Document
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
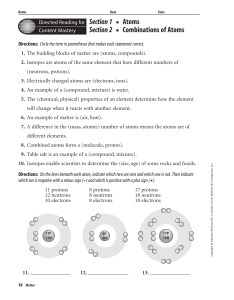
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond
... Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the available electron/s for bonding from the atomic metal, thus creating a positive cation on the atomic metal, and a negative anion from atomic non me ...
... Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the available electron/s for bonding from the atomic metal, thus creating a positive cation on the atomic metal, and a negative anion from atomic non me ...
E/F Physical Science Learning Targets 1 a
... a. All elements are composed of atoms b. Ina particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element 5. Why was Dalton’s model of the atom changed after Thomson’s experiment? ...
... a. All elements are composed of atoms b. Ina particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element 5. Why was Dalton’s model of the atom changed after Thomson’s experiment? ...
Name:
... ___B_ 2. Thought that matter was made of tiny particles that could not be divided ___D_ 3. Provided evidence that an atom contains negatively charged particles ___A_ 4. Stated that matter could be grouped into air, water, fire and earth ___C_ 5. Stated that when elements combine in a compound, the r ...
... ___B_ 2. Thought that matter was made of tiny particles that could not be divided ___D_ 3. Provided evidence that an atom contains negatively charged particles ___A_ 4. Stated that matter could be grouped into air, water, fire and earth ___C_ 5. Stated that when elements combine in a compound, the r ...
Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... • Electrons = Negatively (-) charged particles that orbit around the nucleus. ...
... • Electrons = Negatively (-) charged particles that orbit around the nucleus. ...
History of the atom -naperville north
... the smallest possible piece would be obtained. This piece would be indivisible. He named the smallest piece of matter “atomos,” meaning “not to be cut.” ...
... the smallest possible piece would be obtained. This piece would be indivisible. He named the smallest piece of matter “atomos,” meaning “not to be cut.” ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... COMPOUNDS are composed of the SAME TWO ELEMENTS then the RATIO of the masses of the SECOND ELEMENT combined with a certain mass of the FIRST ELEMENT is always a ratio of ...
... COMPOUNDS are composed of the SAME TWO ELEMENTS then the RATIO of the masses of the SECOND ELEMENT combined with a certain mass of the FIRST ELEMENT is always a ratio of ...
Atomic Structure
... –First person to propose that matter is not infinitely divisible –Atomos –Matter is empty space through which atomos move ...
... –First person to propose that matter is not infinitely divisible –Atomos –Matter is empty space through which atomos move ...
Webquest: Atomic Theories and Models – an Historical Work in
... Go to http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/atoms.html and read the section on “Early Greek Ideas” in order to answer the following questions: 4. What was the “basic idea” about matter that Leucippus and Democritus proposed? 5. How did they use atoms to explain different physical properties? ...
... Go to http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/atoms.html and read the section on “Early Greek Ideas” in order to answer the following questions: 4. What was the “basic idea” about matter that Leucippus and Democritus proposed? 5. How did they use atoms to explain different physical properties? ...
Chemistry Honors Unit 2 Study Guide Atomic Theory Mr. Brown Use
... ____ 4. Calculate the average atomic mass of isotopes in a given problem and/or the relative abundance of an isotope. ____ 5. Understand the significance to the history of the study of chemistry by the following scientists: John Dalton- He explained the three laws stated above with his Atomic Theory ...
... ____ 4. Calculate the average atomic mass of isotopes in a given problem and/or the relative abundance of an isotope. ____ 5. Understand the significance to the history of the study of chemistry by the following scientists: John Dalton- He explained the three laws stated above with his Atomic Theory ...
Introduction to Atoms & Bonding
... • Represent the Electron Orbits First Orbit = holds up to 2 electrons Second Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Third Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Fourth Orbit = at least 8 electrons ...
... • Represent the Electron Orbits First Orbit = holds up to 2 electrons Second Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Third Orbit = holds up to 8 electrons Fourth Orbit = at least 8 electrons ...
Concept Reviews Answer sheet Section: matter and Energy 1. a
... has a definite volume and shape. The same substance as a liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. The same substance as a gas has no definite shape or volume. 3. a 4. c 5. d 6. Either its pressure or volume must also change. Alternatively, both may change. The amplitude and ...
... has a definite volume and shape. The same substance as a liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. The same substance as a gas has no definite shape or volume. 3. a 4. c 5. d 6. Either its pressure or volume must also change. Alternatively, both may change. The amplitude and ...
Glossary
... Cation − positively-charged atom or molecule having fewer electrons than protons. Chemical bond − the force between atoms which maintains molecular stability, due to the interactions of their their electrons and nuclei. Chemical matter − objects that exists up to thermonuclear temperatures, where th ...
... Cation − positively-charged atom or molecule having fewer electrons than protons. Chemical bond − the force between atoms which maintains molecular stability, due to the interactions of their their electrons and nuclei. Chemical matter − objects that exists up to thermonuclear temperatures, where th ...
Chemistry Scavenger Hunt
... 2. There are three main phases of matter: _____________, ____________, and _____________. There is also a fourth phase, ______________, but it exists at very high temperatures. Science Is Fun Go to the “ChemTime Clock” and answer the questions below. http://www.scifun.org/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. A ...
... 2. There are three main phases of matter: _____________, ____________, and _____________. There is also a fourth phase, ______________, but it exists at very high temperatures. Science Is Fun Go to the “ChemTime Clock” and answer the questions below. http://www.scifun.org/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. A ...
Chapter 2 - Hope Charter School
... Chemistry Chapter 2 notes—Matter is Made of Atoms I. Atoms and their structures A. Early Ideas about Matter 1. Greeks— a. all matter was made up of 4 fundamental elements—earth, air, fire, and water b. argued whether or not it could be broken down further 2. Democritus (460-370 B.C.) a. Greek philos ...
... Chemistry Chapter 2 notes—Matter is Made of Atoms I. Atoms and their structures A. Early Ideas about Matter 1. Greeks— a. all matter was made up of 4 fundamental elements—earth, air, fire, and water b. argued whether or not it could be broken down further 2. Democritus (460-370 B.C.) a. Greek philos ...
Atomic Theory Part One
... STM image of a single zigzag chain of cesium atoms (red) on a galliumarsenside surface (blue) ...
... STM image of a single zigzag chain of cesium atoms (red) on a galliumarsenside surface (blue) ...
lsinevrláhistory of chemistry
... astrologer. His full name is Philippus Theophrastus Bombatus von Hohenheim. He was studied attributes of substances and preparation of medicines. Deal – zabývat se něčím Attributes – vlastnosti Physician - lékař ...
... astrologer. His full name is Philippus Theophrastus Bombatus von Hohenheim. He was studied attributes of substances and preparation of medicines. Deal – zabývat se něčím Attributes – vlastnosti Physician - lékař ...
Atom Timeline PPT
... • Use the following information to complete the lecture handout. • On your Atomic Structure Timeline quiz, you will be expected to… – draw the atomic models – match scientists to their experiments and discoveries – place the models in chronological order ...
... • Use the following information to complete the lecture handout. • On your Atomic Structure Timeline quiz, you will be expected to… – draw the atomic models – match scientists to their experiments and discoveries – place the models in chronological order ...
Atomic Theory
... occupying different spherical volumes of different sizes, these levels usually being referred to as shells. It is worth noting that within each shell the electrons are not orbiting the nucleus at a fixed distance but can travel anywhere within the spherical shape of that shell. ...
... occupying different spherical volumes of different sizes, these levels usually being referred to as shells. It is worth noting that within each shell the electrons are not orbiting the nucleus at a fixed distance but can travel anywhere within the spherical shape of that shell. ...
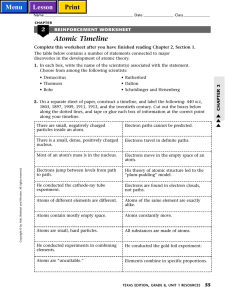
Atomic Timeline
... The table below contains a number of statements connected to major discoveries in the development of atomic theory. 1. In each box, write the name of the scientist(s) associated with the statement. Choose from among the following scientists: • Rutherford • Dalton • Schrödinger and Heisenberg ...
... The table below contains a number of statements connected to major discoveries in the development of atomic theory. 1. In each box, write the name of the scientist(s) associated with the statement. Choose from among the following scientists: • Rutherford • Dalton • Schrödinger and Heisenberg ...
atom-game - WordPress.com
... J.J. Thomson discovered electrons. He was the first scientist to show that the atom was made of even smaller things. He proposed the existence of a positive particle. His atomic model was known as the ‘raisin bun model’ Atoms ...
... J.J. Thomson discovered electrons. He was the first scientist to show that the atom was made of even smaller things. He proposed the existence of a positive particle. His atomic model was known as the ‘raisin bun model’ Atoms ...
History of Atomic Theory - aurora
... with radiation. They were using radioactive materials to generate dense, heavy alpha particles aimed at a very thin piece of gold foil. They expected the particles to barge their way straight through the gold atoms without being affected by the positive charge spread throughout the atom that Thomson ...
... with radiation. They were using radioactive materials to generate dense, heavy alpha particles aimed at a very thin piece of gold foil. They expected the particles to barge their way straight through the gold atoms without being affected by the positive charge spread throughout the atom that Thomson ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.