... CHAPTER 12, Stoichiometry (continued) 4. If the quantities of reactants are given in units other than moles, what is the first step for determining the amount of product? a. Determine the amount of product from the given amount of limiting reagent. b. Convert each given quantity of reactant to moles ...
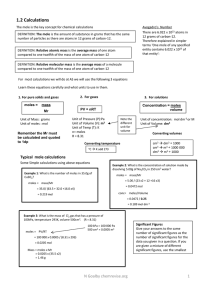
1.2 Calculations
... DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 DEFINITION: Relative molecular mas ...
... DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 DEFINITION: Relative molecular mas ...
Chemistry: Percent Yield
... Unit 3/4 – Moles / Stoichiometry proportion. A chemical compound can be broken down by chemical means. A chemical compound can be represented by a specific chemical formula and assigned a name based on the IUPAC system. 35: 3.3f The percent composition by mass of each element in a compound can be c ...
... Unit 3/4 – Moles / Stoichiometry proportion. A chemical compound can be broken down by chemical means. A chemical compound can be represented by a specific chemical formula and assigned a name based on the IUPAC system. 35: 3.3f The percent composition by mass of each element in a compound can be c ...
5.1 questions - DrBravoChemistry
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change and the standard entropy change for this reaction. Standard enthalpy change ........................................................................... ...
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change and the standard entropy change for this reaction. Standard enthalpy change ........................................................................... ...
Chemistry 8.2
... burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
... burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
redox reaction - Seattle Central College
... d. Balance the electrons lost or gained, to conform to the Law of Conservation of Matter, by placing coefficients in front of the formulas containing the atoms oxidized and reduced to both sides of the equation. e. The remaining atoms are balanced by inspection f. Balance oxygen, or hydrogen by addi ...
... d. Balance the electrons lost or gained, to conform to the Law of Conservation of Matter, by placing coefficients in front of the formulas containing the atoms oxidized and reduced to both sides of the equation. e. The remaining atoms are balanced by inspection f. Balance oxygen, or hydrogen by addi ...
Development of lactate sensor based on an extended gate FET with
... Introduction of L-lactate determination L-Lactate is an important parameter in several areas such as clinical diagnosis, sport medicine and food analysis [1]. It is a metabolite formed from the anaerobic metabolism of glucose in muscles. Generally, the levels of L-lactate in blood range from 0.5 – 1 ...
... Introduction of L-lactate determination L-Lactate is an important parameter in several areas such as clinical diagnosis, sport medicine and food analysis [1]. It is a metabolite formed from the anaerobic metabolism of glucose in muscles. Generally, the levels of L-lactate in blood range from 0.5 – 1 ...
mass mass calc
... In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of t ...
... In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of t ...
Net ionic equation
... electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial posi ...
... electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom (-) and partial posi ...
Ch 3
... in coins, plumbing, and wiring. Copper is obtained from sulfide ores, such as chalcocite, or copper(I) sulfide, by a multistage process. After an initial grinding step, the first stage is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with oxygen gas) to form powdered copper(I) oxide and gaseous sulfur dioxid ...
... in coins, plumbing, and wiring. Copper is obtained from sulfide ores, such as chalcocite, or copper(I) sulfide, by a multistage process. After an initial grinding step, the first stage is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with oxygen gas) to form powdered copper(I) oxide and gaseous sulfur dioxid ...
Stoichiometry notes 1
... 2. Label your given and target substances. 3. Convert your given unit(s) to moles of given substance using the appropriate conversion factor. 4. Convert moles of given substance to moles of target substance using the mole ratio from the balanced equation. 5. Convert moles of target substance to the ...
... 2. Label your given and target substances. 3. Convert your given unit(s) to moles of given substance using the appropriate conversion factor. 4. Convert moles of given substance to moles of target substance using the mole ratio from the balanced equation. 5. Convert moles of target substance to the ...
Slide 1
... proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. ...
... proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. ...
TDB-5: Standards and conventions for TDB publications
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
2 CHEMICAL ARITHMATICS W MODULE - 1
... of atoms shown in a molecular formula cannot be reduced to smaller integers. In such cases molecular and empirical formulae are the same, for example, sucrose C 12H22O11 which is popularly known as cane-sugar. In case of certain elements, a molecule consists of several atoms for example P4, S8, etc. ...
... of atoms shown in a molecular formula cannot be reduced to smaller integers. In such cases molecular and empirical formulae are the same, for example, sucrose C 12H22O11 which is popularly known as cane-sugar. In case of certain elements, a molecule consists of several atoms for example P4, S8, etc. ...
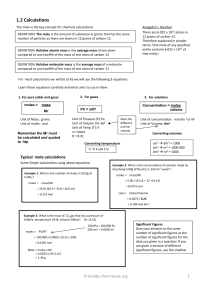
1.2 Calculations
... DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 DEFINITION: Relative molecular mas ...
... DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 DEFINITION: Relative molecular mas ...
Equation of state - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... PRSV2 is particularly advantageous for VLE calculations. While PRSV1 does offer an advantage over the Peng–Robinson model for describing thermodynamic behavior, it is still not accurate enough, in general, for phase equilibrium calculations.[5] The highly non-linear behavior of phaseequilibrium calc ...
... PRSV2 is particularly advantageous for VLE calculations. While PRSV1 does offer an advantage over the Peng–Robinson model for describing thermodynamic behavior, it is still not accurate enough, in general, for phase equilibrium calculations.[5] The highly non-linear behavior of phaseequilibrium calc ...
Atomic Structure
... (c) Sc, V, Cr, Mn increasing number of oxidation state (d) CO3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Sc3+ increasing stability ...
... (c) Sc, V, Cr, Mn increasing number of oxidation state (d) CO3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Sc3+ increasing stability ...