atomic models
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor dest ...
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor dest ...
Name: Per:______ The History of Atomic Theory Homework Due
... meaning “not.” The word “tomos” means “cut.” Therefore, “atomos” or “atoms” means “cannot be cut or divided.” Many people helped develop the theory of atoms. The first was a Greek named Democritus in the 4th century BC. He proposed that all matter was made of tiny particles. Democritus thought that ...
... meaning “not.” The word “tomos” means “cut.” Therefore, “atomos” or “atoms” means “cannot be cut or divided.” Many people helped develop the theory of atoms. The first was a Greek named Democritus in the 4th century BC. He proposed that all matter was made of tiny particles. Democritus thought that ...
7.1 Development of a Modern Atomic Theory notes
... Our theory about the atom has changed over time as new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. What does the Greek word atomos mean? • _____________________________________ ...
... Our theory about the atom has changed over time as new studies are done. Even though no one has ever seen an atom up close we are still able to make new discoveries – just like we have made new discoveries about dinosaurs. What does the Greek word atomos mean? • _____________________________________ ...
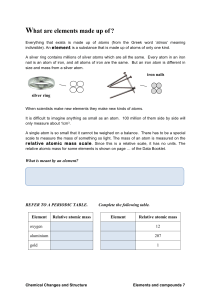
11 what are elements made of
... A silver ring contains millions of silver atoms which are all the same. Every atom in an iron nail is an atom of iron, and all atoms of iron are the same. But an iron atom is different in size and mass from a silver atom. ...
... A silver ring contains millions of silver atoms which are all the same. Every atom in an iron nail is an atom of iron, and all atoms of iron are the same. But an iron atom is different in size and mass from a silver atom. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... around the sun. All we can tell is where an electron is most likely to be found. ...
... around the sun. All we can tell is where an electron is most likely to be found. ...
Biol 1441
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
Atoms {PowerPoint}
... The only thing an atom and the solar system have in common, is both are mostly empty space. ...
... The only thing an atom and the solar system have in common, is both are mostly empty space. ...
8C4AtomicTheoryPresentation
... Rutherford’s team observed that most of the particles passed through the foil undisturbed, as expected. But, to their surprise, a few particles were deflected strongly. Since like charges repel each other, Rutherford inferred that an atom’s positive charge must be clustered in a tiny region in its c ...
... Rutherford’s team observed that most of the particles passed through the foil undisturbed, as expected. But, to their surprise, a few particles were deflected strongly. Since like charges repel each other, Rutherford inferred that an atom’s positive charge must be clustered in a tiny region in its c ...
Structure Changes of Matter
... II. All matter is composed of tiny particles, called atoms. A. Atoms of different elements are different. B. All atoms of one element are basically alike. 1. Atoms are basically electrical (are composed of electrically charged particles). 2. The mass of an atom is concentrated in its center (nucleus ...
... II. All matter is composed of tiny particles, called atoms. A. Atoms of different elements are different. B. All atoms of one element are basically alike. 1. Atoms are basically electrical (are composed of electrically charged particles). 2. The mass of an atom is concentrated in its center (nucleus ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... the times of _____________________. However, these speculations were not scientific theories, because they were not based on any experimental ____________. The first scientific theory of atoms was developed by ___________ in the 18th Century. He based his theory on 3 scientific _____ which he had ob ...
... the times of _____________________. However, these speculations were not scientific theories, because they were not based on any experimental ____________. The first scientific theory of atoms was developed by ___________ in the 18th Century. He based his theory on 3 scientific _____ which he had ob ...
Atom Quiz - IWBchemistry
... How many different isotopes does Carbon have? A- 2 B-3 C-5 Carbon with oxygen Aweeeee D-1 Carbon has 3 different isotopes carbon 12 carbon 13 and carbon 14 ...
... How many different isotopes does Carbon have? A- 2 B-3 C-5 Carbon with oxygen Aweeeee D-1 Carbon has 3 different isotopes carbon 12 carbon 13 and carbon 14 ...
Chapter 4 - Bismuth221
... Third Postulate • Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds – Remember when elements mix they do not have to form compounds ...
... Third Postulate • Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds – Remember when elements mix they do not have to form compounds ...
File
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
Slide 1
... Neutrons – particles of the nucleus with no charge Atomic particles so small, they have their own unit Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – SI unit of mass for atomic particles ...
... Neutrons – particles of the nucleus with no charge Atomic particles so small, they have their own unit Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – SI unit of mass for atomic particles ...
Atomic Theory Notes Page
... A model is a simplified representation of something you want to explain (so a model that represents the structure of an atom is called an atomic model). An Atom- the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element and can exist as a separate particle. Atomic th ...
... A model is a simplified representation of something you want to explain (so a model that represents the structure of an atom is called an atomic model). An Atom- the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element and can exist as a separate particle. Atomic th ...
Note Sheet 6 – Atomic Structure
... o Ex. 1 oxygen atom has _____ protons + neutrons o To figure out the number of neutrons subtract the _______________ from the _______________ o 16 – 8 = 8, so an oxygen atom has _____ neutrons ...
... o Ex. 1 oxygen atom has _____ protons + neutrons o To figure out the number of neutrons subtract the _______________ from the _______________ o 16 – 8 = 8, so an oxygen atom has _____ neutrons ...
Webquest: Atomic Theories and Models – an Historical Work in
... Go to http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/atoms.html and read the section on “Early Greek Ideas” in order to answer the following questions: 4. What was the “basic idea” about matter that Leucippus and Democritus proposed? ...
... Go to http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/atoms.html and read the section on “Early Greek Ideas” in order to answer the following questions: 4. What was the “basic idea” about matter that Leucippus and Democritus proposed? ...
a worksheet on C1.1
... e) In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms have no overall electrical charge. f) All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. g) The number of protons in an atom o ...
... e) In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms have no overall electrical charge. f) All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. g) The number of protons in an atom o ...
At. Theory Timeline - Advanced Placement Chemistry
... electrons in a given shell were further divided into subshells. A spectral line was assumed to be a result of an electron shift between energy levels. Bohr enriched his atom model with quantum theory considerations. In 1916, this concept proved to be superior to the early Rutherford version. ...
... electrons in a given shell were further divided into subshells. A spectral line was assumed to be a result of an electron shift between energy levels. Bohr enriched his atom model with quantum theory considerations. In 1916, this concept proved to be superior to the early Rutherford version. ...
THE ONE MAJOR CONTRIBUTION OF EACH OF THE SCIENTISTS
... • All matter is made of small, solid objects that can’t be divided, created or destroyed • these small objects should be called “atoms” • Different types of matter are made from different types of atoms • Nothing between these atoms except empty space ...
... • All matter is made of small, solid objects that can’t be divided, created or destroyed • these small objects should be called “atoms” • Different types of matter are made from different types of atoms • Nothing between these atoms except empty space ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... elements known at that time into a system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern ...
... elements known at that time into a system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern ...
Unit 2 Chemistry
... electrons in their outermost energy level which is not complete. Valance is the number of extra or deficient electrons in outermost orbital. Anions - extra electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net negative charge. Cation - deficient electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net positi ...
... electrons in their outermost energy level which is not complete. Valance is the number of extra or deficient electrons in outermost orbital. Anions - extra electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net negative charge. Cation - deficient electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net positi ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.