Ring_Laser_crystal resonator
... The Series 125 uses Nd:YAG as the gain medium. This material typically is known for providing gain at 1064 nm; however, it also produces significant gain at a wavelength of 1319 nm. The Series 125 Nd: YAG NPRO may be coated so that it emits at a wavelength of 1064 or 1319 nm.. While Nd:YAG can emit ...
... The Series 125 uses Nd:YAG as the gain medium. This material typically is known for providing gain at 1064 nm; however, it also produces significant gain at a wavelength of 1319 nm. The Series 125 Nd: YAG NPRO may be coated so that it emits at a wavelength of 1064 or 1319 nm.. While Nd:YAG can emit ...
Size reduction
... different scenarios are possible. The oral bioavailability of the solubilized systems is far better than the performance of both the micronized and the nanonized system, whereas there is almost now difference of the performance of the micronized system and the nanonized system. In this case the comp ...
... different scenarios are possible. The oral bioavailability of the solubilized systems is far better than the performance of both the micronized and the nanonized system, whereas there is almost now difference of the performance of the micronized system and the nanonized system. In this case the comp ...
Quantum Dots in Semiconductor Optoelectronic Devices
... Because nano-size is of the same order as the Bohr exciton radius of electron-hole pairs in solids, SQDs exhibit quantum size effects, essentially those of quantum mechanical particles in a threedimensional box. 2 The electronic transition energy from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to ...
... Because nano-size is of the same order as the Bohr exciton radius of electron-hole pairs in solids, SQDs exhibit quantum size effects, essentially those of quantum mechanical particles in a threedimensional box. 2 The electronic transition energy from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to ...
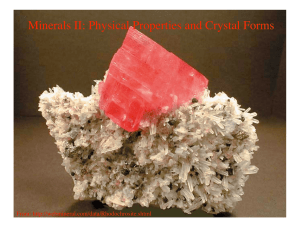
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn’t vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compa ...
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn’t vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compa ...
Physical properties of minerals
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn't vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compar ...
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn't vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compar ...
What is a mineral?
... a pattern that is repeated over and over again. For example, graphite atoms are arranged in layers, but an opal (gemstone) is not a mineral because the pattern does not repeat. ...
... a pattern that is repeated over and over again. For example, graphite atoms are arranged in layers, but an opal (gemstone) is not a mineral because the pattern does not repeat. ...
Chapter 4
... Second Phase • While solute atoms are being added, new compounds / structures may form beyond solubility limit, or solute forms local PRECIPITATES. • Nature of the impurities, their concentration, reactivity, temperature and pressure, etc decides the formation of solid solution or a second phase. S ...
... Second Phase • While solute atoms are being added, new compounds / structures may form beyond solubility limit, or solute forms local PRECIPITATES. • Nature of the impurities, their concentration, reactivity, temperature and pressure, etc decides the formation of solid solution or a second phase. S ...
07_chapter 2
... where Ccryst is the capacitance of the crystal, Cair is the capacitance of same dimension of air, Acryst is the area of the crystal and Aair is the area of same dimension of air. The observations were made while cooling the sample in the frequency range 1 KHz to 1 MHz at the temperature 40oC to100oC ...
... where Ccryst is the capacitance of the crystal, Cair is the capacitance of same dimension of air, Acryst is the area of the crystal and Aair is the area of same dimension of air. The observations were made while cooling the sample in the frequency range 1 KHz to 1 MHz at the temperature 40oC to100oC ...
RESEARCH/RESEARCHERS
... cently, a number of groups have shown that four-wave-mixing (4WM) in silica optical fibers can generate high-quality quantum-correlated photon pairs with much higher spectral brightness than achievable by PDC, but this approach appears to be limited by spontaneous Raman scattering (SRS) in the amorp ...
... cently, a number of groups have shown that four-wave-mixing (4WM) in silica optical fibers can generate high-quality quantum-correlated photon pairs with much higher spectral brightness than achievable by PDC, but this approach appears to be limited by spontaneous Raman scattering (SRS) in the amorp ...
Review of the Dissertation of Elena S. Zhitova «Crystal Chemistry of
... The dissertation of Elena Zhitova contains results of the first detailed crystal chemical study of rare mineral quintinite from the Kovdor alkaline massif (Kola peninsula, Russia) and the Bazhenovo ultrabasic massif (the Middle Urals, Russia). Selection of quintinite as the object of research is due ...
... The dissertation of Elena Zhitova contains results of the first detailed crystal chemical study of rare mineral quintinite from the Kovdor alkaline massif (Kola peninsula, Russia) and the Bazhenovo ultrabasic massif (the Middle Urals, Russia). Selection of quintinite as the object of research is due ...
JaegerCh01overview2015
... • crystal layer thickness beyond which the strained layer can no longer withstand the strain energy (about 100 to 500 Angstrom%) • Strain balancing: alternate layers of compressivelystrained layers with tensile-strained layers (allows exceeding “critical thickness”) • crystal will return to it’s nat ...
... • crystal layer thickness beyond which the strained layer can no longer withstand the strain energy (about 100 to 500 Angstrom%) • Strain balancing: alternate layers of compressivelystrained layers with tensile-strained layers (allows exceeding “critical thickness”) • crystal will return to it’s nat ...
Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 - Handbook of Mineralogy
... rocks and marbles; a gangue in hydrothermal veins; in carbonatites and ultramafic rocks. Association: Fluorite, barite, calcite, siderite, quartz, metal sulfides (hydrothermal); calcite, celestine, gypsum, quartz (sedimentary); talc, serpentine, magnesite, calcite, magnetite, diopside, tremolite, fo ...
... rocks and marbles; a gangue in hydrothermal veins; in carbonatites and ultramafic rocks. Association: Fluorite, barite, calcite, siderite, quartz, metal sulfides (hydrothermal); calcite, celestine, gypsum, quartz (sedimentary); talc, serpentine, magnesite, calcite, magnetite, diopside, tremolite, fo ...
Minerals Study guide Chapter 4 Sections 1 and 2 pgs. 114
... cools the atom(s) leave the solution and crystallize as minerals. ●A SOLUTION is a mixture in which one substance dissolves in another. (Sugar dissolved in water makes a solution). 3. Minerals form by Evaporation ●If you stir salt crystals into a cup of water, the salt dissolves in the water. When t ...
... cools the atom(s) leave the solution and crystallize as minerals. ●A SOLUTION is a mixture in which one substance dissolves in another. (Sugar dissolved in water makes a solution). 3. Minerals form by Evaporation ●If you stir salt crystals into a cup of water, the salt dissolves in the water. When t ...
Formation of intermetallic compounds upon cooling of Sn1
... Upon cooling below the liquidus temperature the crystalline phase appears. The analysis of the diffraction patterns recorded at a temperature corresponding to a two-phase mixture and at room temperature revealed the crystallization of ZrSn2 and tin. These two phases exist also at room temperature, w ...
... Upon cooling below the liquidus temperature the crystalline phase appears. The analysis of the diffraction patterns recorded at a temperature corresponding to a two-phase mixture and at room temperature revealed the crystallization of ZrSn2 and tin. These two phases exist also at room temperature, w ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE 6.0/HP
... form. The formation of igneous & metamorphic rocks destroys and organic matter of fossil contained within. ...
... form. The formation of igneous & metamorphic rocks destroys and organic matter of fossil contained within. ...
R-29_ChenYQ.pdf
... appropriate elastic-plastic constitutive relation with failure strain value is used to describe the material behavior and failure in elements. During the displacement-controlled loading, the different elements would be in different stages of deformation, i.e. linear elastic stage and plastic stage. ...
... appropriate elastic-plastic constitutive relation with failure strain value is used to describe the material behavior and failure in elements. During the displacement-controlled loading, the different elements would be in different stages of deformation, i.e. linear elastic stage and plastic stage. ...
2.6 Summary 2.6.1 Summary to: 2. Semiconductor Materials and Products
... Germanium (Ge) and SiC Germanium was almost "useless" but is experiencing some comeback now (2007) in conjunction with Si technology. SiC is very difficult to obtain as a good single crystal (many polytypes) but has some desirable properties for high speed or high power devices II-Vl semiconductors ...
... Germanium (Ge) and SiC Germanium was almost "useless" but is experiencing some comeback now (2007) in conjunction with Si technology. SiC is very difficult to obtain as a good single crystal (many polytypes) but has some desirable properties for high speed or high power devices II-Vl semiconductors ...
using standard syste
... In the past decade, photonic crystals, also known as photonic band-gap 共PBG兲 materials,1,2 have inspired great interest because of their scientific and engineering applications such as the inhibition of spontaneous emission,3 lasers,4–6 waveguides,7–10 fibers,11 antennas,12,13 detectors,14 optical c ...
... In the past decade, photonic crystals, also known as photonic band-gap 共PBG兲 materials,1,2 have inspired great interest because of their scientific and engineering applications such as the inhibition of spontaneous emission,3 lasers,4–6 waveguides,7–10 fibers,11 antennas,12,13 detectors,14 optical c ...
0378.PDF
... The second goal is to find out if new kinds of defects occur in the quasicrystal. By definition, a real shock wave in a crystal (as opposed to a very strong elastic wave) causes permanent plastic deformation. Usually stacking faults are found caused by slippage or twinning and martensitic deformati ...
... The second goal is to find out if new kinds of defects occur in the quasicrystal. By definition, a real shock wave in a crystal (as opposed to a very strong elastic wave) causes permanent plastic deformation. Usually stacking faults are found caused by slippage or twinning and martensitic deformati ...
1. The central core of the atom, containing protons and usually
... A representation of the number of valence electrons in an atom, using dots placed around the symbol of an element ...
... A representation of the number of valence electrons in an atom, using dots placed around the symbol of an element ...
tutorial - Artifex Engineering
... ultraviolet to beyond 7.0um in the infra red. Because suitable index matching cements do not transmit below 220nm, magnesium fluoride polarizers are manufactured by optically contacting the two prisms. Thin plates can be manufactured from this material for use in achromatic retardation plates. In th ...
... ultraviolet to beyond 7.0um in the infra red. Because suitable index matching cements do not transmit below 220nm, magnesium fluoride polarizers are manufactured by optically contacting the two prisms. Thin plates can be manufactured from this material for use in achromatic retardation plates. In th ...
Normal version 1.00
... particular emphasis of recent work is the understanding of fracture processes in multilayer coatings and the development of predictive modelling approaches to provide data for design. He is currently working on the fracture properties of solar control coatings on glass, Whereas relatively simple bul ...
... particular emphasis of recent work is the understanding of fracture processes in multilayer coatings and the development of predictive modelling approaches to provide data for design. He is currently working on the fracture properties of solar control coatings on glass, Whereas relatively simple bul ...
BASICS OF DIELECTRIC MATERIALS
... • Piezoelectricity is a coupling between a material's mechanical and electrical behaviors. • In the simplest of terms, when a piezoelectric material is squeezed, an electric charge collects on its surface. Conversely, when a piezoelectric material is subjected to a voltage drop, it mechanically defo ...
... • Piezoelectricity is a coupling between a material's mechanical and electrical behaviors. • In the simplest of terms, when a piezoelectric material is squeezed, an electric charge collects on its surface. Conversely, when a piezoelectric material is subjected to a voltage drop, it mechanically defo ...
Colloidal crystal

A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles, analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where spheres of silica assume a close-packed locally periodic structure under moderate compression. Bulk properties of a colloidal crystal depend on composition, particle size, packing arrangement, and degree of regularity. Applications include photonics, materials processing, and the study of self-assembly and phase transitions.