Ch16
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium ...
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium ...
vce chemistry trial exam 1
... all ions formed from Group 1 elements have a valency of +1 and ions formed from Group 2 elements have a valency of +2. Ions formed from Group 15 elements have a valency of – 3, ions formed from Group 16 elements have a valency of –2, ions formed from Group 17 have a valency of –1 and the Group 18 el ...
... all ions formed from Group 1 elements have a valency of +1 and ions formed from Group 2 elements have a valency of +2. Ions formed from Group 15 elements have a valency of – 3, ions formed from Group 16 elements have a valency of –2, ions formed from Group 17 have a valency of –1 and the Group 18 el ...
Lab # 18
... When we go into a lab, we cannot directly measure the number of moles of a substance. Instead, we measure the mass of a substance and can then calculate the number of moles using the gram formula mass. The gram formula mass is the mass, in grams, of 1 mole of a substance. Calculating this is made e ...
... When we go into a lab, we cannot directly measure the number of moles of a substance. Instead, we measure the mass of a substance and can then calculate the number of moles using the gram formula mass. The gram formula mass is the mass, in grams, of 1 mole of a substance. Calculating this is made e ...
Supplemental Notes
... atomic or molecular mass taken in grams, e.g., 1 mole of Fe = 56 g (Atomic mass, Ar) 1 mole of H2O = 18 g (Molecular mass, Mr) 2. In terms of number: One mole of any substance contains particles equal to 6.02 x 1023. For example, 1 mole of Fe = 56 g = 6.02 x 1023 particles 1 mole of H2O = 18 g = 6.0 ...
... atomic or molecular mass taken in grams, e.g., 1 mole of Fe = 56 g (Atomic mass, Ar) 1 mole of H2O = 18 g (Molecular mass, Mr) 2. In terms of number: One mole of any substance contains particles equal to 6.02 x 1023. For example, 1 mole of Fe = 56 g = 6.02 x 1023 particles 1 mole of H2O = 18 g = 6.0 ...
WRITING CHEMICAL FORMULAE
... When we measure out 50cm3 of a solution, e.g., hydrochloric acid, we measure out some solvent (water) and some acid together. In any reactions of the acid, it is the HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want t ...
... When we measure out 50cm3 of a solution, e.g., hydrochloric acid, we measure out some solvent (water) and some acid together. In any reactions of the acid, it is the HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want t ...
syntheses, structures, and their interconversion
... leading to an almost quantitative yield. Furthermore, the reaction can be scaled-up to 25 g per batch, only restricted by the volume of the glass vial within the autoclave. Solvent water in 1 stem from the crystal water in HgSO4·nH2O. The use of dried HgSO4 (n = 0) results in the precipitation of a ...
... leading to an almost quantitative yield. Furthermore, the reaction can be scaled-up to 25 g per batch, only restricted by the volume of the glass vial within the autoclave. Solvent water in 1 stem from the crystal water in HgSO4·nH2O. The use of dried HgSO4 (n = 0) results in the precipitation of a ...
File
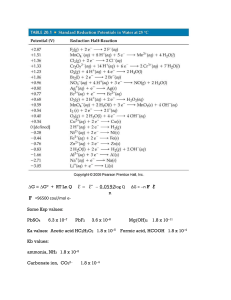
... D. Find the standard molar entropy, S° ̊, of H2 (g) VIII. For the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g), ΔH̊ = –184.6 kJ. Use the information above and the information on the accompanying chart to find the value of ΔS̊ for the reaction given. (at 298 K) ( 3 pts) IX. A standard chemical cell is construc ...
... D. Find the standard molar entropy, S° ̊, of H2 (g) VIII. For the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g), ΔH̊ = –184.6 kJ. Use the information above and the information on the accompanying chart to find the value of ΔS̊ for the reaction given. (at 298 K) ( 3 pts) IX. A standard chemical cell is construc ...
Physical Chemistry Problems. ©Mike Lyons 2009
... equilibrium at a certain temperature the concentrations of NH3 (g), H2(g) and N2(g) are 0.94 M, 1.60 M and 0.52 M respectively. The numerical value of the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction is: (a) 0.415 ; (b) 1.13; (c) 1.06; (d) 0.664; (e) 1.27. Correct answer: a. 2. Calculate the concentrati ...
... equilibrium at a certain temperature the concentrations of NH3 (g), H2(g) and N2(g) are 0.94 M, 1.60 M and 0.52 M respectively. The numerical value of the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction is: (a) 0.415 ; (b) 1.13; (c) 1.06; (d) 0.664; (e) 1.27. Correct answer: a. 2. Calculate the concentrati ...
Chemistry Spell check on
... (c) Carbon dioxide is fed into the phosphine generator to keep the phosphine concentration less than 2·6%. Above this level phosphine can ignite due to the presence of diphosphane, P2H4(g), as an impurity. Draw a structural formula for diphosphane. ...
... (c) Carbon dioxide is fed into the phosphine generator to keep the phosphine concentration less than 2·6%. Above this level phosphine can ignite due to the presence of diphosphane, P2H4(g), as an impurity. Draw a structural formula for diphosphane. ...
Document
... (c) Some amino acids needed to form polypeptides cannot be produced in the human body. State the term used to describe amino acids that the body cannot make. ...
... (c) Some amino acids needed to form polypeptides cannot be produced in the human body. State the term used to describe amino acids that the body cannot make. ...
Chem 171-2-3: Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Problems 1
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
M - GZ @ Science Class Online
... Starting with 540g of glucose what is the maximum amount of ethanol, in moles and also in grams that could be produced. M (C2H5OH) = 46 g mol-1 M (C6H12O6) = 180g mol-1 ...
... Starting with 540g of glucose what is the maximum amount of ethanol, in moles and also in grams that could be produced. M (C2H5OH) = 46 g mol-1 M (C6H12O6) = 180g mol-1 ...
mc_ch08 - MrBrownsChem1LCHS
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical
... through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined ...
... through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined ...
1. (a) Write the electronic structure of a manganese atom and a Mn
... A solution containing both iron(II) and iron(III) ions was titrated with 0.0200 mol dm–3 potassium manganate(VII) solution, 18.20 cm3 being required. Another portion of the same volume of the same solution was reacted with zinc, and then titrated with the same potassium manganate(VII) solution; 25.3 ...
... A solution containing both iron(II) and iron(III) ions was titrated with 0.0200 mol dm–3 potassium manganate(VII) solution, 18.20 cm3 being required. Another portion of the same volume of the same solution was reacted with zinc, and then titrated with the same potassium manganate(VII) solution; 25.3 ...
K c
... experimental conditions may disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product is formed. • In this section we will study 5 factor which can effect chemical equilibrium namely : concentration, pressure, volume, temperature, and catalyst. • Le Châtelier ...
... experimental conditions may disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product is formed. • In this section we will study 5 factor which can effect chemical equilibrium namely : concentration, pressure, volume, temperature, and catalyst. • Le Châtelier ...