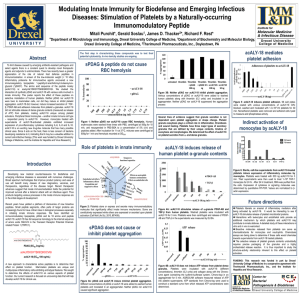
acALY-18 stimulates release of
... acALY-18 stimulates release of platelet microbicidal proteins. Interactions with leukocytes and endothelial cells provide an additional mechanism by which platelets and acALY-18 may contribute to innate defense. A detailed study of these interactions in vitro and in vivo is warranted. Bioactive ...
... acALY-18 stimulates release of platelet microbicidal proteins. Interactions with leukocytes and endothelial cells provide an additional mechanism by which platelets and acALY-18 may contribute to innate defense. A detailed study of these interactions in vitro and in vivo is warranted. Bioactive ...
Linking immune defenses and life history at the
... and understanding such trade-offs, however, is complicated by the complexity of the immune system. The measurement of multiple immune indices in studies of “eco-immunology” has only recently become more common, but has great potential for furthering an understanding of the ecological and evolutionar ...
... and understanding such trade-offs, however, is complicated by the complexity of the immune system. The measurement of multiple immune indices in studies of “eco-immunology” has only recently become more common, but has great potential for furthering an understanding of the ecological and evolutionar ...
Resistance of the body to infection Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
... often survive and function for many more months. Once a foreign particle has been phagocytized, lysosomes and other cytoplasmic granules in the neutrophil or macrophage immediately come in contact with the phagocytic vesicle, and their membranes fuse, thereby dumping many digestive enzymes and bacte ...
... often survive and function for many more months. Once a foreign particle has been phagocytized, lysosomes and other cytoplasmic granules in the neutrophil or macrophage immediately come in contact with the phagocytic vesicle, and their membranes fuse, thereby dumping many digestive enzymes and bacte ...
The HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a
... chronic and relapsing EAE paralysis. Atorvastatin promoted differentiation of Th0 cells to Th2 cells. Atorvastatin treatment induced a population of regulatory T cells that suppressed EAE paralysis. ...
... chronic and relapsing EAE paralysis. Atorvastatin promoted differentiation of Th0 cells to Th2 cells. Atorvastatin treatment induced a population of regulatory T cells that suppressed EAE paralysis. ...
Vaccine
... Immunity to viral infection requires an immune response to antigens located on the surface of the viral particles or on virus-infected cells. For enveloped viruses, these antigens are often surface glycoproteins. The main limitation of viral vaccines occurs with viruses that show a genetically unsta ...
... Immunity to viral infection requires an immune response to antigens located on the surface of the viral particles or on virus-infected cells. For enveloped viruses, these antigens are often surface glycoproteins. The main limitation of viral vaccines occurs with viruses that show a genetically unsta ...
A vaccine for malaria?
... for destruction by white blood cells and making it difficult for them to cause disease. However, because the malaria parasite spends a lot of its life cycle hiding inside human liver cells, antibodies alone may not be protective against malaria. More recent approaches aim to use a different group of ...
... for destruction by white blood cells and making it difficult for them to cause disease. However, because the malaria parasite spends a lot of its life cycle hiding inside human liver cells, antibodies alone may not be protective against malaria. More recent approaches aim to use a different group of ...
Lymphatic System These notes are intended as a comprehensive
... macrophages in specific locations, for example, in the liver and the lungs, have specific names. APCs are also found in the epidermis and other locations. Once again we can take the example of a bacterial attack. Macrophages engulf and ingest bacteria. Enzymes in the cytoplasm fragment them. This is ...
... macrophages in specific locations, for example, in the liver and the lungs, have specific names. APCs are also found in the epidermis and other locations. Once again we can take the example of a bacterial attack. Macrophages engulf and ingest bacteria. Enzymes in the cytoplasm fragment them. This is ...
Immune System Pathways of the Innate and Adaptive Functions of
... Downloaded from http://www.jimmunol.org/ by guest on June 18, 2017 ...
... Downloaded from http://www.jimmunol.org/ by guest on June 18, 2017 ...
Highly multiplexed profiling of single
... lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the ligand of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), reveals previously unobserved deep functional heterogeneity and varying levels of pathogenic activation. Uniquely protein profiling on the same single cells before and after LPS stimulation identified a role for macrophage inhibito ...
... lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the ligand of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), reveals previously unobserved deep functional heterogeneity and varying levels of pathogenic activation. Uniquely protein profiling on the same single cells before and after LPS stimulation identified a role for macrophage inhibito ...
LDN and Fibromyalgia - Medical Home Pharmacy
... The preliminary evidence continues to show that low-dose naltrexone has a specific and clinically beneficial impact on fibromyalgia pain. The medication is widely available, inexpensive, safe, and well-tolerated. (Younger et. al.)! ...
... The preliminary evidence continues to show that low-dose naltrexone has a specific and clinically beneficial impact on fibromyalgia pain. The medication is widely available, inexpensive, safe, and well-tolerated. (Younger et. al.)! ...
Post-traumatic stress disorder - Resurrecting Lives Foundation
... Sympathetic fibers descend from the brain to the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph node tissues.2,3 These fibers may be transmitters of stress-related signals early in trauma response and may be potential mediators of the initial effects of adrenergic and glucocorticoid responses to trauma. They m ...
... Sympathetic fibers descend from the brain to the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph node tissues.2,3 These fibers may be transmitters of stress-related signals early in trauma response and may be potential mediators of the initial effects of adrenergic and glucocorticoid responses to trauma. They m ...
1975–1995 Revised anti-cancer serological response: Biological
... which occurs already in the normal bronchus epithelium. Detection of anti-p53 antibodies in a population at high risk for lung cancer might be a useful indicator for early diagnosis [15]. Moreover, an antibody response to wild type and mutated p21 ras proteins even occurs in 32% of the examined colo ...
... which occurs already in the normal bronchus epithelium. Detection of anti-p53 antibodies in a population at high risk for lung cancer might be a useful indicator for early diagnosis [15]. Moreover, an antibody response to wild type and mutated p21 ras proteins even occurs in 32% of the examined colo ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... patches, spleen and skin) where they become activated on recognising antigen-presenting cells (APC) displaying specific antigen–MHC molecule complexes. Dendritic cells (DC) are the principal APC, but macrophages and B cells can also perform this role. DCs originate in the bone marrow as haematopoiet ...
... patches, spleen and skin) where they become activated on recognising antigen-presenting cells (APC) displaying specific antigen–MHC molecule complexes. Dendritic cells (DC) are the principal APC, but macrophages and B cells can also perform this role. DCs originate in the bone marrow as haematopoiet ...
Licentiate thesis from the Department of Immunology,
... the case of B lymphocytes, somatic hypermutation. The initiation of the adaptive response requires the cooperation of antigen-presenting cells (APC) scanning the periphery for pathogens, phagocytosing and processing proteins before migrating to the lymph nodes or spleen where interaction with adapti ...
... the case of B lymphocytes, somatic hypermutation. The initiation of the adaptive response requires the cooperation of antigen-presenting cells (APC) scanning the periphery for pathogens, phagocytosing and processing proteins before migrating to the lymph nodes or spleen where interaction with adapti ...
IDF Care Guidelines - University Hospitals
... With the exceptions of selective IgA deficiency and transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy, patients with an identified antibody deficiency disorder are generally treated on a periodic basis throughout life with replacement immune globulin, intravenously or subcutaneously. The intervals between ...
... With the exceptions of selective IgA deficiency and transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy, patients with an identified antibody deficiency disorder are generally treated on a periodic basis throughout life with replacement immune globulin, intravenously or subcutaneously. The intervals between ...
Echinoderm immunity - Invertebrate Survival Journal
... The distribution of these cell types is highly variable among species and also even at the individual level. For example, in some sea star species the vast majority (> 90 %) of celomocyte types are amebocytes, while other cell types seem to be exclusive of certain groups (e.g., holothurian crystal c ...
... The distribution of these cell types is highly variable among species and also even at the individual level. For example, in some sea star species the vast majority (> 90 %) of celomocyte types are amebocytes, while other cell types seem to be exclusive of certain groups (e.g., holothurian crystal c ...
EFFECT OF CROTALUS ATROX VENOM ON PERITONEAL AND SPLEEN CELL... PRODUCTION
... Macrophage function is to remove cellular debris generated during normal tissue function while following tissue injury or infection. These cells can respond rapidly to different insults and become activated and have many activities such as lymphocyte activation, tissue damage and microbicidal activi ...
... Macrophage function is to remove cellular debris generated during normal tissue function while following tissue injury or infection. These cells can respond rapidly to different insults and become activated and have many activities such as lymphocyte activation, tissue damage and microbicidal activi ...
A generalized quantitative antibody homeostasis model
... the bone marrow are known to be deleted if they show aggressive self‐binding. What is not known however how self‐molecules get into the bone marrow (except for those present on the developing cells) and how they are presented to the developing cells. Let us slightly rephrase the rules of selection ...
... the bone marrow are known to be deleted if they show aggressive self‐binding. What is not known however how self‐molecules get into the bone marrow (except for those present on the developing cells) and how they are presented to the developing cells. Let us slightly rephrase the rules of selection ...
File - wilson science WEBSITE
... defense by attacking microbes directly or impeding their reproduction • Interferon proteins provide innate defense against viruses and help activate macrophages • About 30 proteins make up the complement system, which causes lysis of invading cells and helps trigger inflammation ...
... defense by attacking microbes directly or impeding their reproduction • Interferon proteins provide innate defense against viruses and help activate macrophages • About 30 proteins make up the complement system, which causes lysis of invading cells and helps trigger inflammation ...
Jeopardy
... IgG antibodies inactivate microbes by blocking their attachment to host cells in the binding process known as a. neutralization. b. agglutination. c. antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. d. opsonization. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... IgG antibodies inactivate microbes by blocking their attachment to host cells in the binding process known as a. neutralization. b. agglutination. c. antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. d. opsonization. ANSWER BACK TO GAME © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Histology Lymphoid system General Concepts Functions Provides
... a. B lymphocytes originate and mature in the bone marrow, then seed secondary lymphoid structures and organs. B cells differentiate into B memory cells and plasma cells, providing humoral immunity. b. T lymphocytes originate in bone marrow, mature in the thymus, and subsequently seed secondary lymph ...
... a. B lymphocytes originate and mature in the bone marrow, then seed secondary lymphoid structures and organs. B cells differentiate into B memory cells and plasma cells, providing humoral immunity. b. T lymphocytes originate in bone marrow, mature in the thymus, and subsequently seed secondary lymph ...
- Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
... for the last several decades should be caused mainly by environmental factors because it is hard to reconcile that genetic factors changed so rapidly. The hygiene hypothesis has proposed that a TH1 deviation on early exposure to bacterial or viral infection protects against allergic diseases by redu ...
... for the last several decades should be caused mainly by environmental factors because it is hard to reconcile that genetic factors changed so rapidly. The hygiene hypothesis has proposed that a TH1 deviation on early exposure to bacterial or viral infection protects against allergic diseases by redu ...
Immunity and the emergence of individuality
... that is, organisms as we perceive them and conceive them (later in this paper, I suggest a scientific definition of the organism, distinct from the phenomenal one). The fact that all multicellular organisms have an immune system should not be surprising, as they must all cope with pathogens – e.g. b ...
... that is, organisms as we perceive them and conceive them (later in this paper, I suggest a scientific definition of the organism, distinct from the phenomenal one). The fact that all multicellular organisms have an immune system should not be surprising, as they must all cope with pathogens – e.g. b ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.























