Immunology_IX__immunity_against_infections
... • Virus infected and tumor cells are killed. • Target cells are characterised namely by decreased HLA-I expression. • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...
... • Virus infected and tumor cells are killed. • Target cells are characterised namely by decreased HLA-I expression. • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...
Immune System
... Immunity that occurs naturally as a result of a person's genetic constitution or physiology and does not arise from a previous infection or vaccination. ...
... Immunity that occurs naturally as a result of a person's genetic constitution or physiology and does not arise from a previous infection or vaccination. ...
Drugs to Treat Autoimmune Diseases
... • Methotrexate • Immunosuppressive effects due to inhibition of enzyme involved in the metabolism of folic acid • Anti-inflammatory effects due to interruption of adenosine • Relatively rapid onset of action (4-6 weeks) • Side effects • Stomatitis • Oral ulcers • GI upset ...
... • Methotrexate • Immunosuppressive effects due to inhibition of enzyme involved in the metabolism of folic acid • Anti-inflammatory effects due to interruption of adenosine • Relatively rapid onset of action (4-6 weeks) • Side effects • Stomatitis • Oral ulcers • GI upset ...
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy: New Insights and
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
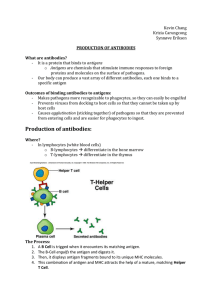
BLOCK F – Krizia,Kevin,Synnove – Production of Antibodies
... 3. Then, it displays antigen fragments bound to its unique MHC molecules. 4. This combination of antigen and MHC attracts the help of a mature, matching Helper T Cell. ...
... 3. Then, it displays antigen fragments bound to its unique MHC molecules. 4. This combination of antigen and MHC attracts the help of a mature, matching Helper T Cell. ...
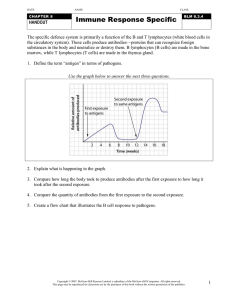
Response of Immune System to Disease
... C. DISPOSAL: antibodies destroy pathogens D. IMMUNITY: some antibodies remain for future use (memory B cells) ...
... C. DISPOSAL: antibodies destroy pathogens D. IMMUNITY: some antibodies remain for future use (memory B cells) ...
The Immune System 2
... 21.21 Where do T cells and B cells develop? 21.22 What are the functions of cell-mediated immunity and antibody mediated immunity? 21.23 How do antigens induce an immune response? Use the terms antigen processing and antigen presentation in your answer. 21.24 What is the normal function of major his ...
... 21.21 Where do T cells and B cells develop? 21.22 What are the functions of cell-mediated immunity and antibody mediated immunity? 21.23 How do antigens induce an immune response? Use the terms antigen processing and antigen presentation in your answer. 21.24 What is the normal function of major his ...
Immune System Disorders (Hypersensitivities ≈ Allergies)
... • IgG and IgM antibodies bind to foreign antigens on the surface of otherwise healthy human blood cell types. • This results in activation of the complement cascade via the classic pathway, which leads to cytolysis of blood cells with the foreign antigen. • Further antibody and complement C3b bindin ...
... • IgG and IgM antibodies bind to foreign antigens on the surface of otherwise healthy human blood cell types. • This results in activation of the complement cascade via the classic pathway, which leads to cytolysis of blood cells with the foreign antigen. • Further antibody and complement C3b bindin ...
Monoclonal Antibodies - The Grange School Blogs
... Points to ponder • After their first manufacture, monoclonal antibodies were quickly and widely used in diagnostic kits such as pregnancy tests. Suggest why their use in human therapy has been much slower. • Discuss how the design of a clinical trial has to consider both ethical and scientific fact ...
... Points to ponder • After their first manufacture, monoclonal antibodies were quickly and widely used in diagnostic kits such as pregnancy tests. Suggest why their use in human therapy has been much slower. • Discuss how the design of a clinical trial has to consider both ethical and scientific fact ...
Antibodies - blobs.org
... The Fab regions are the fragment antigen-binding regions, which are the bits which connect to enemy proteins and which are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, so that lymphocytes can con ...
... The Fab regions are the fragment antigen-binding regions, which are the bits which connect to enemy proteins and which are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, so that lymphocytes can con ...
Crystal Structures of Shark Ig New Antigen Receptor Variable
... Sharks are the most primitive animals to have an advanced adaptive immune system. Their long evolutionary history (~400 million years) is reflected in a diverse array of shark antibodies, including the unique IgNAR (Ig new antigen receptor) isotype. IgNARs are heavy chain homodimers, there is no ass ...
... Sharks are the most primitive animals to have an advanced adaptive immune system. Their long evolutionary history (~400 million years) is reflected in a diverse array of shark antibodies, including the unique IgNAR (Ig new antigen receptor) isotype. IgNARs are heavy chain homodimers, there is no ass ...
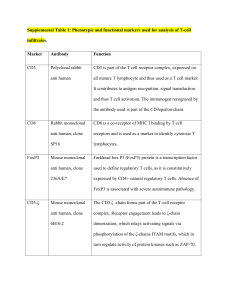
12967_2016_983_MOESM1_ESM
... all mature T lymphocyte and thus used as a T cell marker. It contributes to antigen recognition, signal transduction and thus T cell activation. The immunogen recognized by the antibody used is part of the CD3epsilon chain. ...
... all mature T lymphocyte and thus used as a T cell marker. It contributes to antigen recognition, signal transduction and thus T cell activation. The immunogen recognized by the antibody used is part of the CD3epsilon chain. ...
2.11.15 - WordPress.com
... Live attenuated vaccines such as those against smallpox or yellow fever are the most successful vaccines ever made and can confer lifelong memory, whereas nonliving vaccines induce protection of much shorter duration and require booster vaccination to maintain protective immunity. Thus, a single do ...
... Live attenuated vaccines such as those against smallpox or yellow fever are the most successful vaccines ever made and can confer lifelong memory, whereas nonliving vaccines induce protection of much shorter duration and require booster vaccination to maintain protective immunity. Thus, a single do ...
To the principal Azra naheed Medical college Lahore
... cells/tissue components . Complement activation by Ag /Ab complex e.g. Transfusion reaction . Effects of anti receptors Antibodies e.g. Myasthenia gravis .Ab dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity e.g. Graft rejection ...
... cells/tissue components . Complement activation by Ag /Ab complex e.g. Transfusion reaction . Effects of anti receptors Antibodies e.g. Myasthenia gravis .Ab dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity e.g. Graft rejection ...
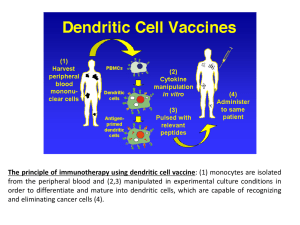
The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic
... The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic cell vaccine: (1) monocytes are isolated from the peripheral blood and (2,3) manipulated in experimental culture conditions in order to differentiate and mature into dendritic cells, which are capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells (4). ...
... The principle of immunotherapy using dendritic cell vaccine: (1) monocytes are isolated from the peripheral blood and (2,3) manipulated in experimental culture conditions in order to differentiate and mature into dendritic cells, which are capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells (4). ...
What is a drug?
... dosing, substance, or targeted species • Most current drugs are small molecules, but the fastest growing group of drugs is biologicals • Most biologics are immune related • Most drugs target humans, but some target pathogens • Most drugs are orally administered ...
... dosing, substance, or targeted species • Most current drugs are small molecules, but the fastest growing group of drugs is biologicals • Most biologics are immune related • Most drugs target humans, but some target pathogens • Most drugs are orally administered ...
History of immunosuppressants
... “Backbone” of most IMS protocols Similar mechanisms of action – Differ in structure and receptor interactions Transplant Proc 2004;36:25S-32S. Am J Kidney Dis 2006;47:S3-21. ...
... “Backbone” of most IMS protocols Similar mechanisms of action – Differ in structure and receptor interactions Transplant Proc 2004;36:25S-32S. Am J Kidney Dis 2006;47:S3-21. ...
Document
... Dr. King Immunopharmacological Agents Page 3 of 5 iv. Prevents B and T-cell proliferation b. Pharmacology i. Rapidly removed from blood and distributed to muscles, liver, skin and intestines. ii. Prednisolone is the biologically active preparation, but is converted in the body to other forms. iii. S ...
... Dr. King Immunopharmacological Agents Page 3 of 5 iv. Prevents B and T-cell proliferation b. Pharmacology i. Rapidly removed from blood and distributed to muscles, liver, skin and intestines. ii. Prednisolone is the biologically active preparation, but is converted in the body to other forms. iii. S ...
35.3 Notes PP
... Cytotoxic T-cells attack and destroy cancer cells when they carry an altered protein on their cell surface If the cytotoxic T-cells have not been activated, cytokines might awaken the immune system and lead to the destruction of cancer Scientists who are engaged in interleukin research believe the i ...
... Cytotoxic T-cells attack and destroy cancer cells when they carry an altered protein on their cell surface If the cytotoxic T-cells have not been activated, cytokines might awaken the immune system and lead to the destruction of cancer Scientists who are engaged in interleukin research believe the i ...