35-2 Defense Against Infection Worksheet
... 10. A substance that triggers the immune response is known as a (n) 11. The main role of immune-system cells. ...
... 10. A substance that triggers the immune response is known as a (n) 11. The main role of immune-system cells. ...
The Immune System : (page 382) Recognizes and destroys
... first. Macrophages engulf them, their antigens moved to the surface of the macrophage. Then your B cells will produce shape specific antibodies that join onto them. This marks them for destruction by T cells. Memory cells are special T cells that ...
... first. Macrophages engulf them, their antigens moved to the surface of the macrophage. Then your B cells will produce shape specific antibodies that join onto them. This marks them for destruction by T cells. Memory cells are special T cells that ...
Document
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
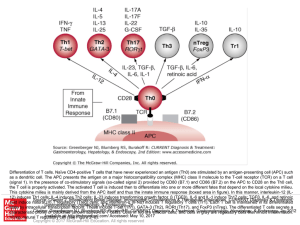
... as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on a T cell (signal 1). In the presence of co-stimulatory signals (so-called signal 2) provided by CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) on the APC to CD28 on the Th0 ce ...
... as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on a T cell (signal 1). In the presence of co-stimulatory signals (so-called signal 2) provided by CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) on the APC to CD28 on the Th0 ce ...
Jeopardy Abbas 1-3 (double) - updated 5/21/2014
... These small cationic peptides are produced by epithelial cells and are directly toxic to microbes. ...
... These small cationic peptides are produced by epithelial cells and are directly toxic to microbes. ...
1. Describe the first non-specific line of defense the
... - marks body cells as “self” - class I found on all nucleated cells - class II only macrophages, B & T cells - job is “antigen presentation” present antigen proteins to T cells (2 types) 1. Cytotoxic T cells antigen receptors bind to fragments (I MHC) 2. Helper T cells bind to fragments fr ...
... - marks body cells as “self” - class I found on all nucleated cells - class II only macrophages, B & T cells - job is “antigen presentation” present antigen proteins to T cells (2 types) 1. Cytotoxic T cells antigen receptors bind to fragments (I MHC) 2. Helper T cells bind to fragments fr ...
here - Molecular Medicine Ireland
... The work of Cornelis (Kees) Melief has contributed fundamental insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) responses, the most important adaptive immune response against viruses and tumors. This includes among the first demonstration ...
... The work of Cornelis (Kees) Melief has contributed fundamental insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) responses, the most important adaptive immune response against viruses and tumors. This includes among the first demonstration ...
the immune response - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Once the entire battle with the foreign invader has been won, these cells signal the immune system to shut down. • Helper T cells and memory B cells, made by the B cells, remain in the blood, ready to trigger another immune response if the body is infected with the same pathogen. ...
... • Once the entire battle with the foreign invader has been won, these cells signal the immune system to shut down. • Helper T cells and memory B cells, made by the B cells, remain in the blood, ready to trigger another immune response if the body is infected with the same pathogen. ...
30_Extracellular bact BA
... Activation of adaptive immunity Successful evasion and subversion of the immune system by pathogens ...
... Activation of adaptive immunity Successful evasion and subversion of the immune system by pathogens ...
Immune System Quiz
... 5. What type of immunity is responsible for agglutination of viruses? A. passive immunity B. cell mediated immunity C. nonspecific immunity D. antibody immunity 6. Which of the following best describes the immunity gained from a vaccine? A. nonspecific B. active C. passive D. artificial 7. What immu ...
... 5. What type of immunity is responsible for agglutination of viruses? A. passive immunity B. cell mediated immunity C. nonspecific immunity D. antibody immunity 6. Which of the following best describes the immunity gained from a vaccine? A. nonspecific B. active C. passive D. artificial 7. What immu ...
Cells and Organs of the Immune System
... Process thru which cells die + later phago’d • decrease in cytoplasmic volume; apoptotic bodies • Clumping/break up of DNA • Phago’d by MØ blocks release of cyto contents no local inflam response ...
... Process thru which cells die + later phago’d • decrease in cytoplasmic volume; apoptotic bodies • Clumping/break up of DNA • Phago’d by MØ blocks release of cyto contents no local inflam response ...
1133693644_460426
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
innate and adaptive immune responses of catfish antigen
... Langerin/CD207-positive cells have been detected in catfish spleen and anterior kidney but not in peripheral blood and skin by using mAbs to human Langerin/CD207. These results lay a foundation for our present study that is to determine the vaccine- induced productive innate and adaptive immune resp ...
... Langerin/CD207-positive cells have been detected in catfish spleen and anterior kidney but not in peripheral blood and skin by using mAbs to human Langerin/CD207. These results lay a foundation for our present study that is to determine the vaccine- induced productive innate and adaptive immune resp ...
Innate immunity against malaria: studies on the mechanisms of Plasmodium -phagocyte interactions and their consequences.
... immunity. The potential for innate immune mechanisms to provide rapid protection against malaria have largely been neglected. Recent studies from animal models, and clinical studies have demonstrated that innate immune cells directed against Plasmodium infected red blood cells contribute to protecti ...
... immunity. The potential for innate immune mechanisms to provide rapid protection against malaria have largely been neglected. Recent studies from animal models, and clinical studies have demonstrated that innate immune cells directed against Plasmodium infected red blood cells contribute to protecti ...
Slide 1
... What is an Antibody??? • Antibodies are special proteins that can bind to the antigen on the surface of a pathogen and help destroy it. ...
... What is an Antibody??? • Antibodies are special proteins that can bind to the antigen on the surface of a pathogen and help destroy it. ...
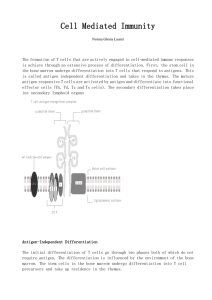
Adaptive Immunity
... mechanisms that take several days to become protective and are designed to remove a specific antigen. This is the immunity one develops throughout life. There are two major branches of the adaptive immune responses: humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity. ...
... mechanisms that take several days to become protective and are designed to remove a specific antigen. This is the immunity one develops throughout life. There are two major branches of the adaptive immune responses: humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity. ...
Introduction to Immuno-Oncology
... Antigen-Specific Lymphocytes ADAPTIVE Natural Killer Cells INNATE Both are derived from the common lymphoid precursor ©2015 MFMER | slide-5 ...
... Antigen-Specific Lymphocytes ADAPTIVE Natural Killer Cells INNATE Both are derived from the common lymphoid precursor ©2015 MFMER | slide-5 ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.