Westwood High School Lesson Plans
... o Coke Classic, Caffeine free, Diet Coke, Diet Coke Caffeine Free o Place each can of soda into a large beaker/containers so students can see whether the can floats or sinks o Why is one can floating and the other sinking? One can is floating and the other is not because while they both have the s ...
... o Coke Classic, Caffeine free, Diet Coke, Diet Coke Caffeine Free o Place each can of soda into a large beaker/containers so students can see whether the can floats or sinks o Why is one can floating and the other sinking? One can is floating and the other is not because while they both have the s ...
Chapter 03 - KFUPM Faculty List
... so on the right hand side we have 2 CO2 + 3 H2O, and thus 2 x 2 + 3 = 7 O atoms. On the left hand side we have 1 O atom in ethanol, so we must provide 6 O atoms from O2 and thus we must have 3 O2, so the balanced equation is C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O: 2C + 6H + 7O both on the left and on the rig ...
... so on the right hand side we have 2 CO2 + 3 H2O, and thus 2 x 2 + 3 = 7 O atoms. On the left hand side we have 1 O atom in ethanol, so we must provide 6 O atoms from O2 and thus we must have 3 O2, so the balanced equation is C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O: 2C + 6H + 7O both on the left and on the rig ...
Preparation and Inner-sphere Oxidation of Ternary Iminodiacetato Chromium [III]
... value for CrVI at the same pH. Addition of Ag NO3 solution to the reaction mixture resulted in a yellowish white precipitate of Ag Br, suggesting the presence of Br- in the product. Ag NO3 solution had no effect on NBS under the experimental conditions. ...
... value for CrVI at the same pH. Addition of Ag NO3 solution to the reaction mixture resulted in a yellowish white precipitate of Ag Br, suggesting the presence of Br- in the product. Ag NO3 solution had no effect on NBS under the experimental conditions. ...
Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium
... concentrations are known, calculate the change in concentration that occurs as the system reaches equilibrium. 3. Use the stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, use the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation) to calculate the changes in concentration of all the other species in the equilibr ...
... concentrations are known, calculate the change in concentration that occurs as the system reaches equilibrium. 3. Use the stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, use the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation) to calculate the changes in concentration of all the other species in the equilibr ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... necessary for the reaction to occur. The equation must be balanced to reflect the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter can neither be gained nor lost in the process of a chemical reaction. Balancing Chemical Equations The chemical equation enables the determination of the quantity o ...
... necessary for the reaction to occur. The equation must be balanced to reflect the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter can neither be gained nor lost in the process of a chemical reaction. Balancing Chemical Equations The chemical equation enables the determination of the quantity o ...
Problem 1-2 - IPN-Kiel
... There is a simple code to characterize fatty acids by giving the proportion of the total number of carbon atoms (m) and the number of double bonds (n) (as it is done in sport results). The code for oleic acid is 18:1. ...
... There is a simple code to characterize fatty acids by giving the proportion of the total number of carbon atoms (m) and the number of double bonds (n) (as it is done in sport results). The code for oleic acid is 18:1. ...
Sulfur Isotope Fractionation during the Thiosulfate
... values slightly deviate from the corresponding experimental data. This result increases confidence in the experimental determination of the temperature-dependent isotope fractionation between sulfur species. Also, such a little difference suggests the possibility that the discrepancy between them ca ...
... values slightly deviate from the corresponding experimental data. This result increases confidence in the experimental determination of the temperature-dependent isotope fractionation between sulfur species. Also, such a little difference suggests the possibility that the discrepancy between them ca ...
kcse chemistry questions
... Describe how the following reagents can be used to prepare lead sulphate solid potassium sulphate, solid lead carbonate, dilute nitric acid and distilled water. Explain why the enthalpy of neutralization of ethanoic acid with sodium hydroxide is different from that of hydrochloric acid with sodium h ...
... Describe how the following reagents can be used to prepare lead sulphate solid potassium sulphate, solid lead carbonate, dilute nitric acid and distilled water. Explain why the enthalpy of neutralization of ethanoic acid with sodium hydroxide is different from that of hydrochloric acid with sodium h ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 20. When HCl was added to a solution containing two metal ions, a precipitate formed with one ion but the other remained soluble. The solution could have contained The solubility rules will tell you the correct choice. A. Ag+ and Cu2+ AgCl(s) is insoluble and precipitates, CuCl2(aq) is soluble corre ...
... 20. When HCl was added to a solution containing two metal ions, a precipitate formed with one ion but the other remained soluble. The solution could have contained The solubility rules will tell you the correct choice. A. Ag+ and Cu2+ AgCl(s) is insoluble and precipitates, CuCl2(aq) is soluble corre ...
Amount of substance
... When an ionic substance dissolves in water, the positive and negative ions separate and become hydrated (they interact with water molecules rather than each other). For example, a solution of sodium chloride could also be described as a mixture of hydrated sodium ions and hydrated chloride ions in w ...
... When an ionic substance dissolves in water, the positive and negative ions separate and become hydrated (they interact with water molecules rather than each other). For example, a solution of sodium chloride could also be described as a mixture of hydrated sodium ions and hydrated chloride ions in w ...
1412_lecture_ch16 Fall_2014
... If 2.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH are added to 1.00 L of 0.100 M CaCl2, will a precipitate form? The ions present in solution are Na+, OH-, Ca2+, Cl-. Only possible precipitate is Ca(OH)2 (solubility rules). Is Q > Ksp for Ca(OH)2? [Ca2+]0 = 0.100 M ...
... If 2.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH are added to 1.00 L of 0.100 M CaCl2, will a precipitate form? The ions present in solution are Na+, OH-, Ca2+, Cl-. Only possible precipitate is Ca(OH)2 (solubility rules). Is Q > Ksp for Ca(OH)2? [Ca2+]0 = 0.100 M ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry
... the molecule. For example, the molecular formula of water is H2O, indicating that a single water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. An empirical formula is the simplest whole‐number ratio of elements in a compound. The empirical formula of water is the same as its mol ...
... the molecule. For example, the molecular formula of water is H2O, indicating that a single water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. An empirical formula is the simplest whole‐number ratio of elements in a compound. The empirical formula of water is the same as its mol ...
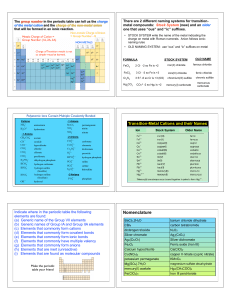
Oxidation numbers
... The word species is used in chemistry to indicate either a compound, a molecule, an ion, an atom or an element. We will use the reaction between magnesium and chlorine as an example. The chemical equation for this reaction is: As a reactant, magnesium has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of ...
... The word species is used in chemistry to indicate either a compound, a molecule, an ion, an atom or an element. We will use the reaction between magnesium and chlorine as an example. The chemical equation for this reaction is: As a reactant, magnesium has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of ...
STUDY MATERIAL 2016-17 CHEMISTRY CLASS XII
... 2. For the solution consisting of two miscible and volatile liquids the partial vapor pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution at particular temperature. pA=P0A. XA, pB=P0B .XB And total vapor pressure is equal to sum of partial pressure. P total = pA ...
... 2. For the solution consisting of two miscible and volatile liquids the partial vapor pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution at particular temperature. pA=P0A. XA, pB=P0B .XB And total vapor pressure is equal to sum of partial pressure. P total = pA ...




![Preparation and Inner-sphere Oxidation of Ternary Iminodiacetato Chromium [III]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008844767_1-9b02a033035d53dea970333df8a85c48-300x300.png)