Atoms of an element are identical
... _____4. According to the law of conservation of mass, when sodium, hydrogen, and oxygen react to form a compound, the mass of the compound is _________ the sum of the masses of the individual elements. a. Equal to. b. Greater than. c. Less than. d. Either greater than or less than. _____5. Accordin ...
... _____4. According to the law of conservation of mass, when sodium, hydrogen, and oxygen react to form a compound, the mass of the compound is _________ the sum of the masses of the individual elements. a. Equal to. b. Greater than. c. Less than. d. Either greater than or less than. _____5. Accordin ...
Chapter 10
... It is correct to say that atoms that make up your body a. were formed in ancient stars. b. were previously a part of your neighbor’s bodies. c. are in motion at all times. d. All of these. ...
... It is correct to say that atoms that make up your body a. were formed in ancient stars. b. were previously a part of your neighbor’s bodies. c. are in motion at all times. d. All of these. ...
Chapter 5 The Structure of the Atom
... • Summarize the essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory. • Describe the particle theory of matter. • Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in an atom • Compare the Bohr atomic model to the electron cloud. ...
... • Summarize the essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory. • Describe the particle theory of matter. • Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in an atom • Compare the Bohr atomic model to the electron cloud. ...
atom
... molecules are close together, a slight attraction can develop between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. Chemists call such intermolecular forces of attraction van der Waals forces, after the scientist who discovered them. ...
... molecules are close together, a slight attraction can develop between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. Chemists call such intermolecular forces of attraction van der Waals forces, after the scientist who discovered them. ...
Chemistry Unit 1 Revision
... Fractional Distillation Separates: multiple liquids from a mixture Physical Property: boiling point How does it work: METHOD 1 • Mixtures is heated to the boiling point of liquid 1 (but not hot enough to boil the second). • The liquid evaporates and enters the condenser. • The condenser cools the g ...
... Fractional Distillation Separates: multiple liquids from a mixture Physical Property: boiling point How does it work: METHOD 1 • Mixtures is heated to the boiling point of liquid 1 (but not hot enough to boil the second). • The liquid evaporates and enters the condenser. • The condenser cools the g ...
Modern Physics - WordPress.com
... bodies Electricity and magnetism we look at interactions between charges Waves and light are about the transfer of energy ...
... bodies Electricity and magnetism we look at interactions between charges Waves and light are about the transfer of energy ...
Atomic Models & Scientists
... 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
... 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
Chapter 2 - Ector County ISD.
... 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
... 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
Atomic_Theory_and_Atomic_Structure__2011.php
... eventually you would end up with a particle that could not be cut. Atom- “not able to be divided” ...
... eventually you would end up with a particle that could not be cut. Atom- “not able to be divided” ...
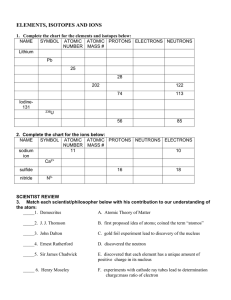
Name Period ______ Unit 4 Study Guide A common isotope of iron
... Which metals have a tendency to gain two electrons in order to be stable? Most non-metals on the periodic table are located on the: The elements that do not naturally form compounds with other atoms belong to the group known as: The element that is the basis of life here on Earth is: What is the lar ...
... Which metals have a tendency to gain two electrons in order to be stable? Most non-metals on the periodic table are located on the: The elements that do not naturally form compounds with other atoms belong to the group known as: The element that is the basis of life here on Earth is: What is the lar ...
ChemicalBondingPowerpoint
... orbital has two electrons. Atoms can be joined by a covalent bond in which each atom’s unpaired electrons are shared by both nuclei to fill their orbitals (Figure 2.7). ...
... orbital has two electrons. Atoms can be joined by a covalent bond in which each atom’s unpaired electrons are shared by both nuclei to fill their orbitals (Figure 2.7). ...
File - Mr. Dang`s Science Classroom Website
... different shapes and sizes. • They are always moving • They form different materials by joining together. ...
... different shapes and sizes. • They are always moving • They form different materials by joining together. ...
Thompson`s “Plum Pudding” Model
... (positively charged) could be deflected backwards was if most of the mass in an atom was concentrated in a nucleus. • He thus developed the “Planetary model” of the atom which put all the protons in the nucleus and the electrons orbited around the nucleus like planets around the sun. ...
... (positively charged) could be deflected backwards was if most of the mass in an atom was concentrated in a nucleus. • He thus developed the “Planetary model” of the atom which put all the protons in the nucleus and the electrons orbited around the nucleus like planets around the sun. ...
hydrogen atom
... matter in a new state...a state in which all matter...is of one and the same kind; this matter being the substance from which all the chemical elements are built up." but... • “What are these particles? Are they atoms, or molecules, or matter in a still finer state of subdivision?” - J. J. Thomson h ...
... matter in a new state...a state in which all matter...is of one and the same kind; this matter being the substance from which all the chemical elements are built up." but... • “What are these particles? Are they atoms, or molecules, or matter in a still finer state of subdivision?” - J. J. Thomson h ...
Atomic Theory Jigsaw
... 1. Summarize the five main points of the Greek atomists. 2. Aristotle did not agree with the ideas concerning atoms that were put forth by Democritus. Describe the differences between Aristotle's and Democritus’ views. 3. Why was the atomic theory discarded until the early 1800's? John Dalton (1766- ...
... 1. Summarize the five main points of the Greek atomists. 2. Aristotle did not agree with the ideas concerning atoms that were put forth by Democritus. Describe the differences between Aristotle's and Democritus’ views. 3. Why was the atomic theory discarded until the early 1800's? John Dalton (1766- ...
Early chemical arts
... ores with charcoal to high temperatures. The use of gold, bronze, tin, iron, and lead would follow in time. ...
... ores with charcoal to high temperatures. The use of gold, bronze, tin, iron, and lead would follow in time. ...
Atomic Structure
... • Electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom • Most stable configuration: electrons occupy lowest-energy orbitals (called the ground state) • An atom in an excited state has absorbed enough energy for one electron to move to a higher-energy orbital • Example: Neo ...
... • Electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom • Most stable configuration: electrons occupy lowest-energy orbitals (called the ground state) • An atom in an excited state has absorbed enough energy for one electron to move to a higher-energy orbital • Example: Neo ...
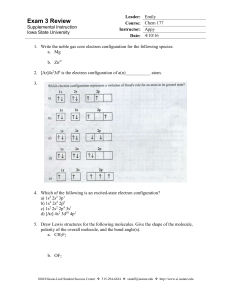
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
Name
... Atoms of different elements can _________________mix together or ___________________ combine. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are__________________, _________________, or _________________________. ...
... Atoms of different elements can _________________mix together or ___________________ combine. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are__________________, _________________, or _________________________. ...
Chapter3 atoms
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.