wave equation while the electromagnetic wave in dielectric media is governed by the vector wave equation for its vector potential. In media such as the earth’s turbulent atmosphere there is negligible depolarization. Thus, by restricting the source to be linearly polarized or ...
as a PDF - Department of Engineering Science
... In what follows we shall confine ourselves to the class of optical systems that are rotationally symmetric about the optic axis and so it is possible to restrict our analysis to the meridional plane without loss of generality. A concept that is useful when considering optical instruments is that of ...
... In what follows we shall confine ourselves to the class of optical systems that are rotationally symmetric about the optic axis and so it is possible to restrict our analysis to the meridional plane without loss of generality. A concept that is useful when considering optical instruments is that of ...
Investigate molecules with light
... An electron building generates, because of his position, an electric force in the surrounding space, the electric field, which decreases as the inverse square of the distance. By swinging a first electron, the electric field is perturbed at the points around due to the change from the electron durin ...
... An electron building generates, because of his position, an electric force in the surrounding space, the electric field, which decreases as the inverse square of the distance. By swinging a first electron, the electric field is perturbed at the points around due to the change from the electron durin ...
Word 97 Format
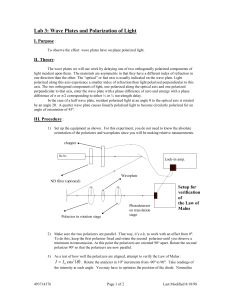
... 4) Place the half wave plate in the 1” rotation stage and put it in between the polarizers. To check alignment, let both polarizers stay at 00 and rotate the half wave plate until you see a minimum in intensity. This corresponds to the half wave plate making an angle of 45 o with respect to the pola ...
... 4) Place the half wave plate in the 1” rotation stage and put it in between the polarizers. To check alignment, let both polarizers stay at 00 and rotate the half wave plate until you see a minimum in intensity. This corresponds to the half wave plate making an angle of 45 o with respect to the pola ...
Waves
... metres (m). It is NOT the height from crest to trough Wave velocity, v, is the speed of propagation of the wave in metres per second (ms-1). In air, sound waves propagate at 340 ms-1. The speed of light in a vacuum, c, is a constant and is 3 x 108 ms-1 ...
... metres (m). It is NOT the height from crest to trough Wave velocity, v, is the speed of propagation of the wave in metres per second (ms-1). In air, sound waves propagate at 340 ms-1. The speed of light in a vacuum, c, is a constant and is 3 x 108 ms-1 ...
... conductivity). The highly predictive character of the expressions derived by Kogelnik made his work one of the most cited by holographic researchers. Nonetheless Kogelnik’s theory assumed some approximations that make it inaccurate for some cases, such as dielectric gratings that are not sinusoidal ...
РЕФЕРАТ
... Object of study is the process of converting the light field in the coherent optical spectrum analyzers by performing spatial Fourier transform of the test signal. The subject of the study is the generalized characteristics of the coherent spectrum analyzers such as the working range of spatial freq ...
... Object of study is the process of converting the light field in the coherent optical spectrum analyzers by performing spatial Fourier transform of the test signal. The subject of the study is the generalized characteristics of the coherent spectrum analyzers such as the working range of spatial freq ...
6.2 Refraction
... When propagating from a higher refractive index region into a region with a lower refractive index, the largest angle that will be transmitted is the critical angle. Light impinging on the refractive index boundary at angles greater than the critical angle will undergo ____________________. The wave ...
... When propagating from a higher refractive index region into a region with a lower refractive index, the largest angle that will be transmitted is the critical angle. Light impinging on the refractive index boundary at angles greater than the critical angle will undergo ____________________. The wave ...
Observation of near-field correlations in spontaneous parametric
... physical origin of this structure can be understood as follows. The crystal acts as a longitudinally extended source of photon pairs. The phase-matching conditions determine the relative phase of photon pairs born at different planes within the pumped region. The final probability amplitude of detec ...
... physical origin of this structure can be understood as follows. The crystal acts as a longitudinally extended source of photon pairs. The phase-matching conditions determine the relative phase of photon pairs born at different planes within the pumped region. The final probability amplitude of detec ...
+ (Z 2 +Z 1 )
... Optics: Modes and occupation number A mode is defined by its throughput: A = 2 The occupation number of a mode is the number of photons in that mode per unit bandwidth ...
... Optics: Modes and occupation number A mode is defined by its throughput: A = 2 The occupation number of a mode is the number of photons in that mode per unit bandwidth ...
6288-18 talk - LOFT, Large Optics Fabrication and Testing group
... Afocal systems • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...
... Afocal systems • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...
Slide 1
... Afocal systems • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...
... Afocal systems • For system with object or image at infinity, effect of element motion is tilt in the light. ...