Covalent Bonding - whitburnscience
... electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesium, which looses two electrons when it forms ions, can be written as Mg2+. The ...
... electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesium, which looses two electrons when it forms ions, can be written as Mg2+. The ...
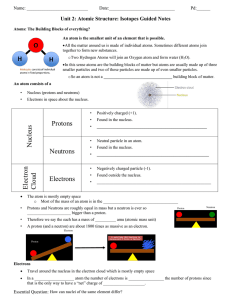
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
110 EXAM Review MATERIALTro
... b. If the number does not have a decimal point, the zeros may/may not be significant it is ...
... b. If the number does not have a decimal point, the zeros may/may not be significant it is ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? [1] 52 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles, why the radius of a chloride ion is larg ...
... may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 What is the total number of electron pairs shared between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule? [1] 52 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles, why the radius of a chloride ion is larg ...
Doug Berman - Scarsdale Schools
... Orbital- Location and movement of electrons The probability of finding an electron decreases as you get further away from the nucleus. Electrons have separate energy levels called principal energy levels. These are divided into sublevels. The number of sublevels increases as the principal energy lev ...
... Orbital- Location and movement of electrons The probability of finding an electron decreases as you get further away from the nucleus. Electrons have separate energy levels called principal energy levels. These are divided into sublevels. The number of sublevels increases as the principal energy lev ...
1 mole = 6.02 X 10 23 Particles
... D. What is the mass of 1 mole of a cmpd? 1) Formula of a cmpd tells us the # of atoms of each element in a rep. particle of that cmpd. 2) Calculate the gram molecular mass (gmm) or gram formula mass (gfm) by adding together the atomic masses of the atoms making up a molecule or F.U. ...
... D. What is the mass of 1 mole of a cmpd? 1) Formula of a cmpd tells us the # of atoms of each element in a rep. particle of that cmpd. 2) Calculate the gram molecular mass (gmm) or gram formula mass (gfm) by adding together the atomic masses of the atoms making up a molecule or F.U. ...
9791/02 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... A 5.00 g sample of dolomite is dissolved in 30.0 cm3 of 5.00 mol dm−3 hydrochloric acid, an excess. The resulting solution is made up to 100 cm3 in a volumetric flask, using distilled water. 10.0 cm3 of this solution is titrated against a 0.100 mol dm−3 solution of sodium hydroxide. An average titre ...
... A 5.00 g sample of dolomite is dissolved in 30.0 cm3 of 5.00 mol dm−3 hydrochloric acid, an excess. The resulting solution is made up to 100 cm3 in a volumetric flask, using distilled water. 10.0 cm3 of this solution is titrated against a 0.100 mol dm−3 solution of sodium hydroxide. An average titre ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • Scientists have succeeded in making about 20 synthetic elements (not found in nature). • The exact number of naturally occurring elements is controversial because some elements previously considered only synthetic may actually occur in nature in very small quantities. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc ...
... • Scientists have succeeded in making about 20 synthetic elements (not found in nature). • The exact number of naturally occurring elements is controversial because some elements previously considered only synthetic may actually occur in nature in very small quantities. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc ...
The Structure of the Atom- Chapter 4, 3
... **The ______________ is defined as the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element.** History 400 BC Democritus, a Greek philosopher expressed his idea that matter was made of very small, indivisible particles that he named “ATOMOS” 1803 John Dalton Assumptions of the ...
... **The ______________ is defined as the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element.** History 400 BC Democritus, a Greek philosopher expressed his idea that matter was made of very small, indivisible particles that he named “ATOMOS” 1803 John Dalton Assumptions of the ...
Chemistry –Worksheet: Atomic structure
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
... 21. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom of tungsten-184 which has an atomic number of 74? # of neutrons:_________________ 22. Which of the following combinations of particles represents an ion of net charge -1 and of mass number 82? (A) 46 neutrons, 35 protons, 36 electrons (C) 46 neutro ...
Chemical Reaction
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
PS 2.2 - S2TEM Centers SC
... Introduction to the lesson: Isotopes have the same atomic number and hence nearly identical chemical behavior but different atomic masses. Most elements found in nature are mixtures of several isotopes; tin, for example, has 10 isotopes. In most cases, only stable isotopes of elements are found in n ...
... Introduction to the lesson: Isotopes have the same atomic number and hence nearly identical chemical behavior but different atomic masses. Most elements found in nature are mixtures of several isotopes; tin, for example, has 10 isotopes. In most cases, only stable isotopes of elements are found in n ...
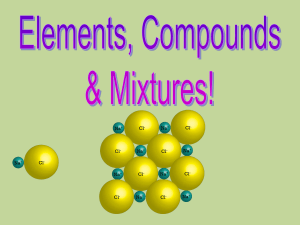
What is a mixture?
... Identifying Elements • Elements are categorized by unique properties on the Periodic Table. • They are arranged in order by their number of protons. (More on this later!) • Each element has unique properties like melting point, boiling point, and whether it is metal, nonmetal or metalloid. ...
... Identifying Elements • Elements are categorized by unique properties on the Periodic Table. • They are arranged in order by their number of protons. (More on this later!) • Each element has unique properties like melting point, boiling point, and whether it is metal, nonmetal or metalloid. ...
Chemistry I Syllabus 2011-2012
... inorganic, kinetic energy, law of conservation of mass, light energy, luster, malleability, melting point, metal, metalloid, molecule, nonmetal, organic, phase change, physical properties, potential energy, pure substance, reactivity with air (oxidation), solute, solution, solvent, strength, sub-let ...
... inorganic, kinetic energy, law of conservation of mass, light energy, luster, malleability, melting point, metal, metalloid, molecule, nonmetal, organic, phase change, physical properties, potential energy, pure substance, reactivity with air (oxidation), solute, solution, solvent, strength, sub-let ...
Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure
... In the operation of a nuclear power station you will deal with "atomic radiation" every day. To understand what radiation is, you must first learn a bit about the atom. Why does each substance possess its own characteristic properties? Why are salt and iron solids under ordinary conditions? Why are ...
... In the operation of a nuclear power station you will deal with "atomic radiation" every day. To understand what radiation is, you must first learn a bit about the atom. Why does each substance possess its own characteristic properties? Why are salt and iron solids under ordinary conditions? Why are ...
practice exercise - Needham.K12.ma.us
... (b) By referring to a periodic table or a table of elements, we see that sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16. Thus, each atom or ion of sulfur must contain 16 protons. We are told that the ion also has 16 neutrons, meaning the mass number of the ion is 16 + 16 = 32. Because the ion has 16 protons ...
... (b) By referring to a periodic table or a table of elements, we see that sulfur (S) has an atomic number of 16. Thus, each atom or ion of sulfur must contain 16 protons. We are told that the ion also has 16 neutrons, meaning the mass number of the ion is 16 + 16 = 32. Because the ion has 16 protons ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... 23. Are the following properties characteristics of ionic, covalent, or metallic bonding? a. These bonds are formed by delocalized electrons in an “electron sea.” b. These bonds involve a transfer of electrons. c. Substances containing these bonds are malleable and have very high melting points. d. ...
... 23. Are the following properties characteristics of ionic, covalent, or metallic bonding? a. These bonds are formed by delocalized electrons in an “electron sea.” b. These bonds involve a transfer of electrons. c. Substances containing these bonds are malleable and have very high melting points. d. ...
avogadro exam 2012 - University of Waterloo
... Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the sheet white again. ...
... Be careful that any erasures are complete—make the sheet white again. ...
honors chem 6 day review packet
... Oxidation = _______ of electrons Reduction = _______ of electrons The oxidizing agent caused the oxidation. (It was reduced) The reducing agent caused the reduction. (It was oxidized) ...
... Oxidation = _______ of electrons Reduction = _______ of electrons The oxidizing agent caused the oxidation. (It was reduced) The reducing agent caused the reduction. (It was oxidized) ...
The discovery of the electron
... 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty throughout which tiny ...
... 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty throughout which tiny ...
Intro to the Periodic Table
... 2. Key Point #2: What shows all of the different types of atoms? 3. Key Point #3: What is term for a substance made up of only one type of atom? 4. How many different types of atoms exist? 5. How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom? Use your periodic table to answer the following ques ...
... 2. Key Point #2: What shows all of the different types of atoms? 3. Key Point #3: What is term for a substance made up of only one type of atom? 4. How many different types of atoms exist? 5. How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom? Use your periodic table to answer the following ques ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... the subsequent balancing operation. *Note: The seven diatomic elements, when uncombined, are written with subscripts of 2 (H2; O2; etc.) 3) Determine the products and write the correct formula for each product. Once the correct formula is written it must not be changed during the subsequent balancin ...
... the subsequent balancing operation. *Note: The seven diatomic elements, when uncombined, are written with subscripts of 2 (H2; O2; etc.) 3) Determine the products and write the correct formula for each product. Once the correct formula is written it must not be changed during the subsequent balancin ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. ...
... The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. ...
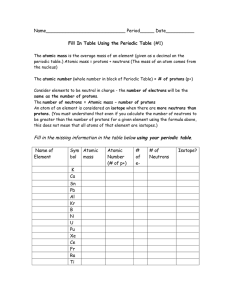
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
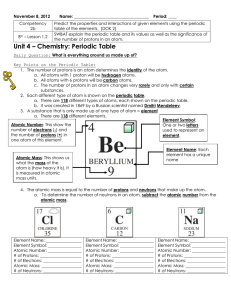
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
Study Guide
... electrons were smaller than atoms? •He used a cathode ray tube •Shot a beam of electrons •Deflected the beam with a magnet •Knew how hard the magnet pulled •Saw how far beam was defected •Calculated mass from those numbers ...
... electrons were smaller than atoms? •He used a cathode ray tube •Shot a beam of electrons •Deflected the beam with a magnet •Knew how hard the magnet pulled •Saw how far beam was defected •Calculated mass from those numbers ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.