reservoirs of pathogens
... transmits an infectious agent from one host to another is called a vector. Majority of vectors are arthropods – fleas, mosquitoes, flies, and ticks Some larger animals can also spread infection – mammals, birds, lower ...
... transmits an infectious agent from one host to another is called a vector. Majority of vectors are arthropods – fleas, mosquitoes, flies, and ticks Some larger animals can also spread infection – mammals, birds, lower ...
“…One can think of the middle of the twentieth century as the end of
... “…One can think of the middle of the twentieth century as the end of one of the most important social revolutions in history, the virtual elimination of the infectious disease as a significant factor in social life.” Burnet, 1962 ...
... “…One can think of the middle of the twentieth century as the end of one of the most important social revolutions in history, the virtual elimination of the infectious disease as a significant factor in social life.” Burnet, 1962 ...
Scientific activities
... Hospital and University of Southern Denmark, Thesis. "Infection with human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Seroconversion, chronic infection and the development of AIDS", University of Copenhagen, 1993. Publications. Author or co-author on more than 300 papers published in peer review journals. First ...
... Hospital and University of Southern Denmark, Thesis. "Infection with human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Seroconversion, chronic infection and the development of AIDS", University of Copenhagen, 1993. Publications. Author or co-author on more than 300 papers published in peer review journals. First ...
CDHA Principles of Transmission of Microorganisms
... 1.1. Direct contact transmission occurs when microorganisms are transferred by direct physical contact between an infected or colonized individual and a susceptible host (body surface to body surface). 1.2. Indirect contact transmission occurs when microorganisms are transferred to a susceptible hos ...
... 1.1. Direct contact transmission occurs when microorganisms are transferred by direct physical contact between an infected or colonized individual and a susceptible host (body surface to body surface). 1.2. Indirect contact transmission occurs when microorganisms are transferred to a susceptible hos ...
blood-borne pathogens
... - Enough of the path. Must be in the fluid - A person must be susceptible that pathogen - Entry site must be available to the pathogen WAYS PATHOGENS CAN ENTER BODY - Direct Contact o Touch body fluid of infected person - Indirect Contact o Touch object that touch body fluid of infected person (soil ...
... - Enough of the path. Must be in the fluid - A person must be susceptible that pathogen - Entry site must be available to the pathogen WAYS PATHOGENS CAN ENTER BODY - Direct Contact o Touch body fluid of infected person - Indirect Contact o Touch object that touch body fluid of infected person (soil ...
Chapter 24 Notes
... Vaccines to Aid the Body’s Defenses: Live-virus vaccines Killed-virus vaccines Toxoids New and second-generation vaccines Common Communicable Diseases: Common Cold Influenza Pneumonia Strep Throat Tuberculosis Hepatitis: Hepatitis A: Virus is most commonly spread through contact ...
... Vaccines to Aid the Body’s Defenses: Live-virus vaccines Killed-virus vaccines Toxoids New and second-generation vaccines Common Communicable Diseases: Common Cold Influenza Pneumonia Strep Throat Tuberculosis Hepatitis: Hepatitis A: Virus is most commonly spread through contact ...
List of Infectious Diseases legally notifiable under the Infectious
... 6. — (1) Every medical practitioner who has reason to believe or suspect that any person attended or treated by him is suffering from an infectious disease or is a carrier of that disease shall notify the Director within the prescribed time and in such form or manner as the Director may require. (2) ...
... 6. — (1) Every medical practitioner who has reason to believe or suspect that any person attended or treated by him is suffering from an infectious disease or is a carrier of that disease shall notify the Director within the prescribed time and in such form or manner as the Director may require. (2) ...
Pre-Lecture Quiz
... True/False 1. Nonpathogens assume one of the two relationships with their human host: mutually beneficial or neither harming nor helping the host. 2. Aerobic bacteria exist without oxygen. 3. Pathogens have high potential for causing infectious communicable diseases. 4. Viruses can pass through very ...
... True/False 1. Nonpathogens assume one of the two relationships with their human host: mutually beneficial or neither harming nor helping the host. 2. Aerobic bacteria exist without oxygen. 3. Pathogens have high potential for causing infectious communicable diseases. 4. Viruses can pass through very ...
Timely identification of optimal control strategies for emerging
... Received in revised form 24 February 2009 Accepted 3 March 2009 ...
... Received in revised form 24 February 2009 Accepted 3 March 2009 ...
Chapter 20: Childhood Diseases and Disorders 1. is the time
... 23. ____________________________________ is a malignant neoplasm that occurs before the age of 20. It is usually located in a long bone such as the femur. 24. __________________________________ is the most common form of cancer in children. 25 ____________________________________ is the most common ...
... 23. ____________________________________ is a malignant neoplasm that occurs before the age of 20. It is usually located in a long bone such as the femur. 24. __________________________________ is the most common form of cancer in children. 25 ____________________________________ is the most common ...
Chapter Outline
... A. Reservoirs: Where Pathogens Persist 1. Nonliving 2. Living Reservoirs a. Carrieri. Human ii. Asymptomatic, chronic or any stage of clinical infection b. Animals-zoonosis c. Vector i. Biological ii. Mechanical B. The Acquisition and Transmission of Infectious Agents 1. Distinctions between Commun ...
... A. Reservoirs: Where Pathogens Persist 1. Nonliving 2. Living Reservoirs a. Carrieri. Human ii. Asymptomatic, chronic or any stage of clinical infection b. Animals-zoonosis c. Vector i. Biological ii. Mechanical B. The Acquisition and Transmission of Infectious Agents 1. Distinctions between Commun ...
Responsibility for Infection Control
... Professional Conduct Standards Failure to adhere to infection control standards Mechanism of Transmission ...
... Professional Conduct Standards Failure to adhere to infection control standards Mechanism of Transmission ...
Chapter 14a
... microorganism and host – Relationships may change depending on state of host and attributes of microbes ...
... microorganism and host – Relationships may change depending on state of host and attributes of microbes ...
XML - Sri Lankan Journal of Infectious Diseases
... strategies for Hepatitis B infection in the population has been established for at least 4 decades. It is disturbing therefore to discover that transmission of Hepatitis B still occurs in a community as described by Biswall et al who attribute such transmission to poor practice by local health worke ...
... strategies for Hepatitis B infection in the population has been established for at least 4 decades. It is disturbing therefore to discover that transmission of Hepatitis B still occurs in a community as described by Biswall et al who attribute such transmission to poor practice by local health worke ...
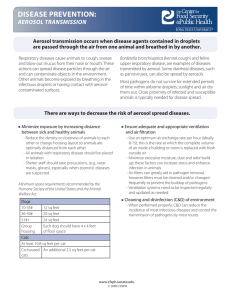
Disease Prevention: Aerosol Transmission
... are passed through the air from one animal and breathed in by another. Respiratory diseases cause animals to cough, sneeze and blow out mucus from their nose or mouth. These actions can spread disease particles through the air and can contaminate objects in the environment. Other animals become expo ...
... are passed through the air from one animal and breathed in by another. Respiratory diseases cause animals to cough, sneeze and blow out mucus from their nose or mouth. These actions can spread disease particles through the air and can contaminate objects in the environment. Other animals become expo ...
Complexity DTC Mini-project Proposal: Blood-borne virus transmission on networks of cliques
... The networks of HCV transmission formed by injecting drug users (IDUs) can be modelled through the making and breaking of cliques. Once this approximation has been made, the population-level transmission dynamics for the virus can be written exactly. The project will look at targeted interventions a ...
... The networks of HCV transmission formed by injecting drug users (IDUs) can be modelled through the making and breaking of cliques. Once this approximation has been made, the population-level transmission dynamics for the virus can be written exactly. The project will look at targeted interventions a ...
SNC 4M Pathogens and Disease Unit homework
... 3) Bruno gets a cut while watching Monday Night Football. He pours beer over it because he heard the alcohol will kill any potential pathogens. Is he correct? Why or why not? 4) What areas of Holy Cross do you feel are potential germ incubators? Why? Disease Transmission (Parts 1 and 2) 1) Complete ...
... 3) Bruno gets a cut while watching Monday Night Football. He pours beer over it because he heard the alcohol will kill any potential pathogens. Is he correct? Why or why not? 4) What areas of Holy Cross do you feel are potential germ incubators? Why? Disease Transmission (Parts 1 and 2) 1) Complete ...
Infectious Process Principles of Immunology
... Obligate intracellular parasites Enveloped vs. non enveloped Latency Host range Tissue/cell specificity Antigenic changes ...
... Obligate intracellular parasites Enveloped vs. non enveloped Latency Host range Tissue/cell specificity Antigenic changes ...
Isolation in ICU
... = designed to prevent droplet (larger particle) transmission of infectious agents when patient talks, coughs or sneezes. ...
... = designed to prevent droplet (larger particle) transmission of infectious agents when patient talks, coughs or sneezes. ...
Another person Direct contact: shaking hands 1. 2. Contaminated
... How Infectious Diseases are Spread Source Example of Method of Transfer ...
... How Infectious Diseases are Spread Source Example of Method of Transfer ...
A1.1.1 Routes of transmission
... Airborne transmission Airborne dissemination may occur via particles containing infectious agents that remain infective over time and distance. Small-particle aerosols are created during breathing, talking, coughing or sneezing and secondarily by evaporation of larger droplets in conditions of low h ...
... Airborne transmission Airborne dissemination may occur via particles containing infectious agents that remain infective over time and distance. Small-particle aerosols are created during breathing, talking, coughing or sneezing and secondarily by evaporation of larger droplets in conditions of low h ...
Communicable Diseases final
... Mode Of Transmission The process where the infectious agent is transferred from one person to the another. ...
... Mode Of Transmission The process where the infectious agent is transferred from one person to the another. ...
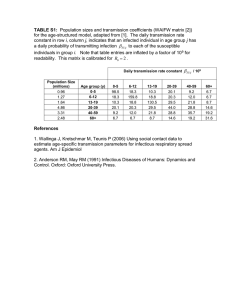
TABLE S1: Population sizes and transmission coefficients (WAIFW
... for the age-structured model, adapted from [1]. The daily transmission rate constant in row i, column j, indicates that an infected individual in age group j has a daily probability of transmitting infection SUij to each of the susceptible individuals in group i. Note that table entries are inflat ...
... for the age-structured model, adapted from [1]. The daily transmission rate constant in row i, column j, indicates that an infected individual in age group j has a daily probability of transmitting infection SUij to each of the susceptible individuals in group i. Note that table entries are inflat ...