imunity-skin-and-soft-tissue-infection-copy
... Better understanding of risk factors predisposing to CAMRSA infection ...
... Better understanding of risk factors predisposing to CAMRSA infection ...
Is there any kind of adaptive immunity in invertebrates?
... with respect to immunoglobulins ŽIgs., T cell receptors ŽTCRs., the Major histocompatibility complex ŽMhc., and memory T cells ŽKlein, 1989.. Based on the assumed lack of antigen receptor diversity in invertebrates, Klein postulated that anticipatory Žmemory. and non-anticipatory immune responses we ...
... with respect to immunoglobulins ŽIgs., T cell receptors ŽTCRs., the Major histocompatibility complex ŽMhc., and memory T cells ŽKlein, 1989.. Based on the assumed lack of antigen receptor diversity in invertebrates, Klein postulated that anticipatory Žmemory. and non-anticipatory immune responses we ...
Ch. 2- BIOCHEMISTRY Macromolecules
... o composed of 3 fatty acids (carbon-hydrogen chain) and 1 glycerol (sugar) through dehydration synthesis into an “E” shape o large molecule which must be broken down in order to release the large amount of stored energy o usually stored under the skin as “fat” o can also collect in the lining of blo ...
... o composed of 3 fatty acids (carbon-hydrogen chain) and 1 glycerol (sugar) through dehydration synthesis into an “E” shape o large molecule which must be broken down in order to release the large amount of stored energy o usually stored under the skin as “fat” o can also collect in the lining of blo ...
NIH Public Access
... antigen has been cleared from the host. These cells must then be able to respond to re-exposure to the same antigen or pathogen in a qualitatively different manner than naïve cells. The recall response can be reflected by faster proliferation or more robust effector functions, such as secreting high ...
... antigen has been cleared from the host. These cells must then be able to respond to re-exposure to the same antigen or pathogen in a qualitatively different manner than naïve cells. The recall response can be reflected by faster proliferation or more robust effector functions, such as secreting high ...
Stem Cell Therapy Reverses Diabetes: Stem Cells
... Stem Cell Therapy Reverses Diabetes: Stem Cells from Cord Blood Used to Re-Educate Diabetic's Own T Cells ScienceDaily (Jan. 9, 2012) — Type 1 diabetes is caused by the body's own immune system attacking its pancreatic islet beta cells and requires daily injections of insulin to regulate the patient ...
... Stem Cell Therapy Reverses Diabetes: Stem Cells from Cord Blood Used to Re-Educate Diabetic's Own T Cells ScienceDaily (Jan. 9, 2012) — Type 1 diabetes is caused by the body's own immune system attacking its pancreatic islet beta cells and requires daily injections of insulin to regulate the patient ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... the whole thing falls apart. Most of the time, mitosis goes very smoothly. However, mistakes can be made. One such mistake has been recently reported in a paper from 2005. The scientists who discovered the mistake found that in some cells, instead of just two centrosomes (one at each side of the cel ...
... the whole thing falls apart. Most of the time, mitosis goes very smoothly. However, mistakes can be made. One such mistake has been recently reported in a paper from 2005. The scientists who discovered the mistake found that in some cells, instead of just two centrosomes (one at each side of the cel ...
No Slide Title - Dental Student Pathology
... • Consists of about 20 plasma proteins (C1, C2, etc.) • Can be activated in a few different ways • By antigen-antibody complexes • By bacterial lipopolysaccharides • By bugs that have mannan on their surfaces • Activation proceeds in a cascade fashion • End results: • Cell lysis • Chemotaxis • Opson ...
... • Consists of about 20 plasma proteins (C1, C2, etc.) • Can be activated in a few different ways • By antigen-antibody complexes • By bacterial lipopolysaccharides • By bugs that have mannan on their surfaces • Activation proceeds in a cascade fashion • End results: • Cell lysis • Chemotaxis • Opson ...
Absorption of water and minerals
... stomata to open. Light triggers this. Stomatal opening also correlates with H ion being transported out of the cell Blue light receptors in the guard cells are triggered at dawn to power proton pumps and promote K ion uptake Also, guard cells begin to photosynthesize, making ATP for proton pumps. Gu ...
... stomata to open. Light triggers this. Stomatal opening also correlates with H ion being transported out of the cell Blue light receptors in the guard cells are triggered at dawn to power proton pumps and promote K ion uptake Also, guard cells begin to photosynthesize, making ATP for proton pumps. Gu ...
Antigen Presentation Lecture
... • Mature in lymphoid tissue to express co-stimulatory surface molecules • Macrophages • Engulf foreign bodies through phagocytosis • Immature in tissue (Called Monocytes) • B cells • Recognize specific soluble antigens ...
... • Mature in lymphoid tissue to express co-stimulatory surface molecules • Macrophages • Engulf foreign bodies through phagocytosis • Immature in tissue (Called Monocytes) • B cells • Recognize specific soluble antigens ...
Cell Organisation
... • Filled with acid hydrolases, cannot function at normal cellular pH, will not destroy other cell components • Lysosomal storage diseases result from absence of enzyme, accumulation/engorgement of lysosomes ...
... • Filled with acid hydrolases, cannot function at normal cellular pH, will not destroy other cell components • Lysosomal storage diseases result from absence of enzyme, accumulation/engorgement of lysosomes ...
viruses - Alergia e Imunopatologia
... LRR- ligand recognition, PYD-PYD association and oligomerization of NACHT domain into high molecular weight complexes. Recruits ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), then caspase-1. Targets substrates IL-1 beta and IL-18- active IL-1R and IL-18R- MyD88 pathway. Activates i ...
... LRR- ligand recognition, PYD-PYD association and oligomerization of NACHT domain into high molecular weight complexes. Recruits ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), then caspase-1. Targets substrates IL-1 beta and IL-18- active IL-1R and IL-18R- MyD88 pathway. Activates i ...
1 - Welcome to people.pharmacy.purdue.edu!
... will kill the cells presenting those peptides b. the next time an effector TH1 cell sees foreign peptides properly presented, it will secrete inflammatory cytokines resulting in macrophage activation c. effector T cells to not need co-stimulation to react to foreign peptide antigens when properly pr ...
... will kill the cells presenting those peptides b. the next time an effector TH1 cell sees foreign peptides properly presented, it will secrete inflammatory cytokines resulting in macrophage activation c. effector T cells to not need co-stimulation to react to foreign peptide antigens when properly pr ...
Slide 1
... A type of lymphocyte that develops in the bone marrow and later produces antibodies, which mediate humoral immunity. One of the classes (as A, B, AB, or O) into which individual vertebrates and especially human beings or their blood can be separated on the basis of the presence or absence of specifi ...
... A type of lymphocyte that develops in the bone marrow and later produces antibodies, which mediate humoral immunity. One of the classes (as A, B, AB, or O) into which individual vertebrates and especially human beings or their blood can be separated on the basis of the presence or absence of specifi ...
BIOL242Chap20,21part2AUT2012
... • Are coded for by genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and are unique to an individual • Each MHC molecule has a deep groove that displays a peptide, which is a normal cellular ...
... • Are coded for by genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and are unique to an individual • Each MHC molecule has a deep groove that displays a peptide, which is a normal cellular ...
Chapter 16
... (-IFN) are produced by virus-infected host cells to cause uninfected neighboring cells to produce antiviral proteins (AVPs) to inhibit viral replication if they get infected (does not work on the infected cells) (Fig. 16.16) • Gamma interferon (-IFN) is produced by lymphocytes to cause neutrophils ...
... (-IFN) are produced by virus-infected host cells to cause uninfected neighboring cells to produce antiviral proteins (AVPs) to inhibit viral replication if they get infected (does not work on the infected cells) (Fig. 16.16) • Gamma interferon (-IFN) is produced by lymphocytes to cause neutrophils ...
The Immune System - Body Defenses
... • Antibodies are produced B cells • B cells that are stimulated will actively secrete antibodies and are called plasma cells • Antibodies (immunoglobulins, Ig) are found in extracellular fluids (blood plasma, lymph, mucus, etc.) and the surface of B cells. • Defend against bacteria, bacterial toxins ...
... • Antibodies are produced B cells • B cells that are stimulated will actively secrete antibodies and are called plasma cells • Antibodies (immunoglobulins, Ig) are found in extracellular fluids (blood plasma, lymph, mucus, etc.) and the surface of B cells. • Defend against bacteria, bacterial toxins ...
The Amazing Cell
... and the concentration of another. • Will continue until the molecule is evenly dispersed throughout the solution • Determining factors for Diffusion thru a membrane: 1. Molecular size – small can move through 2. Lipid solubility – lipids can pass lipid bilayer 3. Molecular charge – ions move through ...
... and the concentration of another. • Will continue until the molecule is evenly dispersed throughout the solution • Determining factors for Diffusion thru a membrane: 1. Molecular size – small can move through 2. Lipid solubility – lipids can pass lipid bilayer 3. Molecular charge – ions move through ...
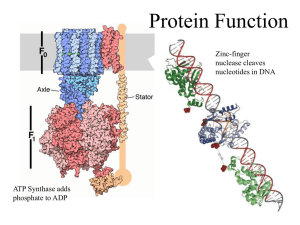
Protein Function - Gleason Chemistry
... • Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up more than a third of the body’s protein. • Composed of 3 chains in a helix. The sequence normally follows the pattern “Gly-Pro-X” and can span over 1,400 residues per chain. • It is the major structural protein of connective tissues (e.g. ...
... • Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up more than a third of the body’s protein. • Composed of 3 chains in a helix. The sequence normally follows the pattern “Gly-Pro-X” and can span over 1,400 residues per chain. • It is the major structural protein of connective tissues (e.g. ...
The Amazing Celllesspics
... and the concentration of another. • Will continue until the molecule is evenly dispersed throughout the solution • Determining factors for Diffusion thru a membrane: 1. Molecular size – small can move through 2. Lipid solubility – lipids can pass lipid bilayer 3. Molecular charge – ions move through ...
... and the concentration of another. • Will continue until the molecule is evenly dispersed throughout the solution • Determining factors for Diffusion thru a membrane: 1. Molecular size – small can move through 2. Lipid solubility – lipids can pass lipid bilayer 3. Molecular charge – ions move through ...
Lecture 1
... Exposure of tissue to extreme heat or cold results in direct injury that is often irreversible, resulting in a pattern of coagulative necrosis (see later). Sudden changes in pressure can cause cellular disruption (e.g. a hammer blow to the thumb). Electrical currents can cause direct breakdown of ce ...
... Exposure of tissue to extreme heat or cold results in direct injury that is often irreversible, resulting in a pattern of coagulative necrosis (see later). Sudden changes in pressure can cause cellular disruption (e.g. a hammer blow to the thumb). Electrical currents can cause direct breakdown of ce ...
1 Ecotoxicology - Biology 5868 Levels of Biological Organization
... or ecosystem levels - however, useful as measures of exposure, e.g. provide clinical evidence of causative agents indicators of exposure; e.g. certain enzyme systems only inhibited by a few classes of chemicals; - induction of certain detoxification mechanisms such as specific mixedfunction oxidases ...
... or ecosystem levels - however, useful as measures of exposure, e.g. provide clinical evidence of causative agents indicators of exposure; e.g. certain enzyme systems only inhibited by a few classes of chemicals; - induction of certain detoxification mechanisms such as specific mixedfunction oxidases ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.