Atomic Theory
... under Rutherford. • Said that atoms contain a unique (+) charge in their nucleus and named it proton. • Said that protons give an element its identity (# of protons = Atomic #) • With the discovery of isotopes he determine the atomic weight was not the major player in the periodic law, but it was th ...
... under Rutherford. • Said that atoms contain a unique (+) charge in their nucleus and named it proton. • Said that protons give an element its identity (# of protons = Atomic #) • With the discovery of isotopes he determine the atomic weight was not the major player in the periodic law, but it was th ...
atomos
... of a specific element are different from those of any other element. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, or destroyed. Different atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined, or rearranged. ...
... of a specific element are different from those of any other element. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, or destroyed. Different atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined, or rearranged. ...
Ch 3 studentElements Ions Isotopes
... – If it’s an atom, the protons and electrons must be the SAME so that it is has a net charge of zero (equal numbers of + and -) – If it does NOT have an equal number of electrons, it is not an atom, it is an ION. For each negative charge, add an extra electron. For each positive charge, subtract an ...
... – If it’s an atom, the protons and electrons must be the SAME so that it is has a net charge of zero (equal numbers of + and -) – If it does NOT have an equal number of electrons, it is not an atom, it is an ION. For each negative charge, add an extra electron. For each positive charge, subtract an ...
6.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, and COMPOUNDS
... -The first energy level, closest to the nucleus, can hold up to ______ electrons. -The second energy level can hold _______electrons. -The third energy level can hold ________electrons. B. Types of Chemical Bonds 1. ___________________—forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons • A _____ ...
... -The first energy level, closest to the nucleus, can hold up to ______ electrons. -The second energy level can hold _______electrons. -The third energy level can hold ________electrons. B. Types of Chemical Bonds 1. ___________________—forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons • A _____ ...
smart_materials_1 - Aldercar High School
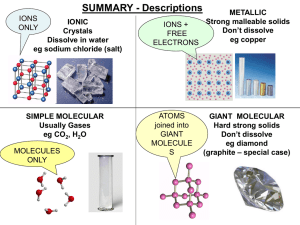
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
atomic structure
... About 2500 years ago, certain Greek thinkers proposed that all matter consisted of extremely tiny particles called atoms. The sizes and shapes of different atoms, they reasoned, was what determined the properties of a substance. This early atomic theory, however, was not widely accepted. Many at the ...
... About 2500 years ago, certain Greek thinkers proposed that all matter consisted of extremely tiny particles called atoms. The sizes and shapes of different atoms, they reasoned, was what determined the properties of a substance. This early atomic theory, however, was not widely accepted. Many at the ...
1 - shawnschmitt
... g. Mole- the amount of particles in 12g of Carbon-12, also, the amount of substance having 6.022x1023 of any kind of particle h. half-life- the amount of time required for ½ of the mass of an isotope to decay i. metalloid- those elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals j. Ionizatio ...
... g. Mole- the amount of particles in 12g of Carbon-12, also, the amount of substance having 6.022x1023 of any kind of particle h. half-life- the amount of time required for ½ of the mass of an isotope to decay i. metalloid- those elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals j. Ionizatio ...
Atomic theory
... Data obtained since Dalton’s time shows that the first 2 principles are NOT true in all cases. 1st principle: all matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms, which can’t be subdivided, created, or destroyed. The atom CAN be divided into smaller particles. What are they? Scienti ...
... Data obtained since Dalton’s time shows that the first 2 principles are NOT true in all cases. 1st principle: all matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms, which can’t be subdivided, created, or destroyed. The atom CAN be divided into smaller particles. What are they? Scienti ...
CHEM 1301 FALL 2003 TEST 1 VERSION 1 NO CHEATING
... The mass of oxygen that is combined with a fixed mass of nitrogen in compounds containing only nitrogen and oxygen can be expressed as a ratio of nice numbers. The atomic masses of all of the elements in the periodic table have fixed values. The % by mass of lead in the compound, lead sulfide, is th ...
... The mass of oxygen that is combined with a fixed mass of nitrogen in compounds containing only nitrogen and oxygen can be expressed as a ratio of nice numbers. The atomic masses of all of the elements in the periodic table have fixed values. The % by mass of lead in the compound, lead sulfide, is th ...
Chemical Equations - Warren County Schools
... Chemical compounds are formed by the union of two or more atoms of the different elements – Atoms combine to form compounds in simple numeric ratios – Atoms of two elements may combine in different ratios to form more than one compound ...
... Chemical compounds are formed by the union of two or more atoms of the different elements – Atoms combine to form compounds in simple numeric ratios – Atoms of two elements may combine in different ratios to form more than one compound ...
Chemistry Part 1
... Rule of eights – Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has 8 electrons – The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold 2 electrons ...
... Rule of eights – Atoms are considered stable when their outermost orbital has 8 electrons – The exception to this rule of eights is Shell 1, which can only hold 2 electrons ...
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford
... Size of Atomic Particles-Sooooo small that scientists use: Atomic Mass Unit (u) – A unit used to express the masses of atomic particles and atoms (1u=1.66 x 10-27Kg) Electron ...
... Size of Atomic Particles-Sooooo small that scientists use: Atomic Mass Unit (u) – A unit used to express the masses of atomic particles and atoms (1u=1.66 x 10-27Kg) Electron ...
Document
... • wave / particle duality of matter (for ex. light: wave / photons, but applies to any object) • Heisenberg uncertainty principle: cannot measure simultaneously the position and momentum of a particle - the greater the precision in one, the less precise the other (uses probabilities) • pairs of part ...
... • wave / particle duality of matter (for ex. light: wave / photons, but applies to any object) • Heisenberg uncertainty principle: cannot measure simultaneously the position and momentum of a particle - the greater the precision in one, the less precise the other (uses probabilities) • pairs of part ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? Bonus question: Give possibilities for the compounds. ...
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? Bonus question: Give possibilities for the compounds. ...
File
... Said matter could be divided to a certain point and then no more Dalton devised a theory based on Democritus’s ideas in the early 1800s Theory had five points ...
... Said matter could be divided to a certain point and then no more Dalton devised a theory based on Democritus’s ideas in the early 1800s Theory had five points ...
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Science
... • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. • In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed in ...
... • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative number of atoms of each kind are definite and constant. • In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed in ...
What is Matter? Anything that can be smelled, tasted, touched… Has
... Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often from Latin or Greek) (1st letter is upper case, 2nd is lower case) ...
... Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often from Latin or Greek) (1st letter is upper case, 2nd is lower case) ...
Bell Ringer
... THINK BACK TO LAST CLASS & The History of the Atom! WITHOUT using your notes match the scientist to the correct statement that describes his work. Ernest Rutherford John Dalton ...
... THINK BACK TO LAST CLASS & The History of the Atom! WITHOUT using your notes match the scientist to the correct statement that describes his work. Ernest Rutherford John Dalton ...
Atomic Structure
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms themselves ...
The Atom
... An atom has three parts: Proton = positive Neutron = no charge Electron = negative The proton & neutron are found in the center of the atom, a place called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. ...
... An atom has three parts: Proton = positive Neutron = no charge Electron = negative The proton & neutron are found in the center of the atom, a place called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. ...
Chemistry of Life
... When atoms share four electrons it is a double bond. When atoms share six or more electrons it is a triple bond. The structure the results when atoms are joined together by covalent bonds is called a MOLECULE. ...
... When atoms share four electrons it is a double bond. When atoms share six or more electrons it is a triple bond. The structure the results when atoms are joined together by covalent bonds is called a MOLECULE. ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.