Adult Infectious Diseases
... paper during his/her training and make a presentation at a national level every year. The fellow will be expected to participate in continuing medical education programmes of the University. Evaluation Continuous assessment and evaluation will be done by all faculty members on a daily basis. The fel ...
... paper during his/her training and make a presentation at a national level every year. The fellow will be expected to participate in continuing medical education programmes of the University. Evaluation Continuous assessment and evaluation will be done by all faculty members on a daily basis. The fel ...
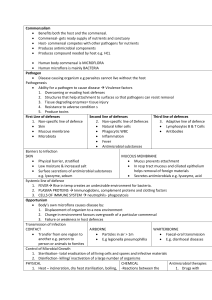
Commensalism • Benefits both the host and the commensal
... Body’s own microflora causes disease by: 1. Displacement of organism to a new environment 2. Change in environment favours overgrowth of a particular commensal 3. Failure or weakness in host defences Transmission of Infection CONTACT AIRBORNE WARTERBORNE Transfer from one region to Particles i ...
... Body’s own microflora causes disease by: 1. Displacement of organism to a new environment 2. Change in environment favours overgrowth of a particular commensal 3. Failure or weakness in host defences Transmission of Infection CONTACT AIRBORNE WARTERBORNE Transfer from one region to Particles i ...
Key words: 1. Pathogen: A microorganism that can cause disease. 2
... Pathogen: A microorganism that can cause disease. Microorganism: A living thing too small to see with only your eyes. Symptom: Effects on your body from a pathogen. Communicable: Diseases can be passed on to other people Antibiotic: A type of drug that can kill bacteria. White Blood Cell: A type of ...
... Pathogen: A microorganism that can cause disease. Microorganism: A living thing too small to see with only your eyes. Symptom: Effects on your body from a pathogen. Communicable: Diseases can be passed on to other people Antibiotic: A type of drug that can kill bacteria. White Blood Cell: A type of ...
INFECTION CONTROL It is possible to acquire infections such as
... INFECTION CONTROL It is possible to acquire infections such as HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C through contact with blood and body fluids. While measures are in place to provide a safe hospital environment, you should always be on the alert for items such as contaminated needles or dressings. If yo ...
... INFECTION CONTROL It is possible to acquire infections such as HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C through contact with blood and body fluids. While measures are in place to provide a safe hospital environment, you should always be on the alert for items such as contaminated needles or dressings. If yo ...
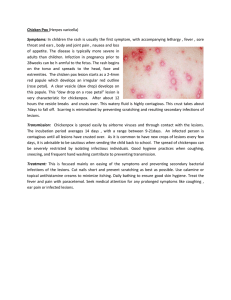
Chicken Pox (Herpes varicella) Symptoms: In children the rash is
... 7days to fall off. Scarring is minimalised by preventing scratching and resulting secondary infections of lesions. Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected p ...
... 7days to fall off. Scarring is minimalised by preventing scratching and resulting secondary infections of lesions. Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected p ...
Complex Diseases
... mucous glands. It primarily affects the respiratory and digestive systems of children and young adults. ...
... mucous glands. It primarily affects the respiratory and digestive systems of children and young adults. ...
How the destruction of rainforest could help create new strains of
... infrastructure for wastewater and solid waste management) gives vector-borne diseases more opportunities to infect humans and animals. So we are not the only ones in danger but other animals are too. Storm drainage and sewerage systems that don’t work increase the spread of waterborne pathogens caus ...
... infrastructure for wastewater and solid waste management) gives vector-borne diseases more opportunities to infect humans and animals. So we are not the only ones in danger but other animals are too. Storm drainage and sewerage systems that don’t work increase the spread of waterborne pathogens caus ...
immune-system-notes
... microbes and secretes lysozyme, which digests bacterial cell walls o If there is a break in the skin, it will try to heal and blood flows outward preventing the infection from getting inside o Our breathing passages are covered in hairs and mucus that are meant to trap foreign organisms and expel th ...
... microbes and secretes lysozyme, which digests bacterial cell walls o If there is a break in the skin, it will try to heal and blood flows outward preventing the infection from getting inside o Our breathing passages are covered in hairs and mucus that are meant to trap foreign organisms and expel th ...
Spreading Disease with Transport
... Transport among regions is found as one of the main factors which affect the outbreak of diseases. It will change the disease dynamics and break infection out even if infectious diseases will go extinct in each city without transport-related infection. In this talk, a mathematical model is proposed ...
... Transport among regions is found as one of the main factors which affect the outbreak of diseases. It will change the disease dynamics and break infection out even if infectious diseases will go extinct in each city without transport-related infection. In this talk, a mathematical model is proposed ...
Fellowship-Training-in-Adult-and-Pediatric-Infectious
... Pakistan is a resource limited nation that faces infectious diseases as its primary healthcare challenge. Significant disease burden and emergence of drug resistance organisms needs ID expertise not only to deal with emerging infections and threats in a variety of hosts, but also for rational use of ...
... Pakistan is a resource limited nation that faces infectious diseases as its primary healthcare challenge. Significant disease burden and emergence of drug resistance organisms needs ID expertise not only to deal with emerging infections and threats in a variety of hosts, but also for rational use of ...
No Slide Title
... Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
The History and Mission of Public Health
... Definition of Public Health • Public health is the science and art of • Preventing disease. • Prolonging life. • Organizing community efforts for the: • Sanitation of the environment. • Control of communicable diseases. • Education of the individual in personal hygiene. • Organization of medical an ...
... Definition of Public Health • Public health is the science and art of • Preventing disease. • Prolonging life. • Organizing community efforts for the: • Sanitation of the environment. • Control of communicable diseases. • Education of the individual in personal hygiene. • Organization of medical an ...
Epidemiology - Ch 20 - Clayton State University
... Prevalence: total number of existing cases Endemic: Diseases that are constantly present Epidemic: Unusually large number of cases in a population When epidemics spread worldwide they are termed ...
... Prevalence: total number of existing cases Endemic: Diseases that are constantly present Epidemic: Unusually large number of cases in a population When epidemics spread worldwide they are termed ...
Some Epidemic Diseases of Animals
... Prof. Chris Gaskell, Principal of the RAC gave the May lecture entitled “Some Epidemic Diseases of Animals”. His particular expertise is related to farm animals and he is an advisor to the Government and to BBSRC. An epidemic is a disease that spreads rapidly by infection through a population. A pan ...
... Prof. Chris Gaskell, Principal of the RAC gave the May lecture entitled “Some Epidemic Diseases of Animals”. His particular expertise is related to farm animals and he is an advisor to the Government and to BBSRC. An epidemic is a disease that spreads rapidly by infection through a population. A pan ...
Microbial Pathogenesis and infection
... Inhalation: the pathogenic agents may be transmitted by inhalation of respiratory secretions of infected patients, or by inhalation of contaminated dust with pathogenic bacteria . Ingestion: the infectious agents can be transmitted by consumption of contaminated water or food. Also the infection ...
... Inhalation: the pathogenic agents may be transmitted by inhalation of respiratory secretions of infected patients, or by inhalation of contaminated dust with pathogenic bacteria . Ingestion: the infectious agents can be transmitted by consumption of contaminated water or food. Also the infection ...
APIC comments
... thought to have exposed EREs. In addition, IPs are an existing conduit for providing ERE companies with necessary information upon their request when a patient is transported with a suspected contagious but yet unknown disease. The IPs currently assist in gathering the necessary medical patient info ...
... thought to have exposed EREs. In addition, IPs are an existing conduit for providing ERE companies with necessary information upon their request when a patient is transported with a suspected contagious but yet unknown disease. The IPs currently assist in gathering the necessary medical patient info ...
The Immune System
... Airborne; droplet infection; direct contact with infected person Airborne; direct contact with infected person Droplets in air; direct contact with secretions of infected person Droplets in air; contaminated milk and dairy products Direct contact with a carrier Contaminated drinking water Contaminat ...
... Airborne; droplet infection; direct contact with infected person Airborne; direct contact with infected person Droplets in air; direct contact with secretions of infected person Droplets in air; contaminated milk and dairy products Direct contact with a carrier Contaminated drinking water Contaminat ...
Projects
... induced by infection, which persists long after the viruses or bacteria have been cleared from the infected tissue. We propose to use molecular signatures to establish the contributory role of infections in cancer development as an alternative approach to the detection of the infectious agents itsel ...
... induced by infection, which persists long after the viruses or bacteria have been cleared from the infected tissue. We propose to use molecular signatures to establish the contributory role of infections in cancer development as an alternative approach to the detection of the infectious agents itsel ...
Principles of Infection control
... • Transmitted by blood and blood containing body fluids • Many individuals who contact the disease are asymptomatic (display no symptoms) • Others have mild symptoms that are often diagnosed as influenza or flu ...
... • Transmitted by blood and blood containing body fluids • Many individuals who contact the disease are asymptomatic (display no symptoms) • Others have mild symptoms that are often diagnosed as influenza or flu ...
Ultra-fast, Meta-genomics Pathogen Detection Software
... Ultra-fast, Meta-genomics Pathogen Detection Software for Diagnosing Infectious Diseases SALT LAKE CITY, UT, May 26, 2016—Scientists at the University of Utah, ARUP Laboratories, and IDbyDNA, Inc., have developed ultra-fast, meta-genomics analysis software called Taxonomer that dramatically improves ...
... Ultra-fast, Meta-genomics Pathogen Detection Software for Diagnosing Infectious Diseases SALT LAKE CITY, UT, May 26, 2016—Scientists at the University of Utah, ARUP Laboratories, and IDbyDNA, Inc., have developed ultra-fast, meta-genomics analysis software called Taxonomer that dramatically improves ...
35.3 WS
... 15. Malaria and tuberculosis are two examples of diseases that have A. been totally eliminated from the human population. B. evolved resistance to many antibiotics. C. increased because of a lack of understanding of how vaccines work. D. recently been discovered in the United States. 16. Failing to ...
... 15. Malaria and tuberculosis are two examples of diseases that have A. been totally eliminated from the human population. B. evolved resistance to many antibiotics. C. increased because of a lack of understanding of how vaccines work. D. recently been discovered in the United States. 16. Failing to ...
IntroEpiSlides
... Chain of Infection Pathogen Reservoir Portal of exit Modes of Transmission Direct - Direct contact - Droplet spread Indirect - Airborne - Vehicleborne - Vectorborne ...
... Chain of Infection Pathogen Reservoir Portal of exit Modes of Transmission Direct - Direct contact - Droplet spread Indirect - Airborne - Vehicleborne - Vectorborne ...