
Week 11 - Immune Responses - NSW and VIC Biology for Year
... blood cells formed in the bone marrow and spleen.) Immune responses include both humoral (‘blood-borne’) and cellmediated mechanisms. In humoral immunity antibodies are released by B cells; in cell-mediated immunity, active destruction is carried out by T cells. Antigens are molecules able to bind t ...
... blood cells formed in the bone marrow and spleen.) Immune responses include both humoral (‘blood-borne’) and cellmediated mechanisms. In humoral immunity antibodies are released by B cells; in cell-mediated immunity, active destruction is carried out by T cells. Antigens are molecules able to bind t ...
elisa
... mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigens and induce immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function. ...
... mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigens and induce immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function. ...
Intro to the Immune System
... Displays four (4) attributes: 1) antibody specificity – distinguishes minute differences in molecular structure to determine non-self antigens. 2) diversity – the immune system can produce a hugely diverse set of recognition molecules which allows us to recognize literally billions of molecular shap ...
... Displays four (4) attributes: 1) antibody specificity – distinguishes minute differences in molecular structure to determine non-self antigens. 2) diversity – the immune system can produce a hugely diverse set of recognition molecules which allows us to recognize literally billions of molecular shap ...
Giladi N.Antibodies and hybridomas
... heavy chains, which are linked by disulfide bonds. •Each heavy chain has an amino-terminal variable region followed by a constant region..In any given antibody molecule, the constant region contains one of five basic heavy-chain sequences (m,d ,a ,e , or c) called isotypes and one of two basic light ...
... heavy chains, which are linked by disulfide bonds. •Each heavy chain has an amino-terminal variable region followed by a constant region..In any given antibody molecule, the constant region contains one of five basic heavy-chain sequences (m,d ,a ,e , or c) called isotypes and one of two basic light ...
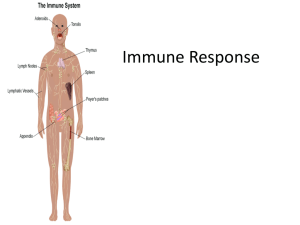
AMS_PowerPoint_The_Lymphatic_System_and_Immunity
... •Briefly outline the major role of the thymus gland in immunity. •Briefly outline the role of the spleen. •List the 7 non-specific defence mechanisms and ...
... •Briefly outline the major role of the thymus gland in immunity. •Briefly outline the role of the spleen. •List the 7 non-specific defence mechanisms and ...
17 Specific Immune Response
... – Express CD4 proteins in their plasma membranes – Amplify the response of B-cells and other helper T-cells – Activated by binding to antigen • Once activated, the Helper T-cell secretes IL-2 • IL-2 is a cytokine that that acts on B-cells and other T-cells ...
... – Express CD4 proteins in their plasma membranes – Amplify the response of B-cells and other helper T-cells – Activated by binding to antigen • Once activated, the Helper T-cell secretes IL-2 • IL-2 is a cytokine that that acts on B-cells and other T-cells ...
Chapter 43 Name_______________________________ Date
... In localized allergies such as hay fever, IgE antibodies produced after first exposure to an allergen attach to receptors on mast cells. The next time the allergen enters the body, it binds to mast cell–associated IgE molecules ...
... In localized allergies such as hay fever, IgE antibodies produced after first exposure to an allergen attach to receptors on mast cells. The next time the allergen enters the body, it binds to mast cell–associated IgE molecules ...
Immunity - MrsCoffinBio
... T cells Involved in CELL MEDIATED RESPONSE Attack, learn & remember pathogens hiding in infected cells ...
... T cells Involved in CELL MEDIATED RESPONSE Attack, learn & remember pathogens hiding in infected cells ...
Cells & Life Chapter 2 Lesson 1
... Basic Cell Substances There are four types of macromolecules in cells: • Nucleic acids are macromolecules that form when long chains of molecules called nucleotides join together. Two types: DNA & RNA • Proteins are long chains of amino acid molecules. Proteins are involved in almost everything t ...
... Basic Cell Substances There are four types of macromolecules in cells: • Nucleic acids are macromolecules that form when long chains of molecules called nucleotides join together. Two types: DNA & RNA • Proteins are long chains of amino acid molecules. Proteins are involved in almost everything t ...
Quarter 4 Study Guide
... If a person produces a great deal of sweat while working out, will this have any impact on the kidneys? Give a reason for your answer. The volume of urine produced will be less as the person has lost water via sweat. The body will try to conserve the rest of the water that it has by only producing a ...
... If a person produces a great deal of sweat while working out, will this have any impact on the kidneys? Give a reason for your answer. The volume of urine produced will be less as the person has lost water via sweat. The body will try to conserve the rest of the water that it has by only producing a ...
Introduction to the immune system
... molecules known as antigens via antigen receptors! 2. Diversity! • The body possesses millions of lymphocytes that can recognise and respond to millions of antigens (one each)! 3. Memory! • 1st exposure to an antigen generates lymphocytes & longlived memory cells – next exposure to the same antige ...
... molecules known as antigens via antigen receptors! 2. Diversity! • The body possesses millions of lymphocytes that can recognise and respond to millions of antigens (one each)! 3. Memory! • 1st exposure to an antigen generates lymphocytes & longlived memory cells – next exposure to the same antige ...
Specialised cells worksheet.
... Designed to __________ _____. Found in the Testes A sperm is ______ and has a long tail that provides ____________ so it can swim and find an egg cell. The _______ contains enzymes which allow it to digest into an egg cell and join with it. ...
... Designed to __________ _____. Found in the Testes A sperm is ______ and has a long tail that provides ____________ so it can swim and find an egg cell. The _______ contains enzymes which allow it to digest into an egg cell and join with it. ...
Human Defence System
... Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as the immunity that develops following an infection". Do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. ...
... Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as the immunity that develops following an infection". Do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. ...
Typical violations of immunobiological supervision 1. The main
... 21. Di Giorgi syndrome characterized by the following features: + a) congenital pathology; b) the genetic nature of the disease; + c) hypoplasia of the thymus; + d) hypocalcemia; e) hypercalcemia. 22. Reduction of efficiency of phagocytosis is observed in the conditions of: + a) leukopenia; b) activ ...
... 21. Di Giorgi syndrome characterized by the following features: + a) congenital pathology; b) the genetic nature of the disease; + c) hypoplasia of the thymus; + d) hypocalcemia; e) hypercalcemia. 22. Reduction of efficiency of phagocytosis is observed in the conditions of: + a) leukopenia; b) activ ...
Chapter 3 Review Answers
... 3. The stomach produces gastric juice, which is very acidic and can destroy bacteria. 4. The innate immune response is quick and general. The immune system does not have to recognize a particular antigen in order to respond. Since phagocytes are already in the blood or tissues, the response time is ...
... 3. The stomach produces gastric juice, which is very acidic and can destroy bacteria. 4. The innate immune response is quick and general. The immune system does not have to recognize a particular antigen in order to respond. Since phagocytes are already in the blood or tissues, the response time is ...
Here
... Respond to antigens by becoming plasma cells Plasma cells make antibodies Memory B cells produce stronger response with next exposure to antigen ...
... Respond to antigens by becoming plasma cells Plasma cells make antibodies Memory B cells produce stronger response with next exposure to antigen ...
The Human Immune System
... ~Antibodies~ - Most infections never make it past the first and second levels of defense - Those that do trigger the production and release of antibodies - Proteins that latch onto, damage, clump, and slow foreign particles - Each antibody binds only to one specific binding site, known as an antigen ...
... ~Antibodies~ - Most infections never make it past the first and second levels of defense - Those that do trigger the production and release of antibodies - Proteins that latch onto, damage, clump, and slow foreign particles - Each antibody binds only to one specific binding site, known as an antigen ...
MCDB 1030
... 12. What are some of the major problems in dealing with AIDS in Africa? The major problem is MONEY. It is expensive to treat HIV, and to provide the right kind of follow-up that allows identification of emerging resistant strains and appropriate changes in treatment strategy. It is also expensive to ...
... 12. What are some of the major problems in dealing with AIDS in Africa? The major problem is MONEY. It is expensive to treat HIV, and to provide the right kind of follow-up that allows identification of emerging resistant strains and appropriate changes in treatment strategy. It is also expensive to ...
Immune Response
... • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substance ...
... • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substance ...
Revise_B2_in_15_mins[1]
... produce antigens which match the pathogens antigens (markers) 5. Special types of White Blood Cells called memory cells are produced so when you come in contact with the real pathogen they REMEMBER IT and produce antibodies SO FAST you don’t get sick; this is immunity. ...
... produce antigens which match the pathogens antigens (markers) 5. Special types of White Blood Cells called memory cells are produced so when you come in contact with the real pathogen they REMEMBER IT and produce antibodies SO FAST you don’t get sick; this is immunity. ...
Electron micrographs of E. coli. Reproduction of prokaryotic cells by
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
... flagella - structures protruding from the cell wall with a corkscrew shape, using energy, they can be rotated, to propel the cell from on area to another unlike eukaryotic flagella, they are solid and inflexible, working like a propeller ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.





















![Revise_B2_in_15_mins[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008375624_1-d5b3eb3fafdc211cff14b81a8ef6ad2d-300x300.png)
