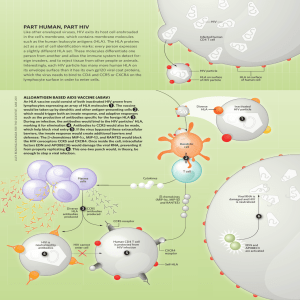
Document
... • They provide general barriers to infection • 1. The skin and Mucous Membranes: skin is a physical barrier to microbes helped by oil and sweat with a low pH. Lysozyme is an enzyme that attacks bacterial cell walls present in tears, saliva and mucus. • 2. Phagocytic White Cells and Natural Killer Ce ...
... • They provide general barriers to infection • 1. The skin and Mucous Membranes: skin is a physical barrier to microbes helped by oil and sweat with a low pH. Lysozyme is an enzyme that attacks bacterial cell walls present in tears, saliva and mucus. • 2. Phagocytic White Cells and Natural Killer Ce ...
The Immune System
... – Secondary immune response o Re-exposure to same antigen gives faster, more prolonged, more effective response – Sensitized memory cells respond within hours – Antibody levels peak in two to three days at much higher levels – Antibodies bind with greater affinity – Antibody level can remain high fo ...
... – Secondary immune response o Re-exposure to same antigen gives faster, more prolonged, more effective response – Sensitized memory cells respond within hours – Antibody levels peak in two to three days at much higher levels – Antibodies bind with greater affinity – Antibody level can remain high fo ...
Assessment Schedule – 2005 Human Biology: Describe how
... from and explains how newborn babies are immune. Any TWO ideas below linked together that indicate that babies have high level of antibodies against disease / natural immunity. ...
... from and explains how newborn babies are immune. Any TWO ideas below linked together that indicate that babies have high level of antibodies against disease / natural immunity. ...
2nd Exam 2015
... Diversity in antibody recognition comes from differences in V-region sequences in the H and L chains and the combinations of various genes coding for V-region components to produce the CDR’s. That diversity is enormously increased by “combinatorial” association. What is “combinatorial association re ...
... Diversity in antibody recognition comes from differences in V-region sequences in the H and L chains and the combinations of various genes coding for V-region components to produce the CDR’s. That diversity is enormously increased by “combinatorial” association. What is “combinatorial association re ...
m1/98 summative mcq
... A type IV is also known as anaphylactoid reaction A type IV is responsible for contact dermatitis A type II is an immune complex antibody mediated reaction Type III immune complexes cause a vasculitis A type I reaction is associated with food allergies ...
... A type IV is also known as anaphylactoid reaction A type IV is responsible for contact dermatitis A type II is an immune complex antibody mediated reaction Type III immune complexes cause a vasculitis A type I reaction is associated with food allergies ...
Chapter 1
... to be ingested by phagocytic cells Activate complement system resulting in lysis of microorganism ...
... to be ingested by phagocytic cells Activate complement system resulting in lysis of microorganism ...
taking advantage of malnourished mice an animal model for
... cells counts in peripheral blood), (b) macrophage activation and phagocytosing capacity, and (c) stimulation of both humoral and cell immune functions, such as antibody response and the reconstitution of delayed-type hypersensitivity response. Different immune cell populations might be induced after ...
... cells counts in peripheral blood), (b) macrophage activation and phagocytosing capacity, and (c) stimulation of both humoral and cell immune functions, such as antibody response and the reconstitution of delayed-type hypersensitivity response. Different immune cell populations might be induced after ...
Historical Perspectives (cont.)
... powder from crusts of smallpox pustules or vesicle fluid applied to skin and the surface scratched - variolation. (Variolation is the process of taking fluid from pustules and scratching the fluid onto skin) ...
... powder from crusts of smallpox pustules or vesicle fluid applied to skin and the surface scratched - variolation. (Variolation is the process of taking fluid from pustules and scratching the fluid onto skin) ...
Immune system
... * cells, which provide defenses by mechanism of phagocytosis * neutrophilic granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages and DC ...
... * cells, which provide defenses by mechanism of phagocytosis * neutrophilic granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages and DC ...
transplantation
... Definition of autoimmune disease Disease caused by failure of self-tolerance and ...
... Definition of autoimmune disease Disease caused by failure of self-tolerance and ...
Lecture 21
... • The lungs and trachea are usually sterile. • The ciliated mucous lining of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles makes up the mucociliary escalator. ...
... • The lungs and trachea are usually sterile. • The ciliated mucous lining of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles makes up the mucociliary escalator. ...
Immunity/Immunology
... invading the blood or tissue fluid will have a _________________ B cell with an antibody on its surface that exactly fits the shape of the foreign antigen. The B cell then divides and multiplies by mitosis to make many new _________________. Each clone will develop in one of two types of cell; a pla ...
... invading the blood or tissue fluid will have a _________________ B cell with an antibody on its surface that exactly fits the shape of the foreign antigen. The B cell then divides and multiplies by mitosis to make many new _________________. Each clone will develop in one of two types of cell; a pla ...
SCHOLAR ROCK`S NICHE
... differentiation into Tregs and suppressed proliferation of effector T cells — effects that should dampen the immune response in inflammatory diseases. In the presentation, the company showed that the first modulator binds latent TGFβ1 with nanomolar affinity, in a way that releases the growth factor ...
... differentiation into Tregs and suppressed proliferation of effector T cells — effects that should dampen the immune response in inflammatory diseases. In the presentation, the company showed that the first modulator binds latent TGFβ1 with nanomolar affinity, in a way that releases the growth factor ...
Diabetes basics: Helping you understand the science Science can
... body as foreign ‐‐ and attacks them. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system destroys the insulin‐producing “beta” cells in the pancreas. ...
... body as foreign ‐‐ and attacks them. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system destroys the insulin‐producing “beta” cells in the pancreas. ...
Pathophysiology of imunity
... - example of localised immune-complexes-mediated inflammatory response. It developes due to repeated local exposure to exogenous antigen which reacts with preformed antibodies in the vessel wall ...
... - example of localised immune-complexes-mediated inflammatory response. It developes due to repeated local exposure to exogenous antigen which reacts with preformed antibodies in the vessel wall ...
immune system 101
... Your immune system has many different ways of fighting off foreign invaders. When confronted with a virus, your body responds by activating specific processes of the immune system. First your body recognizes a foreign antigen and delivers it to the lymph system, where it is ingested by a macrophage. ...
... Your immune system has many different ways of fighting off foreign invaders. When confronted with a virus, your body responds by activating specific processes of the immune system. First your body recognizes a foreign antigen and delivers it to the lymph system, where it is ingested by a macrophage. ...
ANTIGENS
... The age of the hosts influence also the immune response The dose and route of antigen administration also influence the immune response ...
... The age of the hosts influence also the immune response The dose and route of antigen administration also influence the immune response ...
CHAPTER 2 Immune Response to Infection
... 1. Cytokine is a general term for molecules released from one cell population destined to have an effect on another cell population. 2. Chemokines are cytokines chemotactic for inflammatory cell migration 3. Interleukins (IL-1, 2, 3, etc.) regulate growth and differentiation between monocytes and ly ...
... 1. Cytokine is a general term for molecules released from one cell population destined to have an effect on another cell population. 2. Chemokines are cytokines chemotactic for inflammatory cell migration 3. Interleukins (IL-1, 2, 3, etc.) regulate growth and differentiation between monocytes and ly ...
BIO 142 Unit 3 Learning Objectives
... Name the cells that serve as APC. Define Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC). Name two types of MHC molecules. Name the cells that present MHC I and MHC II molecules. Using figure 22.14, identify ...
... Name the cells that serve as APC. Define Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC). Name two types of MHC molecules. Name the cells that present MHC I and MHC II molecules. Using figure 22.14, identify ...
Chapter 7 Cytokines
... 2. Cytokines come from many kinds of cells----activated immune cells, matrix cells and some tumor cells. one cell may secrete many kinds of cytokines, different cells may secrete the same cytokines. ...
... 2. Cytokines come from many kinds of cells----activated immune cells, matrix cells and some tumor cells. one cell may secrete many kinds of cytokines, different cells may secrete the same cytokines. ...
Specific Defenses: Immunity
... • What is the Overview of the Immune Response? • Purpose is to inactivate or destroy: • Pathogens • Abnormal cells • Foreign molecules ...
... • What is the Overview of the Immune Response? • Purpose is to inactivate or destroy: • Pathogens • Abnormal cells • Foreign molecules ...
White Blood Cells
... • Protein receptors within cell membrane of macrophages, called Toll-like receptors • Detect foreign molecules and signal the macrophage to produce chemicals which: – stimulate an inflammatory response (nonspecific) – promote the activity of B and T cells (specific) ...
... • Protein receptors within cell membrane of macrophages, called Toll-like receptors • Detect foreign molecules and signal the macrophage to produce chemicals which: – stimulate an inflammatory response (nonspecific) – promote the activity of B and T cells (specific) ...