free energy
... • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration. • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: • C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + E ...
... • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration. • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: • C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + E ...
Oxidation - medscistudents
... malonyl CoA decreases, releasing the inhibition of CAT-1 and permitting more acetyl CoA for oxidation ...
... malonyl CoA decreases, releasing the inhibition of CAT-1 and permitting more acetyl CoA for oxidation ...
tRNA aminoacylation by arginyltRNA synthetase: induced
... aaRSs, each one of them being responsible for aminoacylating its cognate tRNA(s) with a unique amino acid in a two-step catalytic reaction. The ®rst step, which requires ATP and Mg2+ ions, leads to the formation of an enzymebound aminoacyl-adenylate and is followed by the transfer of the amino acid ...
... aaRSs, each one of them being responsible for aminoacylating its cognate tRNA(s) with a unique amino acid in a two-step catalytic reaction. The ®rst step, which requires ATP and Mg2+ ions, leads to the formation of an enzymebound aminoacyl-adenylate and is followed by the transfer of the amino acid ...
NUCLEOTIDES Occurrence Nucleotides are present in all types of
... Two co-enzymes, which are dinucleotides are NAD+ (NADP+) and FAD. But in these dinucleotides, nucleotides are held together through anhydride linkage formed between phosphate of first nucleotide and phosphate of second nucleotide . Further in FAD the glycosidic linkage between sugar and base is abse ...
... Two co-enzymes, which are dinucleotides are NAD+ (NADP+) and FAD. But in these dinucleotides, nucleotides are held together through anhydride linkage formed between phosphate of first nucleotide and phosphate of second nucleotide . Further in FAD the glycosidic linkage between sugar and base is abse ...
A Contribution of the Mitochondrial
... plex also contain substoichiometric amounts of the ATPase inhibitor protein (IF!). In intact m ito chondria, there is 1 mol of IF^m ol of F t (Hekm an et al., 1991; Abraham s et al., 1994; Walker, 1994; Belogrudov et al., 1995). The mitochondrial ATPase inhibitor protein (IF]), first discovered and ...
... plex also contain substoichiometric amounts of the ATPase inhibitor protein (IF!). In intact m ito chondria, there is 1 mol of IF^m ol of F t (Hekm an et al., 1991; Abraham s et al., 1994; Walker, 1994; Belogrudov et al., 1995). The mitochondrial ATPase inhibitor protein (IF]), first discovered and ...
Biochem09 - Amit Kessel Ph.D
... D. Regulation of the catalytic activities of enzymes. E. Alteration of the amounts of allosteric modifiers (regulator molecules). ...
... D. Regulation of the catalytic activities of enzymes. E. Alteration of the amounts of allosteric modifiers (regulator molecules). ...
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Background - Rose
... structure of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (which is involved in the first substrate-level phosphorylation step in the glycolytic pathway) and succinyl phosphate reveals some significant similarities. The reaction mechanism of succinyl-CoA synthetase, however, differs from that of phosphoglycerate kinase. ...
... structure of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (which is involved in the first substrate-level phosphorylation step in the glycolytic pathway) and succinyl phosphate reveals some significant similarities. The reaction mechanism of succinyl-CoA synthetase, however, differs from that of phosphoglycerate kinase. ...
metabolic factors in fatigue
... Another aspect of central fatigue during prolonged exercise involves the potential interactions among the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA; leucine, isoleucine and valine), cerebral tryptophan uptake, and brain serotonin levels. Tryptophan is a serotonin precursor, and cerebral tryptop ...
... Another aspect of central fatigue during prolonged exercise involves the potential interactions among the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA; leucine, isoleucine and valine), cerebral tryptophan uptake, and brain serotonin levels. Tryptophan is a serotonin precursor, and cerebral tryptop ...
Chem 499 Final Exam Name
... located on the surface of cells and does not cross the cell membrane. However, the larger steroid estrone can cross cell membranes and interact with proteins located in the cell nucleus. Why is a larger steroid molecule able to cross the cell membranes while a smaller molecule, such as adrenaline ca ...
... located on the surface of cells and does not cross the cell membrane. However, the larger steroid estrone can cross cell membranes and interact with proteins located in the cell nucleus. Why is a larger steroid molecule able to cross the cell membranes while a smaller molecule, such as adrenaline ca ...
The mitochondrial respiratory chain
... other cellular processes and controls, resulting in the present-day non-autonomous mitochondrial organelles. Many features of mitochondria, including their shapes and overall structures, reflect their bacterial origin. Particularly convincing is the fact that they retain some of their original DNA. ...
... other cellular processes and controls, resulting in the present-day non-autonomous mitochondrial organelles. Many features of mitochondria, including their shapes and overall structures, reflect their bacterial origin. Particularly convincing is the fact that they retain some of their original DNA. ...
Exercise and Cellular Respiration
... • Provides most of the high energy phosphate needed in the early phase of exercise ...
... • Provides most of the high energy phosphate needed in the early phase of exercise ...
Acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate – what would accumulate? In cells that rely on glucose for fuel (do not use fats) – the energy that is provided when pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA is not generated Which cells in the body rely primarily on glucose for energy? Cells of the nervous system and heart, t ...
... of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate – what would accumulate? In cells that rely on glucose for fuel (do not use fats) – the energy that is provided when pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA is not generated Which cells in the body rely primarily on glucose for energy? Cells of the nervous system and heart, t ...
Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of intracellular
... and iodoacetate inhibition of glycolysis. After addition of substrate the pH in the compartment containing the second phosphate pool decreased. A parallel response was observed for a significant fraction of the terminal and penultimate phosphates of the polyphosphate observed by 3~p NMR. This sugges ...
... and iodoacetate inhibition of glycolysis. After addition of substrate the pH in the compartment containing the second phosphate pool decreased. A parallel response was observed for a significant fraction of the terminal and penultimate phosphates of the polyphosphate observed by 3~p NMR. This sugges ...
Fundamentals
... At the same time, the reverse pathway will be allosterically regulated negatively. People have observed this over and over in many different pathways. ...
... At the same time, the reverse pathway will be allosterically regulated negatively. People have observed this over and over in many different pathways. ...
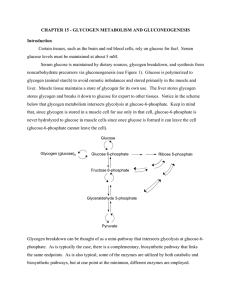
CHAPTER 15 - GLYCOGEN METABOLISM AND
... The role of the insulin-dependent protein kinase in dephosphorylation in muscle is seen below in Figure 15-19. This kinase exerts its effect on PP1, which binds to the glycogen particle via its G subunit. Insulin will be secreted from the pancreas when the energy demands of the cell have been met. U ...
... The role of the insulin-dependent protein kinase in dephosphorylation in muscle is seen below in Figure 15-19. This kinase exerts its effect on PP1, which binds to the glycogen particle via its G subunit. Insulin will be secreted from the pancreas when the energy demands of the cell have been met. U ...
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Is a GABAA Receptor
... Mannheim) or an anti-GAPDH antibody (4.9 mg/ml; Chemicon, Temecula, CA) in a final volume of 200 l with phosphate buffer containing 0.1% Triton X-100. After the addition of 200 l of goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to agarose with 1% bovine serum albumin, the samples were carefully shaken for 16 hr ...
... Mannheim) or an anti-GAPDH antibody (4.9 mg/ml; Chemicon, Temecula, CA) in a final volume of 200 l with phosphate buffer containing 0.1% Triton X-100. After the addition of 200 l of goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to agarose with 1% bovine serum albumin, the samples were carefully shaken for 16 hr ...
15Nitrogen metabolism
... group of glutamine that transported to liver or kidneys. - Glutamine: non-toxic transport form of NH4+ and also source of amino group in many biosynthesis reactions. - The amide nitrogen of glutamine is released as ammonia only in liver and kidney’s mitochondria by the enzyme “Glutaminase” which con ...
... group of glutamine that transported to liver or kidneys. - Glutamine: non-toxic transport form of NH4+ and also source of amino group in many biosynthesis reactions. - The amide nitrogen of glutamine is released as ammonia only in liver and kidney’s mitochondria by the enzyme “Glutaminase” which con ...
The Biosynthesis of N-Phosphorylcreatine: an Investigation of the
... under conditions similar to those described by these authors. Further fractionation, however, caused a loss of activity and, since this could be recovered in greater than additive amounts by recombination of fractions, it seemed that more than one enzyme was involved. Furthermore, it has been found ...
... under conditions similar to those described by these authors. Further fractionation, however, caused a loss of activity and, since this could be recovered in greater than additive amounts by recombination of fractions, it seemed that more than one enzyme was involved. Furthermore, it has been found ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... 26.59 The fumarate formed in the urea cycle enters the citric acid cycle, where it is converted to malate and then to oxaloacetate, which is then converted to aspartate through transamination. 26.60 The fumarate from the urea cycle is a citric acid cycle intermediate. 26.61 Each of the 20 amino acid ...
... 26.59 The fumarate formed in the urea cycle enters the citric acid cycle, where it is converted to malate and then to oxaloacetate, which is then converted to aspartate through transamination. 26.60 The fumarate from the urea cycle is a citric acid cycle intermediate. 26.61 Each of the 20 amino acid ...
Muscle relaxants
... – Enzymatic breakdown of the glucose to pyruvate and lactate liberates energy that is used to convert ADP to ATP, glycolysis can sustain contraction for about 1 min – Twofold importance of glycolysis • Reactions occurs in the absence of oxygen (muscle contraction can be sustained for a short time wh ...
... – Enzymatic breakdown of the glucose to pyruvate and lactate liberates energy that is used to convert ADP to ATP, glycolysis can sustain contraction for about 1 min – Twofold importance of glycolysis • Reactions occurs in the absence of oxygen (muscle contraction can be sustained for a short time wh ...
Opener 1/6/2015 1. What is biology? 2. What are the four classroom
... What do pyramid models tell us about energy flow between the tropic levels? ...
... What do pyramid models tell us about energy flow between the tropic levels? ...
lecture5
... As in the dehydrogenation of succinate in the citric acid cycle, FAD rather than NAD+ is the electron acceptor because the value of D G for this reaction is insufficient to drive the reduction of NAD+. Electrons from the FADH2 prosthetic group of the reduced acyl CoA dehydrogenase are transferred to ...
... As in the dehydrogenation of succinate in the citric acid cycle, FAD rather than NAD+ is the electron acceptor because the value of D G for this reaction is insufficient to drive the reduction of NAD+. Electrons from the FADH2 prosthetic group of the reduced acyl CoA dehydrogenase are transferred to ...
Carbohydrates Metabolism OVERVIEW Carbohydrates (saccharides
... This oxidation provides energy for the production of the majority of ATP in most animals, including humans. The cycle occurs totally in the mitochondria and is, therefore, in close proximity to the reactions of electron transport, which oxidize the reduced coenzymes produced by the cycle. The TCA cy ...
... This oxidation provides energy for the production of the majority of ATP in most animals, including humans. The cycle occurs totally in the mitochondria and is, therefore, in close proximity to the reactions of electron transport, which oxidize the reduced coenzymes produced by the cycle. The TCA cy ...
Diabetes (type II) treatment, Dec. 7
... What is AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its main role in the body? • Balances catabolism (processes that produce ATP) with ATP consumption to maintain high levels of ATP • Expressed primarily in liver, skeletal muscle, and the brain, which are all involved in energy intake, consumption, and ...
... What is AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its main role in the body? • Balances catabolism (processes that produce ATP) with ATP consumption to maintain high levels of ATP • Expressed primarily in liver, skeletal muscle, and the brain, which are all involved in energy intake, consumption, and ...
Anatomy of a Cell :
... a program from which ribosomes can manufacture the proteins needed. A living cell needs all these things: the genetic information, the mechanisms and machinery to use the information to build cell parts, and the ability to harness energy to do so. As we will see in chapter 3, the physical laws of na ...
... a program from which ribosomes can manufacture the proteins needed. A living cell needs all these things: the genetic information, the mechanisms and machinery to use the information to build cell parts, and the ability to harness energy to do so. As we will see in chapter 3, the physical laws of na ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.