The effectiveness of a human tyrosinase DNA vaccine in dogs with
... catalyses the first reaction. Without tyrosinase, this reaction cannot occur and no melanin can be produced.16 Several studies using mice showed that no immune response occurred after administration of syngeneic tyrosinase. However, the immune system seemed to be triggered in C57BL/6 mice when using ...
... catalyses the first reaction. Without tyrosinase, this reaction cannot occur and no melanin can be produced.16 Several studies using mice showed that no immune response occurred after administration of syngeneic tyrosinase. However, the immune system seemed to be triggered in C57BL/6 mice when using ...
Antigen Presentation to T Lymphocytes
... have adapted to resist intracellular killing, and the macrophages in which they live require these cytokines to kill the pathogen: this is one of the roles of the TH1 subset of CD4 T cells. Other CD4 T cell subsets have roles in regulating other aspects of the immune response, and some CD4 T cells e ...
... have adapted to resist intracellular killing, and the macrophages in which they live require these cytokines to kill the pathogen: this is one of the roles of the TH1 subset of CD4 T cells. Other CD4 T cell subsets have roles in regulating other aspects of the immune response, and some CD4 T cells e ...
Mast Cells in Autoimmune Disease - Direct-MS
... prominent feature of the skin blisters of individuals affected with bullous pemphigoid44, and mast-cell-derived chemoattractants are present at high concentrations in blister fluids45,46. There are several other examples of autoimmune disorders in which mast cells have been implicated, although ofte ...
... prominent feature of the skin blisters of individuals affected with bullous pemphigoid44, and mast-cell-derived chemoattractants are present at high concentrations in blister fluids45,46. There are several other examples of autoimmune disorders in which mast cells have been implicated, although ofte ...
Modeling the effector - regulatory T cell cross
... distributions along time have not been associated with any specific pattern or precipitator [2,7] although it has been estimated that the presences of such relapses are preceded in one third of cases by either infections or stressful events [8,9]. In any case, a clear understanding of environmental ...
... distributions along time have not been associated with any specific pattern or precipitator [2,7] although it has been estimated that the presences of such relapses are preceded in one third of cases by either infections or stressful events [8,9]. In any case, a clear understanding of environmental ...
Read the text. - Cornell Virology
... immune defects (4, 5). However, how inflammasomes are activated to elicit adaptive immunity following respiratory influenza infection in vivo remains unclear. Commensal bacteria are essential in shaping intestinal immune responses in both health and disease (7, 8). Germ-free mice have underdeveloped g ...
... immune defects (4, 5). However, how inflammasomes are activated to elicit adaptive immunity following respiratory influenza infection in vivo remains unclear. Commensal bacteria are essential in shaping intestinal immune responses in both health and disease (7, 8). Germ-free mice have underdeveloped g ...
Modeling the effector - regulatory T cell cross
... distributions along time have not been associated with any specific pattern or precipitator [2,7] although it has been estimated that the presences of such relapses are preceded in one third of cases by either infections or stressful events [8,9]. In any case, a clear understanding of environmental ...
... distributions along time have not been associated with any specific pattern or precipitator [2,7] although it has been estimated that the presences of such relapses are preceded in one third of cases by either infections or stressful events [8,9]. In any case, a clear understanding of environmental ...
Toll-like receptor-4 agonist in post-haemorrhage pneumonia: role
... the intensive care unit and the risk of death [1]. Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) is the main pathogen involved in post-traumatic pneumonia [2]. This post-traumatic susceptibility to sepsis has been related to a state of immunosuppression lasting 7–10 days followed by an immuno ...
... the intensive care unit and the risk of death [1]. Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) is the main pathogen involved in post-traumatic pneumonia [2]. This post-traumatic susceptibility to sepsis has been related to a state of immunosuppression lasting 7–10 days followed by an immuno ...
PDF
... to reject allografts sub-acutely. These facts led Horton (1970) to suggest that the graft rejection system of Xenopus illustrates an evolutionary intermediate between that of the more primitive Apoda and Urodela and the more advanced members of the Anura. Our interest in this subject arose out of si ...
... to reject allografts sub-acutely. These facts led Horton (1970) to suggest that the graft rejection system of Xenopus illustrates an evolutionary intermediate between that of the more primitive Apoda and Urodela and the more advanced members of the Anura. Our interest in this subject arose out of si ...
Signaling pathways implicated in the cellular innate immune
... as with fungi and LPS. Functions uniquely manifested by insect PGRPs include activation of the Toll and Imd pathways, activation of prophenoloxidase-mediated melanization, and phagocytosis (Michel et al., 2001). In Drosophila, three PGRPs have been identified as being involved in immune related proc ...
... as with fungi and LPS. Functions uniquely manifested by insect PGRPs include activation of the Toll and Imd pathways, activation of prophenoloxidase-mediated melanization, and phagocytosis (Michel et al., 2001). In Drosophila, three PGRPs have been identified as being involved in immune related proc ...
Poster Abstracts - Midwinter Conference of Immunologists
... Although efforts to induce protection from malaria through vaccination have been ongoing for over sixty years, none have produced long-lasting immunity in malariaendemic areas. This is likely due to a lack of knowledge of the immunological mechanisms required for protection. While it is clear that b ...
... Although efforts to induce protection from malaria through vaccination have been ongoing for over sixty years, none have produced long-lasting immunity in malariaendemic areas. This is likely due to a lack of knowledge of the immunological mechanisms required for protection. While it is clear that b ...
Initiation of HAART during acute simian immunodeficiency virus
... responses in the periphery and CNS have not yet managed to suppress virus replication. The 21-day p.i. time point was chosen to allow for a direct insight into the brain parenchyma to determine the impact of HAART on the pathophysiology in the brain at a time when animals either coordinately regulat ...
... responses in the periphery and CNS have not yet managed to suppress virus replication. The 21-day p.i. time point was chosen to allow for a direct insight into the brain parenchyma to determine the impact of HAART on the pathophysiology in the brain at a time when animals either coordinately regulat ...
Examination of Amino Acid Differences as a Means
... Conserved changes in Subject 7’s amino acid sequences indicate functional differences between Visits consistent with a Best Fit immune response pattern • The multiple conserved changes between the Visit 4 sequences and the other two Visits indicate Visit 4 has a drastically different function than ...
... Conserved changes in Subject 7’s amino acid sequences indicate functional differences between Visits consistent with a Best Fit immune response pattern • The multiple conserved changes between the Visit 4 sequences and the other two Visits indicate Visit 4 has a drastically different function than ...
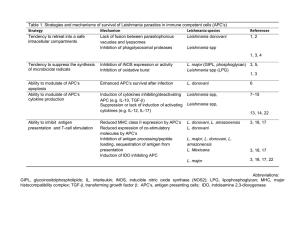
Table 1. Strategies and mechanisms of survival of Leishmania
... Table 1. Strategies and mechanisms of survival of Leishmania parasites in immune competent cells (APC’s) Strategy Mechanism Leishmania species Tendency to retreat into a safe Lack of fusion between parasitophorous Leishmania donovani intracellular compartments vacuoles and lysosomes Inhibition of ph ...
... Table 1. Strategies and mechanisms of survival of Leishmania parasites in immune competent cells (APC’s) Strategy Mechanism Leishmania species Tendency to retreat into a safe Lack of fusion between parasitophorous Leishmania donovani intracellular compartments vacuoles and lysosomes Inhibition of ph ...
Up-regulated interleukin-4 production by peripheral T
... interleukin (IL)-2 and mainly promote cell-mediated immunity. On the other hand, Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13 and induce antibody production. It has been demonstrated that imbalances between Th1 and Th2 cytokine production play a key role in the induction and development of various human ...
... interleukin (IL)-2 and mainly promote cell-mediated immunity. On the other hand, Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13 and induce antibody production. It has been demonstrated that imbalances between Th1 and Th2 cytokine production play a key role in the induction and development of various human ...
"Autoimmune Disease". - University of St Andrews
... interaction of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule–peptide complexes and T-cell receptors (TCRs), and (2) an activating costimulatory signal which is also necessary for activation. Signalling through the TCR ...
... interaction of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule–peptide complexes and T-cell receptors (TCRs), and (2) an activating costimulatory signal which is also necessary for activation. Signalling through the TCR ...
Immunology for physicists - Laboratoire de Physique Statistique
... Lymphocytes are subdivided into two major classes: B cells and T cells. B lymphocytes secrete antibodies, one of the major protective molecules in our bodies. T cells function mainly by interacting with other cells and have been subdivided into helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Helper T cells, w ...
... Lymphocytes are subdivided into two major classes: B cells and T cells. B lymphocytes secrete antibodies, one of the major protective molecules in our bodies. T cells function mainly by interacting with other cells and have been subdivided into helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Helper T cells, w ...
Fc receptors: Cell activators of antibody functions
... At the onset of an infection by different types of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, early defense systems, such as constitutive expression of antimicrobial peptides, and activation of complement get into action. These systems are rapid but not particularly specific. ...
... At the onset of an infection by different types of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, early defense systems, such as constitutive expression of antimicrobial peptides, and activation of complement get into action. These systems are rapid but not particularly specific. ...
A potential solution to the critical organ donor shortage
... If HAR is averted, xenografts are still rejected in days instead of minutes or hours by a process referred to as ‘delayed xenograft rejection’ (DXR), also termed ‘acute vascular xenograft rejection’ (19). This process is characterized pathologically by infiltration of leukocytes (particularly monocy ...
... If HAR is averted, xenografts are still rejected in days instead of minutes or hours by a process referred to as ‘delayed xenograft rejection’ (DXR), also termed ‘acute vascular xenograft rejection’ (19). This process is characterized pathologically by infiltration of leukocytes (particularly monocy ...
Characterization of immune cells in psoriatic adipose tissue
... [15]-[17], while eosinophils [18] and T regulatory cells (Tregs) may protect against insulin resistance [19],[20], and NKT cell function is equivocal [21]-[24]. Adipose specimens from obese humans have demonstrated increased frequencies of T cells [3],[25], dendritic cells [10], mast cells [14], neu ...
... [15]-[17], while eosinophils [18] and T regulatory cells (Tregs) may protect against insulin resistance [19],[20], and NKT cell function is equivocal [21]-[24]. Adipose specimens from obese humans have demonstrated increased frequencies of T cells [3],[25], dendritic cells [10], mast cells [14], neu ...
transplantation - Shandong University
... – An allogenetic MHC molecule with a bound peptide can mimic the determinant formed by a self MHC molecule plus foreign peptide – A cross-reaction of a normal TCR, which was selected to recognize a self MHC molecules plus foreign peptide, with an allogenetic MHC molecule plus peptide ...
... – An allogenetic MHC molecule with a bound peptide can mimic the determinant formed by a self MHC molecule plus foreign peptide – A cross-reaction of a normal TCR, which was selected to recognize a self MHC molecules plus foreign peptide, with an allogenetic MHC molecule plus peptide ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.