111 Exam II Outline
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
Slide 1
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory According to Dalton, elements are composed of only one kind of atom and compounds are made from two or more kinds of atoms. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory According to Dalton, elements are composed of only one kind of atom and compounds are made from two or more kinds of atoms. ...
Carbon Chemistry - North Allegheny School District
... compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms is called a hydrocarbon. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, the primary component of natural gas. If you have a gas stove or gas furnace in your home, methane usually is the fuel that is burned in these appliances. Methane consists of a single ...
... compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms is called a hydrocarbon. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, the primary component of natural gas. If you have a gas stove or gas furnace in your home, methane usually is the fuel that is burned in these appliances. Methane consists of a single ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... many of their observations. However, as new information was discovered that could not be explained by Dalton's ideas, the atomic theory was revised to more correctly describe the atom. As you read on, you will learn how Dalton's theory has changed, step by step, into the current atomic theory. ...
... many of their observations. However, as new information was discovered that could not be explained by Dalton's ideas, the atomic theory was revised to more correctly describe the atom. As you read on, you will learn how Dalton's theory has changed, step by step, into the current atomic theory. ...
The Masses of Atoms
... This book started out as a short chemistry book intended for amateur mineralogists. However, I became fond of the characters in the World of Atoms, and expanded on their anatomy and genetic illnesses. This allows the reader to tackle as area of physics that is often talked about but poorly understoo ...
... This book started out as a short chemistry book intended for amateur mineralogists. However, I became fond of the characters in the World of Atoms, and expanded on their anatomy and genetic illnesses. This allows the reader to tackle as area of physics that is often talked about but poorly understoo ...
Chemistry Basics Review
... Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons Formed the atomic theory model of th ...
... Used by Rutherford in his experiment; made of two protons and two neutrons The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons Formed the atomic theory model of th ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. The following properties are observed for an unknown element, Z: at room temperature, it is gray, lustrous solid. The compound ZCl2 dissolves in wat ...
... D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. The following properties are observed for an unknown element, Z: at room temperature, it is gray, lustrous solid. The compound ZCl2 dissolves in wat ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. b. Students know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2 and many large biological molecules are covalent. ...
... a. Students know atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. b. Students know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2 and many large biological molecules are covalent. ...
The Atom -From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory Introduction
... The Atom -From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory Introduction: If you were asked to draw the structure of an atom, what would you draw? Throughout history scientists have accepted five atomic models. Our perception of the atom has changed from the early Greek model because of clues or evidence ...
... The Atom -From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory Introduction: If you were asked to draw the structure of an atom, what would you draw? Throughout history scientists have accepted five atomic models. Our perception of the atom has changed from the early Greek model because of clues or evidence ...
Atoms contain 3 particles
... We can “see” them with special microscope called a scanning tunneling electron microscope. ...
... We can “see” them with special microscope called a scanning tunneling electron microscope. ...
CH 5 Periodic Law
... - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
... - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
Elemental Symbol - Calculating Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
... Note that once you have the atomic number you know the number of electrons which is also equal to the number of protons. In order to find the number of neutrons, you subtract the atomic number from the mass number. ...
... Note that once you have the atomic number you know the number of electrons which is also equal to the number of protons. In order to find the number of neutrons, you subtract the atomic number from the mass number. ...
Chapter 3
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ▶Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ▶The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ▶Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ▶The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
Atom Internet Scavenger Hunt
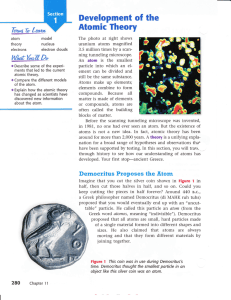
... In the 5th century B.C., a Greek philosopher named Democritus proposed that matter was made up of smaller particles and was the first person to write it down. But he had no experimental proof. A number of scientists after this attempted to prove Democritus’ theory. It wasn’t until the late 1700’s/ e ...
... In the 5th century B.C., a Greek philosopher named Democritus proposed that matter was made up of smaller particles and was the first person to write it down. But he had no experimental proof. A number of scientists after this attempted to prove Democritus’ theory. It wasn’t until the late 1700’s/ e ...
AtomMoleculeNaming_G1
... differences in particle size. Filtration usually involves separating a precipitate from solution. Crystallization: Separation is based upon differences in solubility of the components in a mixture. Distillation: Separation is based upon differences in volatility. Extraction: Separation is based upon ...
... differences in particle size. Filtration usually involves separating a precipitate from solution. Crystallization: Separation is based upon differences in solubility of the components in a mixture. Distillation: Separation is based upon differences in volatility. Extraction: Separation is based upon ...
Academic Chemistry Final Exam Review
... a. EXAMPLE: The unit abbreviation “m” stands for ____meter___ and is a unit of ___length___. b. The unit abbreviation “g” stands for ________________ and is a unit of _______________. c. The unit abbreviation “mL” stands for _____________________ and is a unit of ________________. d. The unit abbrev ...
... a. EXAMPLE: The unit abbreviation “m” stands for ____meter___ and is a unit of ___length___. b. The unit abbreviation “g” stands for ________________ and is a unit of _______________. c. The unit abbreviation “mL” stands for _____________________ and is a unit of ________________. d. The unit abbrev ...
How many protons, electrons and neutrons are in an atom of krypton
... charged electrons. Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. Electrons are arranged around atoms in a special way. If you need to know how the electrons are arranged around an atom, take a look ...
... charged electrons. Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. Electrons are arranged around atoms in a special way. If you need to know how the electrons are arranged around an atom, take a look ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... Laws/ Dalton’s Atomic Theory John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary c ...
... Laws/ Dalton’s Atomic Theory John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary c ...
Station 1 - The Periodic Table, Molecules and Molecular
... 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals react with nonmetals, an ionic compound gene ...
... 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals react with nonmetals, an ionic compound gene ...
Chapter 7
... • These are negatively charged ions resulting from a gain of electrons. • Nonmetals tend to add or share electrons into their highest occupied energy levels to become anions. This allows them to achieve an octet in their highest occupied energy level. • The charge for an anion is written with a numb ...
... • These are negatively charged ions resulting from a gain of electrons. • Nonmetals tend to add or share electrons into their highest occupied energy levels to become anions. This allows them to achieve an octet in their highest occupied energy level. • The charge for an anion is written with a numb ...
February Homework Packet
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
IGCSE Revision document
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.