Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease
... transmembrane proteins, peripheral membrane (scaffolding) proteins and regulatory molecules that include kinases. The most important of the transmembrane proteins are members of the claudin family, which define several aspects of tight junction permeability, as discussed below. Claudins are expresse ...
... transmembrane proteins, peripheral membrane (scaffolding) proteins and regulatory molecules that include kinases. The most important of the transmembrane proteins are members of the claudin family, which define several aspects of tight junction permeability, as discussed below. Claudins are expresse ...
Molecular and phenotypic studies of human antigen - edoc
... innate and the adaptive immune system, the latter which constitutes the other arm of the immune system. The adaptive immune system consists of B- and T lymphocytes (B and T cells) carrying highly diverse specialized antigen recognition receptors on their cell surfaces. These receptors are capable of ...
... innate and the adaptive immune system, the latter which constitutes the other arm of the immune system. The adaptive immune system consists of B- and T lymphocytes (B and T cells) carrying highly diverse specialized antigen recognition receptors on their cell surfaces. These receptors are capable of ...
陶秘華 Mi-Hua Tao Institution Institute of Biomedical Sciences
... Phillips, M. L., M. H. Tao, S. L. Morrison, & V. N. Schumaker. (1994) Human/mouse chimeric monoclonal antibodies with human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 constant domains: electron microscopic and hydrodynamic characterization. ...
... Phillips, M. L., M. H. Tao, S. L. Morrison, & V. N. Schumaker. (1994) Human/mouse chimeric monoclonal antibodies with human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 constant domains: electron microscopic and hydrodynamic characterization. ...
Basophils and Mast Cells
... Three groups have succeeded in producing mouse knockouts of certain mast cell–associated mediators. Wastling et al. [40••] produced mice that lack expression of mouse mast cell protease-1 (mMCP-1). These mice exhibited striking histochemical and ultrastructural abnormalities in the cytoplasmic granu ...
... Three groups have succeeded in producing mouse knockouts of certain mast cell–associated mediators. Wastling et al. [40••] produced mice that lack expression of mouse mast cell protease-1 (mMCP-1). These mice exhibited striking histochemical and ultrastructural abnormalities in the cytoplasmic granu ...
[NOTE: if using this form [bracketed] text is guidance
... 7. T.S. Devera, G.A. Lang, H.B. Shah and M.L. Lang (2008) Glycolipid-activated NKT cells support the induction of persistent plasma cell responses and sustained antibody titer. European Journal of Immunology 38: 1001-1011. This article was featured in the “In this issue” section of the journal 8. G. ...
... 7. T.S. Devera, G.A. Lang, H.B. Shah and M.L. Lang (2008) Glycolipid-activated NKT cells support the induction of persistent plasma cell responses and sustained antibody titer. European Journal of Immunology 38: 1001-1011. This article was featured in the “In this issue” section of the journal 8. G. ...
Prevalence of Serum IgG and Neutralizing Factors Against
... genomes were quantified by real-time polymerase chain reaction and vector titers are expressed as viral genomes per milliliter (VG=ml), and contaminant proteins were quantified by the Bradford protein assay. Antibody subclass enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Recombinant AAV particles were diluted i ...
... genomes were quantified by real-time polymerase chain reaction and vector titers are expressed as viral genomes per milliliter (VG=ml), and contaminant proteins were quantified by the Bradford protein assay. Antibody subclass enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Recombinant AAV particles were diluted i ...
to View the Official Conference Program Book
... of innate immunity and how various cardiovascular diseases affect these functions. Particular areas of interest include monocyte/macrophages, complement and reactive oxygen species. As well as review fundamentals of adaptive immunity, and in particular discuss T cell function and why many facets of ...
... of innate immunity and how various cardiovascular diseases affect these functions. Particular areas of interest include monocyte/macrophages, complement and reactive oxygen species. As well as review fundamentals of adaptive immunity, and in particular discuss T cell function and why many facets of ...
Sex steroid hormones
... decline slowly with age2, a phenomenon popularly referred to as the “andropause”. In females, androgens are produced mainly by the ovaries and testosterone is the most important androgen also in females, although the levels are ≈10% of those in men3. Androgens mediate their effect mainly through the ...
... decline slowly with age2, a phenomenon popularly referred to as the “andropause”. In females, androgens are produced mainly by the ovaries and testosterone is the most important androgen also in females, although the levels are ≈10% of those in men3. Androgens mediate their effect mainly through the ...
Mastitis, Mammary Gland Immunity, and Nutrition
... For the best protection of the mammary gland against intramammary infections, innate and acquired immune systems must interact in a synchronized fashion. Some pathogens have developed mechanisms to avoid the host immune system and survive causing disease. Staphylococcus aureus, for example, survives ...
... For the best protection of the mammary gland against intramammary infections, innate and acquired immune systems must interact in a synchronized fashion. Some pathogens have developed mechanisms to avoid the host immune system and survive causing disease. Staphylococcus aureus, for example, survives ...
the Immune Response Psychological Stress in Children May Alter
... varies according to the previous stress experience of the individual, whereas various stressors may act in the same or in opposite ways on the same immune parameter. The kind and the magnitude of alterations of immune response depend on several factors, including the severity and the duration of the ...
... varies according to the previous stress experience of the individual, whereas various stressors may act in the same or in opposite ways on the same immune parameter. The kind and the magnitude of alterations of immune response depend on several factors, including the severity and the duration of the ...
Original Article
... maternal immune system.13,14 To date, it has not been determined whether any of these TNF superfamily members and their receptors is expressed in maternal decidual cells. BAFF was known as B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family, also called B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) TNF- and Apop- ...
... maternal immune system.13,14 To date, it has not been determined whether any of these TNF superfamily members and their receptors is expressed in maternal decidual cells. BAFF was known as B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family, also called B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) TNF- and Apop- ...
Chapter 17: Immunization and Immune Testing
... – Attenuated (live) vaccines – Contain active pathogens with reduced virulence – stimulate a strong immune response due to the large number of antigen molecules – Can result in mild infections but no serious disease ...
... – Attenuated (live) vaccines – Contain active pathogens with reduced virulence – stimulate a strong immune response due to the large number of antigen molecules – Can result in mild infections but no serious disease ...
The vitamin D receptor and T cell function
... variety of inflammatory diseases has been suggested. It is also becoming increasingly clear that microbes slow down immune reactivity by dysregulating the VDR ultimately to increase their chance of survival. Immune modulatory therapies that enhance VDR expression and activity are therefore considere ...
... variety of inflammatory diseases has been suggested. It is also becoming increasingly clear that microbes slow down immune reactivity by dysregulating the VDR ultimately to increase their chance of survival. Immune modulatory therapies that enhance VDR expression and activity are therefore considere ...
REIGN IN BLOOD IMMUNE REGULATION IN TYPE 1 DIABETES Mikael Pihl
... on team radio while leading the 2012 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix ...
... on team radio while leading the 2012 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix ...
Hemolin development and its effect on malaria parasites
... mammals, about 450 million years ago [1]. Human beings combat pathogenic microbes not only with their immune system, but also by inventing antibiotics and other drugs. Although the human intelligence surpasses all or almost all other animals, microorganisms evolve quickly to circumvent the effects o ...
... mammals, about 450 million years ago [1]. Human beings combat pathogenic microbes not only with their immune system, but also by inventing antibiotics and other drugs. Although the human intelligence surpasses all or almost all other animals, microorganisms evolve quickly to circumvent the effects o ...
Toll-like receptor 9 activation: a novel mechanism
... of LPS (lipopolysaccharide; a TLR4 ligand) on gestational day 15 decreased myogenic tone and increased wall thickness of posterior cerebral arteries in pregnant, but not in non-pregnant, rats [33]. These investigators did not examine the role of TLR4 signalling in LPSmediated vascular effects, but p ...
... of LPS (lipopolysaccharide; a TLR4 ligand) on gestational day 15 decreased myogenic tone and increased wall thickness of posterior cerebral arteries in pregnant, but not in non-pregnant, rats [33]. These investigators did not examine the role of TLR4 signalling in LPSmediated vascular effects, but p ...
KUOPION YLIOPISTON JULKAISUJA C. LUONNONTIETEET JA YMPÄRISTÖTIETEET 264
... The bioactive form of vitamin D, 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1α,25(OH)2D3), is a secosteroid hormone that binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily expressed in many cell types, and modulates a variety of biological functions. 1α,25(OH)2D3 is essential for bo ...
... The bioactive form of vitamin D, 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1α,25(OH)2D3), is a secosteroid hormone that binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily expressed in many cell types, and modulates a variety of biological functions. 1α,25(OH)2D3 is essential for bo ...
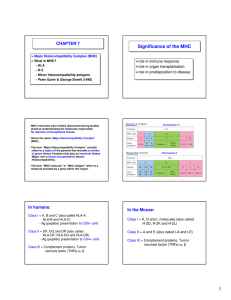
Significance of the MHC Significance of the MHC
... T cells are MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on MHC. CD4+ T cells are class II MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on class II MHC. CD8+ T cells are class I MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on class I MHC. A particular T cell cl ...
... T cells are MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on MHC. CD4+ T cells are class II MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on class II MHC. CD8+ T cells are class I MHC-restricted i.e. they must recognize antigen presented on class I MHC. A particular T cell cl ...
Immunity and Gastrointestinal Disease: A Role for Lymphatic Vessels
... Mathias R, von der Weid PY (2014) Immunity and Gastrointestinal Disease: A Role for Lymphatic Vessels. J Clin Cell Immunol 5: 262. ...
... Mathias R, von der Weid PY (2014) Immunity and Gastrointestinal Disease: A Role for Lymphatic Vessels. J Clin Cell Immunol 5: 262. ...
Pathogens, Infection, and Innate Immunity
... body. Second, individual human cells possess some intrinsic defensive capabilities; for example, cells aggressively degrade double-stranded RNA molecules, which are a hallmark of certain kinds of viral infections. To combat especially powerful pathogens that breach these barricades, vertebrates use ...
... body. Second, individual human cells possess some intrinsic defensive capabilities; for example, cells aggressively degrade double-stranded RNA molecules, which are a hallmark of certain kinds of viral infections. To combat especially powerful pathogens that breach these barricades, vertebrates use ...
Gut Bacteria Metabolism Impacts Immune Recovery in HIV
... Here, we determine whether gut microbiota contribute to inflammation and immune recovery in HIV-infected individuals, and, if they do, which molecular agents are implicated. The present investigation demonstrates an association between an optimal immunovirological ART response and the active fraction ...
... Here, we determine whether gut microbiota contribute to inflammation and immune recovery in HIV-infected individuals, and, if they do, which molecular agents are implicated. The present investigation demonstrates an association between an optimal immunovirological ART response and the active fraction ...
Novel vaccines from biotechnology
... a single F protein. This ‘string of beads’ vaccine should be capable of inducing protective immunity to a wide range of viruses in a single subunit. The combination of genomics, bioinformatics and recombinant technology has even allowed for the development of vaccine candidates before the pathogen c ...
... a single F protein. This ‘string of beads’ vaccine should be capable of inducing protective immunity to a wide range of viruses in a single subunit. The combination of genomics, bioinformatics and recombinant technology has even allowed for the development of vaccine candidates before the pathogen c ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.




![[NOTE: if using this form [bracketed] text is guidance](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007988671_1-14bcfda27166539897509a7a0f8c9da0-300x300.png)