The Citric acid cycle
... acetate succinate, malate, a-ketoglutaric acid (dicarboxylic acids) and citrate and isocitrate (tricarboxylic acids) when added to muscle mince that they stimulated oxygen consumption and release of CO2 1935Albert Szent-Gyorgyi showed that ...
... acetate succinate, malate, a-ketoglutaric acid (dicarboxylic acids) and citrate and isocitrate (tricarboxylic acids) when added to muscle mince that they stimulated oxygen consumption and release of CO2 1935Albert Szent-Gyorgyi showed that ...
Enzymes and Metabolism - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Electron Transport Chain Food (glucose) is oxidized and the released hydrogens with electrons: Are transported by coenzymes NADH and FADH2 Enter a chain of proteinsAt the end of chain combine with molecular oxygen to form water Release energy The energy released is harnessed to make a H+ ...
... Electron Transport Chain Food (glucose) is oxidized and the released hydrogens with electrons: Are transported by coenzymes NADH and FADH2 Enter a chain of proteinsAt the end of chain combine with molecular oxygen to form water Release energy The energy released is harnessed to make a H+ ...
Why nature chose phosphate to modify proteins
... The selection of ATP as the major energy storage compound also meant the ready availability of activated phosphate groups for transfer to other molecules. Because of its energy storage function, ATP is very abundant in cells with concentrations typically ranging from 2 to 4 mM. ATP is highly soluble ...
... The selection of ATP as the major energy storage compound also meant the ready availability of activated phosphate groups for transfer to other molecules. Because of its energy storage function, ATP is very abundant in cells with concentrations typically ranging from 2 to 4 mM. ATP is highly soluble ...
Muscle Metabolic Adaptation to Exercise
... They generate ATP mainly by aerobic cellular respiration because they have many large mitochondria and are called oxidative fibers. ...
... They generate ATP mainly by aerobic cellular respiration because they have many large mitochondria and are called oxidative fibers. ...
Poster
... normal development of an embryo and physiology of cells. But inhibition of signaling or aberrant activation of the pathway can have deleterious consequences. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase, which plays a key role in Wnt/β-catenin signaling during embryonic de ...
... normal development of an embryo and physiology of cells. But inhibition of signaling or aberrant activation of the pathway can have deleterious consequences. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase, which plays a key role in Wnt/β-catenin signaling during embryonic de ...
Molecular Interactions in Cell events
... Activation occurs when trypsinogen has amino acids removed in the duodenum by another protease enzyme This changes the trypsinogen into the active form trypsin Trypsin then helps to activate more trypsinogen molecules ...
... Activation occurs when trypsinogen has amino acids removed in the duodenum by another protease enzyme This changes the trypsinogen into the active form trypsin Trypsin then helps to activate more trypsinogen molecules ...
lecture1
... erythrocytes and lactating mammary glands. Importance:- It is a device for generating NADPH (Dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). By the oxidation of Glucose 6 Po4 to ribulose - 5 - PO4 and CO2. 2 moles of NADPH is produced for each mole of glucose ester oxidized. Function of NADPH: ...
... erythrocytes and lactating mammary glands. Importance:- It is a device for generating NADPH (Dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). By the oxidation of Glucose 6 Po4 to ribulose - 5 - PO4 and CO2. 2 moles of NADPH is produced for each mole of glucose ester oxidized. Function of NADPH: ...
Effect of triiodothyronine on mitochondrial energy coupling in human
... humans has yet been demonstrated, due to the difficulty in extrapolating in vitro measurements of isolated mitochondrial membrane permeability to the in vivo situation. Another difficulty in extrapolating the in vitro data to in vivo conditions is that the in vitro measurements are usually performed ...
... humans has yet been demonstrated, due to the difficulty in extrapolating in vitro measurements of isolated mitochondrial membrane permeability to the in vivo situation. Another difficulty in extrapolating the in vitro data to in vivo conditions is that the in vitro measurements are usually performed ...
Slide 1
... Coenzymes from niacin and riboflavin transfer H and electrons to Electron Transport Chain (ETC) ...
... Coenzymes from niacin and riboflavin transfer H and electrons to Electron Transport Chain (ETC) ...
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the citric acid cycle enzymes exist in the matrix of the mitochondrion in eukaryotes Pyruvate in generated by glycolysis in the cytosol and needs to be moved into the mitochondria MITOCHONDRIAL STRUCTURE ...
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the citric acid cycle enzymes exist in the matrix of the mitochondrion in eukaryotes Pyruvate in generated by glycolysis in the cytosol and needs to be moved into the mitochondria MITOCHONDRIAL STRUCTURE ...
A2 Biology Revision Tips
... • Same point as above, but worth emphasising that little heat is generated, which would be a big problem for cells. • ATP is regenerated, therefore it doesn’t need to be stored and you don’t need much of it! • ATP is soluble • ATP is small and can pass in / out of cells easily • You can generate ATP ...
... • Same point as above, but worth emphasising that little heat is generated, which would be a big problem for cells. • ATP is regenerated, therefore it doesn’t need to be stored and you don’t need much of it! • ATP is soluble • ATP is small and can pass in / out of cells easily • You can generate ATP ...
Trans-Tonoplast Transport of the Sulfur Containing
... protoplasts. Uptake rates were similar in the light and in the dark and roughly linear with time. In the presence of 1 mM substrate concentrations, GSH was taken up at a rate of 0.11 and 0.15 umol 10? protoplasts-1 h-i in the light and in the dark, respectively. The corresponding rates for GSSG were ...
... protoplasts. Uptake rates were similar in the light and in the dark and roughly linear with time. In the presence of 1 mM substrate concentrations, GSH was taken up at a rate of 0.11 and 0.15 umol 10? protoplasts-1 h-i in the light and in the dark, respectively. The corresponding rates for GSSG were ...
References - The University of New Mexico
... there would be some metabolites of reactions with adjusted data, and others (most) without. Finally, and as clearly revealed within the NIST database (10), the dissociation constants are influenced not just by the ionic strength, but also the ionic composition of the reaction milieu at a given ionic ...
... there would be some metabolites of reactions with adjusted data, and others (most) without. Finally, and as clearly revealed within the NIST database (10), the dissociation constants are influenced not just by the ionic strength, but also the ionic composition of the reaction milieu at a given ionic ...
pyruvate
... carbon will be directed to the 2 main storage forms of carbon--glycogen via gluconeogenesis and fat production via fatty acid synthesis---where acetyl-CoA is the principal carbon donor. Although the regulation of Pdh-b phosphatase is not well understood, it is quite likely regulated to maximize pyru ...
... carbon will be directed to the 2 main storage forms of carbon--glycogen via gluconeogenesis and fat production via fatty acid synthesis---where acetyl-CoA is the principal carbon donor. Although the regulation of Pdh-b phosphatase is not well understood, it is quite likely regulated to maximize pyru ...
CreaPrime™ Blend
... Creatine is used in the high-energy phosphate or ATP-PCr system to regenerate ATP. ATP, the body's main source of energy, is a molecule of adenosine (adenine + the sugar ribose) linked to three phosphate molecules by high-energy bonds. Breaking of the two outer bonds results in the release of energy ...
... Creatine is used in the high-energy phosphate or ATP-PCr system to regenerate ATP. ATP, the body's main source of energy, is a molecule of adenosine (adenine + the sugar ribose) linked to three phosphate molecules by high-energy bonds. Breaking of the two outer bonds results in the release of energy ...
7 | cellular respiration
... The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule requires energy. Phosphate groups are negatively charged and thus repel one another when they are arranged in series, as they are in ADP and ATP. This repulsion makes the ADP and ATP molecules inherently unstable. The release of one or two phosphate gr ...
... The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule requires energy. Phosphate groups are negatively charged and thus repel one another when they are arranged in series, as they are in ADP and ATP. This repulsion makes the ADP and ATP molecules inherently unstable. The release of one or two phosphate gr ...
No Slide Title
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
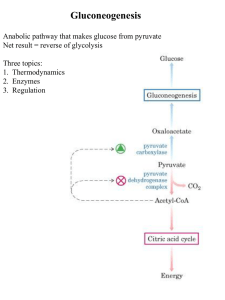
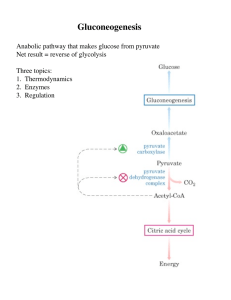
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
Enzymatic Synthesis of Arginine Phosphate with Coupled ATP
... Three successive reactions were carried out using the same preparation of enzyme-containing gel. The results were comparable for the three. In the last, it was possible to reach a concentration of 0.2 M in ArgP with a yield of 75% based on PEP and an ATP turnover number of 64 (Table 1). We did not o ...
... Three successive reactions were carried out using the same preparation of enzyme-containing gel. The results were comparable for the three. In the last, it was possible to reach a concentration of 0.2 M in ArgP with a yield of 75% based on PEP and an ATP turnover number of 64 (Table 1). We did not o ...
Cellular Respiration
... The main energy-yielding foods, carbohydrates and fats, are reservoirs of electrons associated with hydrogen. These molecules are stable because of the barrier of activation energy. Without this barrier, a food molecule like glucose would combine almost instantaneously with O2. o If activation energ ...
... The main energy-yielding foods, carbohydrates and fats, are reservoirs of electrons associated with hydrogen. These molecules are stable because of the barrier of activation energy. Without this barrier, a food molecule like glucose would combine almost instantaneously with O2. o If activation energ ...
Chapter 8 PowerPoint - Campbell County Schools
... helps control metabolism • Chemical chaos would result if a cell’s metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated • A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes ...
... helps control metabolism • Chemical chaos would result if a cell’s metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated • A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Energy-Releasing Pathways Anaerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the cell cytoplasm that does not use oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the mitochondria using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Energy-Releasing Pathways Anaerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the cell cytoplasm that does not use oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic Definition Energy exchange occurring in the mitochondria using oxygen as the final electron acceptor. ...
The ATP synthase is involved in generating mitochondrial cristae
... and DTIM11 mutant cells grew using lactate as carbon source either at 28 or 37°C, thus indicating that they were able to generate ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. However, they had generation times longer than that of the wild-type strain. Indeed, 40% of DATP20 and DTIM11 mutant cells spontaneousl ...
... and DTIM11 mutant cells grew using lactate as carbon source either at 28 or 37°C, thus indicating that they were able to generate ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. However, they had generation times longer than that of the wild-type strain. Indeed, 40% of DATP20 and DTIM11 mutant cells spontaneousl ...
Adaptations of anaerobic archaea to life under extreme energy
... possible by a chemiosmotic mechanism that involves the generation of an electrochemical ion gradient across the cytoplasmatic membrane that then drives ATP synthesis via an A1AO ATP synthase. The minimal amount of energy required is thus depending on the magnitude of the electrochemical ion gradient ...
... possible by a chemiosmotic mechanism that involves the generation of an electrochemical ion gradient across the cytoplasmatic membrane that then drives ATP synthesis via an A1AO ATP synthase. The minimal amount of energy required is thus depending on the magnitude of the electrochemical ion gradient ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.