The Journal of Clinical Investigation
... Key immune cells in cancer The main immune cells that play a role in the protection against tumours and their rejection are Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) MHC restricted - recognize only small endogenously processed protein fragments (peptides) that must be presented in a surface protein called ...
... Key immune cells in cancer The main immune cells that play a role in the protection against tumours and their rejection are Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) MHC restricted - recognize only small endogenously processed protein fragments (peptides) that must be presented in a surface protein called ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Bacteria can cause disease in two ways. One way is by breaking down our body’s cells as food. What is the other way? ...
... Bacteria can cause disease in two ways. One way is by breaking down our body’s cells as food. What is the other way? ...
drugs and meds answers antivirals
... 1) Compare viruses and bacteria in terms of size, cell structure, and reproduction. Bacteria are a cell and have cell wall, cytoplasm, and nucleus, virus just dna in protein coat Bacteria are much larger than virus Bacteria reproduce by cell division, virus uses host cell to replicate its dna ...
... 1) Compare viruses and bacteria in terms of size, cell structure, and reproduction. Bacteria are a cell and have cell wall, cytoplasm, and nucleus, virus just dna in protein coat Bacteria are much larger than virus Bacteria reproduce by cell division, virus uses host cell to replicate its dna ...
The Immune System
... – Since helper T cells activate B cells, your body can no longer activate B cells or killer T cells – The immune system has no way to fight the pathogen – In other words, the immune system shuts down – Other antigens or pathogens can enter and your body has no way to fight against them ...
... – Since helper T cells activate B cells, your body can no longer activate B cells or killer T cells – The immune system has no way to fight the pathogen – In other words, the immune system shuts down – Other antigens or pathogens can enter and your body has no way to fight against them ...
Immune System Reading and Questions
... Immune System Reading and Questions – Use this reading to take notes on the overall functions of the immune system and what each of the specific cell types are doing during an immune response. You will have a starter next class. The human immune system protects our bodies from various intruders, bot ...
... Immune System Reading and Questions – Use this reading to take notes on the overall functions of the immune system and what each of the specific cell types are doing during an immune response. You will have a starter next class. The human immune system protects our bodies from various intruders, bot ...
Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization
... 5) IgE – involved in allergic responses and parasitic worm infections ...
... 5) IgE – involved in allergic responses and parasitic worm infections ...
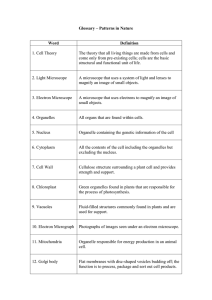
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...
... The theory that all living things are made from cells and come only from pre-existing cells; cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. ...
Hygiene III The Hugiene Hypothesis
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
Basic Principles of Immunology and Ag
... Determined by blood group genes Antigens are integral structural component of the RBC ...
... Determined by blood group genes Antigens are integral structural component of the RBC ...
Cytokines and Chemokines
... 2. CD4 and CD8 Coreceptors Involved in MHC-Restricted T Cell Activation Function:CD4 and CD8 are T cell proteins that bind to nonpolymorphic regions of MHC molecules and transduce signals that together with signals delivered by the TCR complex initiate T cell activation. CD4:Receptor of HIV ...
... 2. CD4 and CD8 Coreceptors Involved in MHC-Restricted T Cell Activation Function:CD4 and CD8 are T cell proteins that bind to nonpolymorphic regions of MHC molecules and transduce signals that together with signals delivered by the TCR complex initiate T cell activation. CD4:Receptor of HIV ...
TAT-mediated gp96 transduction to APCs enhances gp96
... intracellular bacterial sources to enhance APC recognition Interaction of gp96 with cell surface receptor CD91 or scavenger receptor-A (SRA) on APCs promotes internalization of the gp96peptide complexes Cross-presentation of gp96-antigen complex peptides to MHC class I and II activate peptide-sp ...
... intracellular bacterial sources to enhance APC recognition Interaction of gp96 with cell surface receptor CD91 or scavenger receptor-A (SRA) on APCs promotes internalization of the gp96peptide complexes Cross-presentation of gp96-antigen complex peptides to MHC class I and II activate peptide-sp ...
1999 examination
... the inability to activate the system in the presence of IgG antibodies. the natural affinity of complement for antigen presenting cells. none of the above ...
... the inability to activate the system in the presence of IgG antibodies. the natural affinity of complement for antigen presenting cells. none of the above ...
Immune System Period 1 - Mercer Island School District
... has infected the body once. This kind of immunity is a reaction so a pathogen can be dealt with easily the next time it enters the body. This is why people can't catch the same disease twice. (The cold and the flu mutate rapidly and if you catch the flu multiple times, you are infected by a differen ...
... has infected the body once. This kind of immunity is a reaction so a pathogen can be dealt with easily the next time it enters the body. This is why people can't catch the same disease twice. (The cold and the flu mutate rapidly and if you catch the flu multiple times, you are infected by a differen ...
nucleic acids
... Macromolecule: a larger molecule--there are 4 types that make up all living things!! ...
... Macromolecule: a larger molecule--there are 4 types that make up all living things!! ...
No Slide Title
... These variations are critical for effector functions and are achieved in two different ways, RNA splicing and DNA switch recombination. The signals regulating these changes come from antigen binding to the B cell receptor and antigen specific T cells. During the immune response B cells mutate their ...
... These variations are critical for effector functions and are achieved in two different ways, RNA splicing and DNA switch recombination. The signals regulating these changes come from antigen binding to the B cell receptor and antigen specific T cells. During the immune response B cells mutate their ...
immune system-struct and func
... is broken into non-infective pieces & attached to the cell’s MHC when processed through the cell’s machinery MHC-antigen complex is placed on the cell membrane surface where it is recognized by the T Helper cell ...
... is broken into non-infective pieces & attached to the cell’s MHC when processed through the cell’s machinery MHC-antigen complex is placed on the cell membrane surface where it is recognized by the T Helper cell ...
1. The Cell-Mediated Immune Response
... • this is the basis for immunizations • the enhanced secondary response is so much more effective that the individual is largely protected from re-infection with the same pathogen ...
... • this is the basis for immunizations • the enhanced secondary response is so much more effective that the individual is largely protected from re-infection with the same pathogen ...
PPT21Chapter21ImmuneSystem
... Try to provide immediate protection if you are exposed to a disease. No lasting immunity. ...
... Try to provide immediate protection if you are exposed to a disease. No lasting immunity. ...
Questions for week 2 - Seattle Central College
... 3. What three cytoskeletal elements provide structure for a cell? What type of organic molecules are they made of? Microfilaments, microtubules & intermediate filaments; all are made of protein. 4. How would a cell import a large, polar molecule into its cytoplasm if the concentration of that molecu ...
... 3. What three cytoskeletal elements provide structure for a cell? What type of organic molecules are they made of? Microfilaments, microtubules & intermediate filaments; all are made of protein. 4. How would a cell import a large, polar molecule into its cytoplasm if the concentration of that molecu ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.