Chemical reactions unit
... 1. You CANNOT balance an equation by changing the chemical formulas. You must leave the subscripts in the formulas alone!! 2. An equation can be balanced only by: putting numbers, called coefficients, in front of the chemical formulas. The coefficients tell how many molecules of that compound ar ...
... 1. You CANNOT balance an equation by changing the chemical formulas. You must leave the subscripts in the formulas alone!! 2. An equation can be balanced only by: putting numbers, called coefficients, in front of the chemical formulas. The coefficients tell how many molecules of that compound ar ...
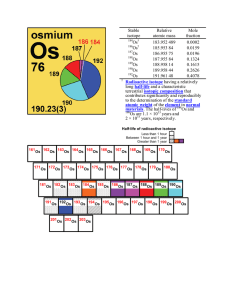
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... positron – the antimatter counterpart of the electron, with a mass identical to that of the electron and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal a ...
... positron – the antimatter counterpart of the electron, with a mass identical to that of the electron and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal a ...
Of Atoms, Molecules & Ions I Sing
... The Atomic Theory of Matter At its lowest level, matter is made up of atoms. The current theory is most directly traceable to John Dalton in the early 1800s. ...
... The Atomic Theory of Matter At its lowest level, matter is made up of atoms. The current theory is most directly traceable to John Dalton in the early 1800s. ...
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Periodic Table (nonmetals combined with nonmetals) or when EN < 1.7. Know that the diatomic elements have single, double, or triple bonds (For example: F2, O2, N2). Describe carbon bonds as either single, double ...
... Periodic Table (nonmetals combined with nonmetals) or when EN < 1.7. Know that the diatomic elements have single, double, or triple bonds (For example: F2, O2, N2). Describe carbon bonds as either single, double ...
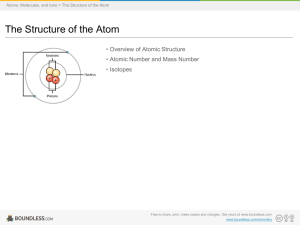
Structure of the Atom
... The name atom comes from the Greek word ἄτομος (atomos, "indivisible") from ἀ- (a-, "not") and τέμνω (temnō, "I cut"), which means indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosop ...
... The name atom comes from the Greek word ἄτομος (atomos, "indivisible") from ἀ- (a-, "not") and τέμνω (temnō, "I cut"), which means indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosop ...
Structure of the Atom: Study Guide
... 2) Atoms are composed of two regions, what are they and what do they contain? 3) What does the Atomic Number tell you about an atom? 4) Which two particles add up to equal the mass number? 5) Solve this equation: ...
... 2) Atoms are composed of two regions, what are they and what do they contain? 3) What does the Atomic Number tell you about an atom? 4) Which two particles add up to equal the mass number? 5) Solve this equation: ...
Phys Sci I, Quiz #3 - Electriciy and Magnetism, Atomic and Nuclear
... 1. Which of the following is not matter? A) Air B) Heat C) Charcoal D) Electrons 2. Which science deals with the composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter? A) Thermodynamics B) Geology C) Physics D) Chemistry 3. If all samples of a material have identical properties and composition ...
... 1. Which of the following is not matter? A) Air B) Heat C) Charcoal D) Electrons 2. Which science deals with the composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter? A) Thermodynamics B) Geology C) Physics D) Chemistry 3. If all samples of a material have identical properties and composition ...
Sec. 10.3 - Midland Park School District
... Relate numbers of particles and volumes by using Avogadro’s principle. Recognize the mole relationships shown by a chemical formula. Determine the number of atoms or ions in a mass of a compound. ...
... Relate numbers of particles and volumes by using Avogadro’s principle. Recognize the mole relationships shown by a chemical formula. Determine the number of atoms or ions in a mass of a compound. ...
Atomic Theory
... • The symbols normally consist of the first letter or first two letters or first letter and next available letter of the element name. ...
... • The symbols normally consist of the first letter or first two letters or first letter and next available letter of the element name. ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... 15. A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid ...
... 15. A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid ...
The Nuclear Model of the Atom
... 27. The particles used in Rutherford’s experiment were about _____ times the size of the hydrogen atom and were ___________ charged. 28. Rutherford’s atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In this model, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are locate ...
... 27. The particles used in Rutherford’s experiment were about _____ times the size of the hydrogen atom and were ___________ charged. 28. Rutherford’s atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In this model, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are locate ...
Counting Atoms
... • Your exam scores would count more heavily toward your final grade. • In this section, you will learn that the atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. ...
... • Your exam scores would count more heavily toward your final grade. • In this section, you will learn that the atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. ...
Chapter 4 ppt.
... i.. Only a certain number of electrons are found in each energy level *electrons cannot be found in-between energy levels ii. Levels Level 1 2 eLevel 2 8 eLevel 3 18 eLevel 4 32 e*back in CPE we followed the 2,8,8,8,8,8 rule, but that’s not really how many electrons each level can hold because each ...
... i.. Only a certain number of electrons are found in each energy level *electrons cannot be found in-between energy levels ii. Levels Level 1 2 eLevel 2 8 eLevel 3 18 eLevel 4 32 e*back in CPE we followed the 2,8,8,8,8,8 rule, but that’s not really how many electrons each level can hold because each ...
File
... 1) Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table 2) Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher 3) Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4) The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5) The positive particle ...
... 1) Represented by a symbol; all are found on the Periodic Table 2) Made a mental model of the atom; Greek philosopher 3) Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons 4) The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5) The positive particle ...
Chemical Reactions
... 26. A solution is prepared by mixing 10.0 grams of benzene (C 6H6) in 150 g of water to create a solution total volume of 102 ml. Calculate the molarity, mass percent, and molality of benzene in the solution. 27. 1 gram of salt (NaCl) is added to 100 mL of water. What are the new freezing and boilin ...
... 26. A solution is prepared by mixing 10.0 grams of benzene (C 6H6) in 150 g of water to create a solution total volume of 102 ml. Calculate the molarity, mass percent, and molality of benzene in the solution. 27. 1 gram of salt (NaCl) is added to 100 mL of water. What are the new freezing and boilin ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10-24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic mass unit (amu) or one Dalton. • Each electron has a negative charge equal to the positive charge of a proton. • Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10-24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic mass unit (amu) or one Dalton. • Each electron has a negative charge equal to the positive charge of a proton. • Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus. ...
Part 3 Answers Only for Questions, Exercises, and Problems in The
... 26. Yes, the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous refer to the macroscopic appearance of a sample. A container filled with ice and liquid water is heterogeneous in appearance but is also pure, as long as in both phases the water is pure. 28. Homogeneous: a, c. Heterogeneous: b. 30. The cylinder app ...
... 26. Yes, the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous refer to the macroscopic appearance of a sample. A container filled with ice and liquid water is heterogeneous in appearance but is also pure, as long as in both phases the water is pure. 28. Homogeneous: a, c. Heterogeneous: b. 30. The cylinder app ...
solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute
... _Electrostatic attraction*_ is an attraction or repulsion between charged species. ...
... _Electrostatic attraction*_ is an attraction or repulsion between charged species. ...
Ionic Bonding - KMChemistryMatters
... • Lattice energies compensate for the loss of up to three electrons. • In general, electrons are removed from orbitals in order of decreasing n (i.e. electrons are removed from 4s before the 3d). Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are formed when there is an overall charge on a compound containing co ...
... • Lattice energies compensate for the loss of up to three electrons. • In general, electrons are removed from orbitals in order of decreasing n (i.e. electrons are removed from 4s before the 3d). Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are formed when there is an overall charge on a compound containing co ...
CHEMISTRY REVIEW - Haystack Observatory
... 2,400 years ago, Democritus proposed That the world is made of atoms. The word atom is Greek for “not breakable.” (learn more) In the early 1800’s John Dalton revived atomic theory. He argued that chemical reactions were the rearrangement of atoms. ...
... 2,400 years ago, Democritus proposed That the world is made of atoms. The word atom is Greek for “not breakable.” (learn more) In the early 1800’s John Dalton revived atomic theory. He argued that chemical reactions were the rearrangement of atoms. ...
Atomic orbital
... Thomson found that a cathode ray is deflected by electrically charged metal plates. Thompson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel, so he hypothesized that a cathode ray is a stream of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed; now called electrons. To test his hypo ...
... Thomson found that a cathode ray is deflected by electrically charged metal plates. Thompson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel, so he hypothesized that a cathode ray is a stream of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed; now called electrons. To test his hypo ...
Adv review key
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
Atomic Structure and Elements
... – Electrons – (e-) – negative charge - In a neutral atom: Number of protons (+)= Number of electrons (-) ...
... – Electrons – (e-) – negative charge - In a neutral atom: Number of protons (+)= Number of electrons (-) ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
... B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more electrons than protons) E) Metals lend and n ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.