17 - Wiley
... characteristics of the cation and anion. Because Na+ has no acid–base tendencies, the anions in these compounds determine the pH of their solutions. Solution pH increases with the strength of the basic anion, which in turn is inversely proportional to the strength of the parent weak acid. Here is th ...
... characteristics of the cation and anion. Because Na+ has no acid–base tendencies, the anions in these compounds determine the pH of their solutions. Solution pH increases with the strength of the basic anion, which in turn is inversely proportional to the strength of the parent weak acid. Here is th ...
How does it vary with the charge and distance of the ions?
... 39. Derive the expression for viscosity coefficient of gas, clearly mentioning the assumption. 40. In the absolute method of determination of viscocity coefficient() by Poiseuille formula. What should be the error in radius if error in is to be kept within 4%. 41. Comment on the temperature depen ...
... 39. Derive the expression for viscosity coefficient of gas, clearly mentioning the assumption. 40. In the absolute method of determination of viscocity coefficient() by Poiseuille formula. What should be the error in radius if error in is to be kept within 4%. 41. Comment on the temperature depen ...
Unit 3: 1 Equilibrium and the Constant, K
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
Document
... • A catalyst changes the mechanism of a reaction to one with a lower activation energy. • A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium concentrations and constant. – But does affect the rate at which equilibrium is attained! ...
... • A catalyst changes the mechanism of a reaction to one with a lower activation energy. • A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium concentrations and constant. – But does affect the rate at which equilibrium is attained! ...
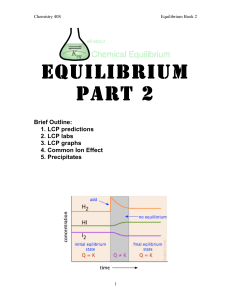
Equilibrium Part 2
... equilibrium to the right, favouring products. This would cause an increase in product concentration and a reduction in reactant concentration. This would result in an increase in the value of K. A decrease in temperature causes a shift to the left, reducing product concentration and increasing react ...
... equilibrium to the right, favouring products. This would cause an increase in product concentration and a reduction in reactant concentration. This would result in an increase in the value of K. A decrease in temperature causes a shift to the left, reducing product concentration and increasing react ...
Amount of Substance
... 4. Soda lime is a mixture containing 85.0% NaOH and 15.0% CaO. What volume of 0.500M nitric acid is needed to neutralise 2.50g of soda lime? 5. A 1.00g sample of limestone is allowed to react with 100cm 3 of 0.200M hydrochloric acid. The excess acid required 24.8cm3 of 0.100M sodium hydroxide for ti ...
... 4. Soda lime is a mixture containing 85.0% NaOH and 15.0% CaO. What volume of 0.500M nitric acid is needed to neutralise 2.50g of soda lime? 5. A 1.00g sample of limestone is allowed to react with 100cm 3 of 0.200M hydrochloric acid. The excess acid required 24.8cm3 of 0.100M sodium hydroxide for ti ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
... oxygen. The compound forms a white precipitate when it reacts with barium nitrate solution. ...
... oxygen. The compound forms a white precipitate when it reacts with barium nitrate solution. ...
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance ...
... To Predict Products and Balance Chemical Equations: 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance ...
Task 4 6 points - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... In this task all data given and asked for are referred to standard conditions . Two isomeric, liquid hydrocarbons (C8H8) have been investigated: cycloocta-1,3,5,7-tetraene and styrene = vinylbenzene = ethenyl benzene. They were burnt in a bomb calorimeter with an excess of oxygen so that H2O(l) and ...
... In this task all data given and asked for are referred to standard conditions . Two isomeric, liquid hydrocarbons (C8H8) have been investigated: cycloocta-1,3,5,7-tetraene and styrene = vinylbenzene = ethenyl benzene. They were burnt in a bomb calorimeter with an excess of oxygen so that H2O(l) and ...
+ 2 H2O(l Ca(OH)2 aq)
... c) 2 KMnO4(aq) + 3 Na2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) 2 MnO2(s) + 3 Na2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) KMnO4 is the oxidizing agent (O.N.(Mn) goes from +7 to +4). Na2SO3 is the reducing agent (O.N.(S) goes from +4 to +6). d) 2 CrO42–(aq) + 3 HSnO2–(aq) + H2O(l) 2 CrO2–(aq) + 3 HSnO3–(aq) + 2 OH–(aq) CrO42– is the oxidizin ...
... c) 2 KMnO4(aq) + 3 Na2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) 2 MnO2(s) + 3 Na2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) KMnO4 is the oxidizing agent (O.N.(Mn) goes from +7 to +4). Na2SO3 is the reducing agent (O.N.(S) goes from +4 to +6). d) 2 CrO42–(aq) + 3 HSnO2–(aq) + H2O(l) 2 CrO2–(aq) + 3 HSnO3–(aq) + 2 OH–(aq) CrO42– is the oxidizin ...
stoichiometric relationships - Assets
... enough information to work out the number of moles of more than one reactant you must consider that one of these reactants will be the limiting reactant. The amount of product formed is determined by the amount of the limiting reactant.The other reactants (not the limiting reactant) are present in e ...
... enough information to work out the number of moles of more than one reactant you must consider that one of these reactants will be the limiting reactant. The amount of product formed is determined by the amount of the limiting reactant.The other reactants (not the limiting reactant) are present in e ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
CHAPTER 3
... 1. What is the average mass in grams of one avg. chlorine atom ? (5.89 X 10-23 g) 2. What is the avg. mass in grams of one ethanol (C2H5OH) molecule ? (7.65 X 10-23 g) 3. How many moles of PbCrO4 (Lead Chromate) are in 45.6 grams ? (0.141 mol) 4. How many HCl (hydrogen chloride) molecules are in 46. ...
... 1. What is the average mass in grams of one avg. chlorine atom ? (5.89 X 10-23 g) 2. What is the avg. mass in grams of one ethanol (C2H5OH) molecule ? (7.65 X 10-23 g) 3. How many moles of PbCrO4 (Lead Chromate) are in 45.6 grams ? (0.141 mol) 4. How many HCl (hydrogen chloride) molecules are in 46. ...
Section 4.9 Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
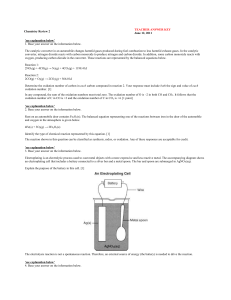
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
STOICHIOMETRY REVIEW WORKSHEET
... Part 2: Solve the following stoichiometry grams-grams problems: 1) The combustion of a sample of butane, C4H10 (lighter fluid), produced 2.46 grams of water. C4H10 + ...
... Part 2: Solve the following stoichiometry grams-grams problems: 1) The combustion of a sample of butane, C4H10 (lighter fluid), produced 2.46 grams of water. C4H10 + ...