Ch 3: Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Quantum theory provides a modern picture of the atom Quantum theory - the field of physics based on the idea that energy is quantitized and that this has significant effects on the atomic level. Present Day - Charge/Cloud Model of the Atom Data collected: ...
... Quantum theory provides a modern picture of the atom Quantum theory - the field of physics based on the idea that energy is quantitized and that this has significant effects on the atomic level. Present Day - Charge/Cloud Model of the Atom Data collected: ...
Helpful Science Notes Chapter 4.1 Atomic Structure Vocabulary: 1
... Studying the structure of atoms is like studying wind. We must use indirect evidence to determine atomic structure. Ancient Greek Models of Atoms A. Democritus Believed that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could not be divided. Called these particles atoms from the Greek word ...
... Studying the structure of atoms is like studying wind. We must use indirect evidence to determine atomic structure. Ancient Greek Models of Atoms A. Democritus Believed that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could not be divided. Called these particles atoms from the Greek word ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Early Ideas about Matter Name
... / charge) ratio e– 1910 AD discovered the charge of the electron 1911 AD nuclear model – small, dense nucleus with esurrounding empty ...
... / charge) ratio e– 1910 AD discovered the charge of the electron 1911 AD nuclear model – small, dense nucleus with esurrounding empty ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
Nano-transistors Sensitive to Vibrations in a Single Molecule
... Nanoparticles of many materials have been prepared in the laboratory and all are very fine powders in pure form. We have discovered that nano-particles below a certain size can be transformed into pure liquids by attaching the right molecules to the surface of each particle. The addition of a second ...
... Nanoparticles of many materials have been prepared in the laboratory and all are very fine powders in pure form. We have discovered that nano-particles below a certain size can be transformed into pure liquids by attaching the right molecules to the surface of each particle. The addition of a second ...
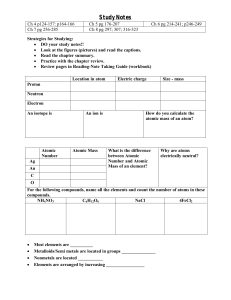
Study Notes
... Strategies for Studying: • DO your study notes!! • Look at the figures (pictures) and read the captions. • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
... Strategies for Studying: • DO your study notes!! • Look at the figures (pictures) and read the captions. • Read the chapter summary. • Practice with the chapter review. • Review pages in Reading-Note Taking Guide (workbook) Location in atom ...
Activity 3: Atomic theory
... ‘Matter can neither be created nor destroyed in any physical or chemical change.’ ...
... ‘Matter can neither be created nor destroyed in any physical or chemical change.’ ...
Concepts of Physical Science
... Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At) 13. A horizontal row on the periodic table numbered 1 through 7 14. any electron in the outermost occupied shell of an atom. 15. the electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 16. the different components of a mixture are in different phases 17 ...
... Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At) 13. A horizontal row on the periodic table numbered 1 through 7 14. any electron in the outermost occupied shell of an atom. 15. the electrical force of attraction that holds ions of opposite charge together 16. the different components of a mixture are in different phases 17 ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
... Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical charge. A proton always has an electrical charge of +1. An electron always has an electrical charge of -1. A neutron has no electrical charge associated with it, a charge of 0. Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the c ...
... Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical charge. A proton always has an electrical charge of +1. An electron always has an electrical charge of -1. A neutron has no electrical charge associated with it, a charge of 0. Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the c ...
File
... determines its __properties____________. The configuration of the three particles is the only thing that makes one element ___different____________ from another. The modern table organizes elements so it is easier to see how elements are __related___________ to each other. The elements are listed by ...
... determines its __properties____________. The configuration of the three particles is the only thing that makes one element ___different____________ from another. The modern table organizes elements so it is easier to see how elements are __related___________ to each other. The elements are listed by ...
Here
... the liquid lacks a fixed structure, like that seen in most solids. Gases-Fluids in which atoms and molecules are in rapid motion, freely moving about with no fixed structure. Gases expand to fill the available space. ...
... the liquid lacks a fixed structure, like that seen in most solids. Gases-Fluids in which atoms and molecules are in rapid motion, freely moving about with no fixed structure. Gases expand to fill the available space. ...
CHAPTER 2 - Net Start Class
... 1,000 B.C.—processing of ores to produce metals for weapons and ornaments; use of embalming fluids 400 B.C.—Greeks—proposed all matter was make up of 4 “elements” : fire, earth, water and air Democritus—first to use the term atomos to describe the ultimate, smallest particles of matter Next 2,000 ye ...
... 1,000 B.C.—processing of ores to produce metals for weapons and ornaments; use of embalming fluids 400 B.C.—Greeks—proposed all matter was make up of 4 “elements” : fire, earth, water and air Democritus—first to use the term atomos to describe the ultimate, smallest particles of matter Next 2,000 ye ...
CHEM_Review - Kenston Local Schools
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
Problem Set 4
... 28) Why do you think we are starting with the atom in chemistry class? Answers will vary, but defining the word “chemistry” is a good place to start… it is the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. IF we can understand elements on the atomic level, we will have a better understandi ...
... 28) Why do you think we are starting with the atom in chemistry class? Answers will vary, but defining the word “chemistry” is a good place to start… it is the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. IF we can understand elements on the atomic level, we will have a better understandi ...
4. - period2chem
... point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I would also recommend going through all of your tests since these questions are only samples and do not include specific examples ...
... point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I would also recommend going through all of your tests since these questions are only samples and do not include specific examples ...
Unit 4 – Atomic Structure Study Guide
... All matter is composed of atoms Atoms of a given element differ from atoms of other elements Compounds are formed when atoms chemically combine in specific whole number ratios Chemical reactions change the way atoms are combined 2. Based upon Dalton’s Atomic Theory, explain the difference be ...
... All matter is composed of atoms Atoms of a given element differ from atoms of other elements Compounds are formed when atoms chemically combine in specific whole number ratios Chemical reactions change the way atoms are combined 2. Based upon Dalton’s Atomic Theory, explain the difference be ...
Document
... Lewis Dot diagrams – dots around the symbol represent valence electrons around the nucleus. ...
... Lewis Dot diagrams – dots around the symbol represent valence electrons around the nucleus. ...
Atoms- Basic Units of Matter
... • A chemical reaction is a process in which atoms in the starting materials rearrange to form products with different properties ...
... • A chemical reaction is a process in which atoms in the starting materials rearrange to form products with different properties ...
elements_and_the_periodic_table_2011
... Aristotle and Plato believed there were four elements: Earth, Fire, Air and Water. Their ideas stayed for 2000 year because of their position as philosophers. ...
... Aristotle and Plato believed there were four elements: Earth, Fire, Air and Water. Their ideas stayed for 2000 year because of their position as philosophers. ...
The Atom
... a. the same number of protons. b. the same number of neutrons. c. a different atomic number. d. the same mass. ______14. Which of the following is NOT true about unstable atoms? a. They are radioactive. b. They have a nucleus that always remains the same. c. They give off energy as they fall apart. ...
... a. the same number of protons. b. the same number of neutrons. c. a different atomic number. d. the same mass. ______14. Which of the following is NOT true about unstable atoms? a. They are radioactive. b. They have a nucleus that always remains the same. c. They give off energy as they fall apart. ...
Distinguishing Among Atoms
... Learning Targets1. I can describe the structure of atoms. 2. I can describe how structure of an atom affects it’s properties. 3. I can create a timeline that shows the developments that lead to the current model of the atom. ...
... Learning Targets1. I can describe the structure of atoms. 2. I can describe how structure of an atom affects it’s properties. 3. I can create a timeline that shows the developments that lead to the current model of the atom. ...
Chapter 18
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
... same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Average atomic mass—the weighted average mass of an element’s mixture of isotopes (used because most elements have more than one isotope) ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.