2.-Specific-Cellular
... 6) a) What is autoimmunity? b) Give a condition linked to autoimmunity. 7) How does a TC cell lead to the destruction of an infected cell? 8) a) What does an activated B cell produce? b) How do these molecules bring about destruction of a pathogen? 9) What term is used to describe the first infectio ...
... 6) a) What is autoimmunity? b) Give a condition linked to autoimmunity. 7) How does a TC cell lead to the destruction of an infected cell? 8) a) What does an activated B cell produce? b) How do these molecules bring about destruction of a pathogen? 9) What term is used to describe the first infectio ...
Big_Idea_2-4D_Immune_Response
... Leukocytes are different from other cells of the body in that they are not tightly associated with a particular organ or tissue; thus, they function similar to independent, single-celled organisms. Leukocytes are able to move freely and interact with and capture cellular debris, foreign parti es, or ...
... Leukocytes are different from other cells of the body in that they are not tightly associated with a particular organ or tissue; thus, they function similar to independent, single-celled organisms. Leukocytes are able to move freely and interact with and capture cellular debris, foreign parti es, or ...
Immune System PowerPoint
... leak out of the blood vessels and into the tissues. The white blood cells fight the pathogens During an inflammatory response, the blood vessel get wider to increase the flow of blood to that area Because of the increase blood flow and the fluid leaking into the tissue, an inflamed area will look re ...
... leak out of the blood vessels and into the tissues. The white blood cells fight the pathogens During an inflammatory response, the blood vessel get wider to increase the flow of blood to that area Because of the increase blood flow and the fluid leaking into the tissue, an inflamed area will look re ...
lymphatic outline
... B. B cells or B lymphocytes: oversee humoral immunity 1. work chiefly by secreting antibodies 2. Each B cells makes 1 specific anti 3. When a B cell encounters its triggering antigen it gives rise to many large plasma cells that produce that specific antibody. 4. Antibody structure 2 identical heavy ...
... B. B cells or B lymphocytes: oversee humoral immunity 1. work chiefly by secreting antibodies 2. Each B cells makes 1 specific anti 3. When a B cell encounters its triggering antigen it gives rise to many large plasma cells that produce that specific antibody. 4. Antibody structure 2 identical heavy ...
Congaplex Flyer L4905
... 2 (IL-2) is a cytokine that stimulates T cell response to an immune challenge ...
... 2 (IL-2) is a cytokine that stimulates T cell response to an immune challenge ...
Defense against infectious disease
... • Pathogen is being recognized as many antigens and not just one • Each of the protein types can cause an immune response and thus several different kinds of plasma B cells undergo clonal selection, so several different kinds of antibodies are produced and several different kinds of memory cells rem ...
... • Pathogen is being recognized as many antigens and not just one • Each of the protein types can cause an immune response and thus several different kinds of plasma B cells undergo clonal selection, so several different kinds of antibodies are produced and several different kinds of memory cells rem ...
Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine (WIMM) University of
... Use TIRF to visualize the movement of different fluorescently labeled molecules during T-cell activation ...
... Use TIRF to visualize the movement of different fluorescently labeled molecules during T-cell activation ...
Antibody Isotypes
... Antibody Isotypes Antibodies can come in different varieties known as isotypes or classes. In placental mammals there are five antibody isotypes known as IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM. They are each named with an “Ig” prefix that stands for immunoglobulin, another name for antibody, and differ in their ...
... Antibody Isotypes Antibodies can come in different varieties known as isotypes or classes. In placental mammals there are five antibody isotypes known as IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM. They are each named with an “Ig” prefix that stands for immunoglobulin, another name for antibody, and differ in their ...
Chapter 17
... are presented on specific cells (APCs) using MHC II complexes - Dendritic cells - Macrophage ...
... are presented on specific cells (APCs) using MHC II complexes - Dendritic cells - Macrophage ...
Immunity AIM: How does the immune system protect the body
... 3. Describe • It works against specific pathogens. the function of the immune system. ...
... 3. Describe • It works against specific pathogens. the function of the immune system. ...
Immune_System_Vocabulary
... Lymphocytes – T and B cells Cell mediated response – part of the adaptive immune response, in which T cells elicit B cells to produce antibodies, and also go themselves to destroy pathogens Humoral response – part of the adaptive immune response, in which B cells produce antibodies to incapacitate ...
... Lymphocytes – T and B cells Cell mediated response – part of the adaptive immune response, in which T cells elicit B cells to produce antibodies, and also go themselves to destroy pathogens Humoral response – part of the adaptive immune response, in which B cells produce antibodies to incapacitate ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Detect and eliminate cells that harbor intracellular pathogens. Ag-specific cells – CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells Ag-nonspecific cells – NK cells macrophages neutrophils eosinophils ...
... Detect and eliminate cells that harbor intracellular pathogens. Ag-specific cells – CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells Ag-nonspecific cells – NK cells macrophages neutrophils eosinophils ...
Immunity PP - TeacherWeb
... 2. Lymph cancer- immune cells reproduce uncontrollably Leukemia, and Hodgkin’s disease 3. HIV - AIDS- reduced Th cell count, suppresses both H and T cells *Don’t die of AID’s , but of a 20 infection *HIV is provirus, attaches to CDH receptor complex to ...
... 2. Lymph cancer- immune cells reproduce uncontrollably Leukemia, and Hodgkin’s disease 3. HIV - AIDS- reduced Th cell count, suppresses both H and T cells *Don’t die of AID’s , but of a 20 infection *HIV is provirus, attaches to CDH receptor complex to ...
T cell targeting of latent cytomegalovirus infected cells: can viral
... Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a pathogen that can cause significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in the immunocompromised or immunonaive. HCMV disease is regularly seen after primary infection of individuals with an underdeveloped or suppressed immune system, such as transplant patients o ...
... Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a pathogen that can cause significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in the immunocompromised or immunonaive. HCMV disease is regularly seen after primary infection of individuals with an underdeveloped or suppressed immune system, such as transplant patients o ...
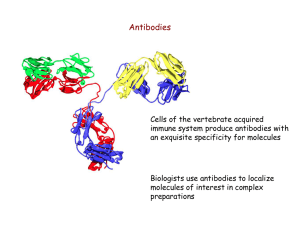
antibodies
... Vaccination stimulates the production of antibody-producing cells Biologists use antibodies produced in animals to localize molecules ...
... Vaccination stimulates the production of antibody-producing cells Biologists use antibodies produced in animals to localize molecules ...
11.1 Immunity Notes - Twanow
... antibodies acquired from another organism through the placenta, colostrum, or injection ...
... antibodies acquired from another organism through the placenta, colostrum, or injection ...
Time course of immune response
... • Produced in response to an activating stimulus • Function by binding to a specific receptor • Usually soluble, but can be membrane associated • Can work locally or at a distance ...
... • Produced in response to an activating stimulus • Function by binding to a specific receptor • Usually soluble, but can be membrane associated • Can work locally or at a distance ...
Day 6 Basics of the Immune System B-Cells - Answer
... The B lymphocyte cell searches for antigen matching its receptors. If it finds such antigen it connects to it, and inside the B cell a triggering signal is set off. The B cell now needs proteins produced by helper T cells to become fully activated. When this happens, the B cell starts to divide to p ...
... The B lymphocyte cell searches for antigen matching its receptors. If it finds such antigen it connects to it, and inside the B cell a triggering signal is set off. The B cell now needs proteins produced by helper T cells to become fully activated. When this happens, the B cell starts to divide to p ...
Dental Microbiology #211 IMMUNOLOGY Lecture 1
... returns it to the blood. The fluid is called the lymph, and the vessels are called lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels collect the lymph into a central vessel called the thoracic duct which releases the lymph into the blood stream via the left subclavian vein. ...
... returns it to the blood. The fluid is called the lymph, and the vessels are called lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels collect the lymph into a central vessel called the thoracic duct which releases the lymph into the blood stream via the left subclavian vein. ...
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
... - fatal in up to 50% of patients - survivors -> exercise impairment and may require heart transplant - ?myocarditis from virus or autoimmune mediated - ?immune reaction to fetal cells -> migration to myocardium -> provocation of an immune response DEFINITION = echo evidence of idiopathic cardiomyopa ...
... - fatal in up to 50% of patients - survivors -> exercise impairment and may require heart transplant - ?myocarditis from virus or autoimmune mediated - ?immune reaction to fetal cells -> migration to myocardium -> provocation of an immune response DEFINITION = echo evidence of idiopathic cardiomyopa ...
Physiology of the Blood III. White Blood Cells and the Immune
... 2. STRANGER CELLS and MOLECULES (transplantation, allergic reactions) 3. SELF CELLS (autoimmunity, tumor cells) 4. DANGER SIGNALS (e.g., after tissue injury) Enemy in general – e.g., differentiation of bacteria from self cells Enemy specifically – recognition of one particular bacterium or its subty ...
... 2. STRANGER CELLS and MOLECULES (transplantation, allergic reactions) 3. SELF CELLS (autoimmunity, tumor cells) 4. DANGER SIGNALS (e.g., after tissue injury) Enemy in general – e.g., differentiation of bacteria from self cells Enemy specifically – recognition of one particular bacterium or its subty ...
Kuby Immunology 6/e - Dr. Jennifer Capers, PhD
... Various cytokines and inflammatory mediators act on local blood vessels 4 steps of extravasation: ○ Rolling, mediated by selectins ○ Activation by chemoattractant stimulus ○ Arrest and adhesion, mediated by integrins binding to ...
... Various cytokines and inflammatory mediators act on local blood vessels 4 steps of extravasation: ○ Rolling, mediated by selectins ○ Activation by chemoattractant stimulus ○ Arrest and adhesion, mediated by integrins binding to ...