PHASES OF MATTER -4 PHASE DIAGRAMS
... • A heating graph shows how the temperature changes the phases of a substance. • Until point A the phase and temperature are both changes. Between B and C also the phase changes as the temperature increases. ...
... • A heating graph shows how the temperature changes the phases of a substance. • Until point A the phase and temperature are both changes. Between B and C also the phase changes as the temperature increases. ...
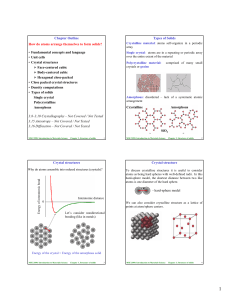
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... over the entire extent of the material Polycrystalline material: comprised of many small crystals or grains. The grains have different crystallographic orientation. There exist atomic mismatch within the regions where grains meet. These regions are ...
... over the entire extent of the material Polycrystalline material: comprised of many small crystals or grains. The grains have different crystallographic orientation. There exist atomic mismatch within the regions where grains meet. These regions are ...
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... In amorphous solids, there is no long-range order. But amorphous does not mean random, in many cases there is some form of short-range order. ...
... In amorphous solids, there is no long-range order. But amorphous does not mean random, in many cases there is some form of short-range order. ...
Kennemur - FSU Faculty Profile
... or the formation of periodic nanostructures densely populated in either segment. The size and morphology of these structures can be controlled by the size of each polymer segment. Our research will explore new avenues of this self-assembly process and utilize some of the types of polymers described ...
... or the formation of periodic nanostructures densely populated in either segment. The size and morphology of these structures can be controlled by the size of each polymer segment. Our research will explore new avenues of this self-assembly process and utilize some of the types of polymers described ...
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids
... Calculated the theoretical density for sodium chloride. The atomic weight of sodium and chloride, ANa and ACl are given as 22.99 g/mol and 35.45 g/mol respectively. The ionic radii of sodium and chloride, rNa+ and rCl- are given as 0.102 nm and 0.181 nm respectively. Compare the result with its meas ...
... Calculated the theoretical density for sodium chloride. The atomic weight of sodium and chloride, ANa and ACl are given as 22.99 g/mol and 35.45 g/mol respectively. The ionic radii of sodium and chloride, rNa+ and rCl- are given as 0.102 nm and 0.181 nm respectively. Compare the result with its meas ...
FIR CENTER SEMINAR Title: THz Spectroscopy and Simulation of
... Applying the “Driven Molecular Dynamics” approach, we watch the energy flow from solute to water. We find much larger and faster energy flow from the solute to the water when exciting THz modes compared to IR modes. This indicates a strong coupling of solute and water dynamics in the THz regime. Fur ...
... Applying the “Driven Molecular Dynamics” approach, we watch the energy flow from solute to water. We find much larger and faster energy flow from the solute to the water when exciting THz modes compared to IR modes. This indicates a strong coupling of solute and water dynamics in the THz regime. Fur ...
Experimental set-up for particle detection in solid crystals of inert
... the 50’s to study reactive species in a low interacting environment 1,2 . In this technique, named matrix isolation spectroscopy, the guest particles (atoms, molecules or ions) are embedded in a continuous matrix of solid crystal. As the matrix is made of un-reactive materials, diffusion processes a ...
... the 50’s to study reactive species in a low interacting environment 1,2 . In this technique, named matrix isolation spectroscopy, the guest particles (atoms, molecules or ions) are embedded in a continuous matrix of solid crystal. As the matrix is made of un-reactive materials, diffusion processes a ...
Crystal Ceramic Material
... OF CERAMICS • Ceramic materials disseminated to electromagnetic circuits, this is because the constant dielectric this material is high, even at the moment of the transition elements are almost all semiconductors. • There are a variety of oxides which acts as an insulator is good, because the valenc ...
... OF CERAMICS • Ceramic materials disseminated to electromagnetic circuits, this is because the constant dielectric this material is high, even at the moment of the transition elements are almost all semiconductors. • There are a variety of oxides which acts as an insulator is good, because the valenc ...
Crystal structure
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
Thermal Analysis Infrared Microscopy During device functioning, the
... During device functioning, the zones affected by defects have a higher local temperature than the defect-free ones. The infrared microscope can be used at wafer level, for thermal analysis, displaying the temperature distribution. Thermal images based on the infrared radiance emitted from the struct ...
... During device functioning, the zones affected by defects have a higher local temperature than the defect-free ones. The infrared microscope can be used at wafer level, for thermal analysis, displaying the temperature distribution. Thermal images based on the infrared radiance emitted from the struct ...
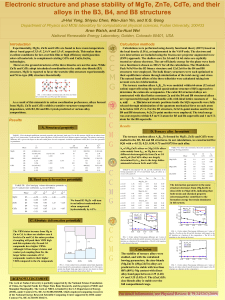
Electronic structure and phase stability of MgTe, ZnTe, CdTe, and
... core interactions are included using the frozen-core projector augmented wave (PAW) approach. The shallow-core Zn 3d and Cd 4d states are explicitly treated as valence electrons. The cut-off kinetic energy for the plane wave basis wave functions is chosen as 300 eV for all the calculations. The Monk ...
... core interactions are included using the frozen-core projector augmented wave (PAW) approach. The shallow-core Zn 3d and Cd 4d states are explicitly treated as valence electrons. The cut-off kinetic energy for the plane wave basis wave functions is chosen as 300 eV for all the calculations. The Monk ...
SEDIMENTARY TEXTURES (GEOL 243.3) Sediment texture refers
... commonly secondary, because they have been altered in some way from their original condition. The most common effect is compaction, where the weight of overlying sediments causes the component grains to rearrange themselves or even become fractured. ...
... commonly secondary, because they have been altered in some way from their original condition. The most common effect is compaction, where the weight of overlying sediments causes the component grains to rearrange themselves or even become fractured. ...
9223_fel - Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource
... radiation pulses; and bulk and surface ionization-related damage effects. 9.2.3.3.3 Beam splitting Beam splitters (see figure 9.2.3.3.3.1) can be made from thin crystals (Bragg or Laue ) or multilayers, a technique that has been developed in recent years at LLNL [1,2]. Blurring of the temporal struc ...
... radiation pulses; and bulk and surface ionization-related damage effects. 9.2.3.3.3 Beam splitting Beam splitters (see figure 9.2.3.3.3.1) can be made from thin crystals (Bragg or Laue ) or multilayers, a technique that has been developed in recent years at LLNL [1,2]. Blurring of the temporal struc ...
Nickel-Titanium Memory Metal
... of NiTi in the austenite phase is dropped, a sound wave propagates relatively unimpeded through the material, yielding a ringing sound; in contrast, when a rod of NiTi in the martensite phase is dropped, its different orientations of groups of atoms act as sound absorbing boundaries and will create ...
... of NiTi in the austenite phase is dropped, a sound wave propagates relatively unimpeded through the material, yielding a ringing sound; in contrast, when a rod of NiTi in the martensite phase is dropped, its different orientations of groups of atoms act as sound absorbing boundaries and will create ...
The challenge is to make an X-ray beam bright enough
... patterns could be mathematically decoded to figure out the distances between atomic planes, and thus the atomic structure of the crystal. It gradually became possible to decode more complex diffraction patterns, to the point where the structures of molecules such as proteins with thousands of atoms ...
... patterns could be mathematically decoded to figure out the distances between atomic planes, and thus the atomic structure of the crystal. It gradually became possible to decode more complex diffraction patterns, to the point where the structures of molecules such as proteins with thousands of atoms ...
chapter 8 ceramic/metal nanocomposites
... intense shearing strain, usually of plastic nature, developing during severe deformation of ductile materials. two X-shaped shear bands are clearly visible (see also the sketch on the right, where initial vertical scratches on the external surface help understanding the shear deformation). ...
... intense shearing strain, usually of plastic nature, developing during severe deformation of ductile materials. two X-shaped shear bands are clearly visible (see also the sketch on the right, where initial vertical scratches on the external surface help understanding the shear deformation). ...
Galena Quartz
... Please fold a triangle divider into your notebooks and write the following on it: Chapters 2 & 3 – Rocks and Minerals ...
... Please fold a triangle divider into your notebooks and write the following on it: Chapters 2 & 3 – Rocks and Minerals ...
structure and properties of severe deformed nanocomposite
... properties of nanocomposite materials fabricated by severe plastic deformation of twophase alloys with both plastic components. Typical specimen of this class of materials is Cu-Nb alloy. Severe deformation was produced by cold drawing rods (Ø10mm) to wires Ø0,1mm. The distinctive size of niobium fi ...
... properties of nanocomposite materials fabricated by severe plastic deformation of twophase alloys with both plastic components. Typical specimen of this class of materials is Cu-Nb alloy. Severe deformation was produced by cold drawing rods (Ø10mm) to wires Ø0,1mm. The distinctive size of niobium fi ...
chm 434f/1206f solid state materials chemistry
... microelectronics, telecommunications, optical applications, coatings, etc. ...
... microelectronics, telecommunications, optical applications, coatings, etc. ...
DX4301741751
... residue gives a weight loss for a wider range of temperature between 600 and 750 °C. The total weight loss of this stage is found to be 38 %. As the total weight loss in the entire temperature range considered corresponds to 100%, no residue is observed. There is a sharp weight loss at 148 °C due to ...
... residue gives a weight loss for a wider range of temperature between 600 and 750 °C. The total weight loss of this stage is found to be 38 %. As the total weight loss in the entire temperature range considered corresponds to 100%, no residue is observed. There is a sharp weight loss at 148 °C due to ...
5.2 Composition and Structure of Minerals
... • The arrangement of ions, molecules, or atoms in any mineral determines the shape of the crystal • Each type of mineral has its own crystal form ...
... • The arrangement of ions, molecules, or atoms in any mineral determines the shape of the crystal • Each type of mineral has its own crystal form ...
Topic 3: Structure of Materials
... In a metallic solid, the atoms give up all valence electrons to a “common pool” or “sea” of electrons. The remaining non-valence electrons and nuclei form positive ion “cores”. The valence electrons are free to drift throughout the entire lattice and act as electron glue holding the material togethe ...
... In a metallic solid, the atoms give up all valence electrons to a “common pool” or “sea” of electrons. The remaining non-valence electrons and nuclei form positive ion “cores”. The valence electrons are free to drift throughout the entire lattice and act as electron glue holding the material togethe ...
12.26MB - Stanford University
... Cambridge University Press, 399 pp. (2002) Last update: March 23, 2005 The photographs shown here appear in the textbook and are provided to facilitate their display during course instruction. Permissions for publication of photographs must be requested from individual copyright holders. The source ...
... Cambridge University Press, 399 pp. (2002) Last update: March 23, 2005 The photographs shown here appear in the textbook and are provided to facilitate their display during course instruction. Permissions for publication of photographs must be requested from individual copyright holders. The source ...
Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials
... practical interest from the bottom up by developing and using atomic-scale computational and theoretical tools • Simple models for fundamental understanding – General physical phenomena of wide applicability – Novel concepts of general validity – Qualitative results • Realistic models for accurate p ...
... practical interest from the bottom up by developing and using atomic-scale computational and theoretical tools • Simple models for fundamental understanding – General physical phenomena of wide applicability – Novel concepts of general validity – Qualitative results • Realistic models for accurate p ...
Colloidal crystal

A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles, analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where spheres of silica assume a close-packed locally periodic structure under moderate compression. Bulk properties of a colloidal crystal depend on composition, particle size, packing arrangement, and degree of regularity. Applications include photonics, materials processing, and the study of self-assembly and phase transitions.