Pharynx Larynx - Dr. Gudas
... the pterygomandibular raphe, which extends between these bony structures. Recall that the buccinator attaches to the anterior aspect of this raphe. Also note that this raphe is one of the few in the body that does not lie in the midline and is therefore paired. The middle pharyngeal constricto ...
... the pterygomandibular raphe, which extends between these bony structures. Recall that the buccinator attaches to the anterior aspect of this raphe. Also note that this raphe is one of the few in the body that does not lie in the midline and is therefore paired. The middle pharyngeal constricto ...
Radiology Packet 1
... centrally in the laterally view. Cortical destruction is visible on the lateral and cranial margin of the bone. A fluffy periosteal response is seen circumferentially at the level of the lytic lesion. Superimposition of this periosteal response with the humerus creates the patchy pattern that is vis ...
... centrally in the laterally view. Cortical destruction is visible on the lateral and cranial margin of the bone. A fluffy periosteal response is seen circumferentially at the level of the lytic lesion. Superimposition of this periosteal response with the humerus creates the patchy pattern that is vis ...
Skull
... (b). Lesser palatine foramen: transmits lesser palatine nerve and vessels d. Choana (= posterior nasal aperture) (1). Bounded by palatine, vomer, & sphenoid (2). Opening from nasal cavity into nasopharynx 2. Cheekbone: zygomatic arch, formed by zygomatic bone & zygomatic part of temporal bone 3. Jaw ...
... (b). Lesser palatine foramen: transmits lesser palatine nerve and vessels d. Choana (= posterior nasal aperture) (1). Bounded by palatine, vomer, & sphenoid (2). Opening from nasal cavity into nasopharynx 2. Cheekbone: zygomatic arch, formed by zygomatic bone & zygomatic part of temporal bone 3. Jaw ...
Thorax-intercostal spaces Anshu
... Present in middle two fourths of the lower intercostal spaces. Poorly developed or even absent in the upper spaces. Direction of fibres: Same as internal intercostal (at right angle to the direction of external ...
... Present in middle two fourths of the lower intercostal spaces. Poorly developed or even absent in the upper spaces. Direction of fibres: Same as internal intercostal (at right angle to the direction of external ...
Anatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus
... GALT – Gut associated Lymphoid Tissue i.e. an unencapsulated lymphoid tissue in the lamina propria of upper aero digestive tract The nasopharyngeal, tubal, palatine and lingual tonsils form a ring of GALT at the level of the oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal isthmus, known as Waldeyer's ring. THE PAL ...
... GALT – Gut associated Lymphoid Tissue i.e. an unencapsulated lymphoid tissue in the lamina propria of upper aero digestive tract The nasopharyngeal, tubal, palatine and lingual tonsils form a ring of GALT at the level of the oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal isthmus, known as Waldeyer's ring. THE PAL ...
o The primary function of the lower limb is to support the weight of
... are known as retincula,they carry blood vessels toward the head ...
... are known as retincula,they carry blood vessels toward the head ...
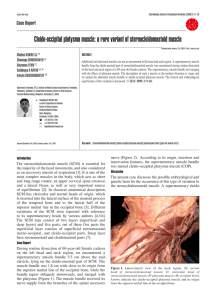
Cleido-occipital platysma muscle: a rare variant of
... as an accessory muscle of respiration [1]. It is one of the most complex muscles in the body, which acts as short and long range rotator, an upper cervical spine extensor, and a lateral flexor, as well as very important source of equilibrium [2]. In classical anatomical description, SCM has clavicul ...
... as an accessory muscle of respiration [1]. It is one of the most complex muscles in the body, which acts as short and long range rotator, an upper cervical spine extensor, and a lateral flexor, as well as very important source of equilibrium [2]. In classical anatomical description, SCM has clavicul ...
Ankle Joint Type
... Lateral ligament: Composed of three separate ligaments. Anterior talofibular: from anterior margin of lateral malleolus to adjacent lateral aspect of body and neck of talus. Posterior talofibular: horizontally, backwards and medially from lateral margin to posterior process of talus. Calcaneofibula ...
... Lateral ligament: Composed of three separate ligaments. Anterior talofibular: from anterior margin of lateral malleolus to adjacent lateral aspect of body and neck of talus. Posterior talofibular: horizontally, backwards and medially from lateral margin to posterior process of talus. Calcaneofibula ...
notes#10 - DENTISTRY 2012
... - it will pass “medial” to zygomatic arch to be inserted into coronoid process - then extend to anterior border of the ramus until it reaches the lower third molar - action : - biscuits elvation - retract protruded mandible by lateral pterygoid ...
... - it will pass “medial” to zygomatic arch to be inserted into coronoid process - then extend to anterior border of the ramus until it reaches the lower third molar - action : - biscuits elvation - retract protruded mandible by lateral pterygoid ...
Nerves - Drhannah.org
... sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis and divides into several branches Enters gluteal regions through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis; descends posterior to (outer side of) sacrospinous ...
... sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis and divides into several branches Enters gluteal regions through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis; descends posterior to (outer side of) sacrospinous ...
TransCom Page 1 of 6 extends from the skull to the top of the coccyx
... laminae and the pedicles (paired) **Spinous and transverse processes serve as levers and receive attachments of muscles and ligaments c. Articular processes (4)-vertically arranged - consists of 2 superior and 2 inferior processes - arise from the junction of laminae and pedicles - covered with hyal ...
... laminae and the pedicles (paired) **Spinous and transverse processes serve as levers and receive attachments of muscles and ligaments c. Articular processes (4)-vertically arranged - consists of 2 superior and 2 inferior processes - arise from the junction of laminae and pedicles - covered with hyal ...
UPPER EXTREMITY BLOCKS
... and asked to elevate the head, bringing the sternocleidomastoid muscle into prominence. The index and middle fingers are places behind the clavicular head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the patient is asked to relax and turn the head and onto the opposite side with the chin in the midclavicul ...
... and asked to elevate the head, bringing the sternocleidomastoid muscle into prominence. The index and middle fingers are places behind the clavicular head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the patient is asked to relax and turn the head and onto the opposite side with the chin in the midclavicul ...
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
... THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STERNUM → breastbone → a flat, narrow bone located in the center of the anterior thoracic wall that measures about 15cm (6 in) in length → 3 parts: o Manubrium o Body o Xiphoid process ...
... THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STERNUM → breastbone → a flat, narrow bone located in the center of the anterior thoracic wall that measures about 15cm (6 in) in length → 3 parts: o Manubrium o Body o Xiphoid process ...
Kramer DL, Booth RE, Albert TJ, Balderston RA. Posterior Lumbar
... ventral surface of the spine from the skull to the sacrum. This broad anterior ligament is intimately related to the periosteum of the anterior vertebral bodies and loosely adherent to the intervening intervertebral disks. In contrast to this, the posterior longitudinal ligament is a thick but narro ...
... ventral surface of the spine from the skull to the sacrum. This broad anterior ligament is intimately related to the periosteum of the anterior vertebral bodies and loosely adherent to the intervening intervertebral disks. In contrast to this, the posterior longitudinal ligament is a thick but narro ...
BRACHIUM & CUBITAL FOSSA
... Medial continuation of dorsal venous arch. Ascends in superficial fascia along lateral aspect of forearm and arm to middle of arm. Pierces deep fascia and ascends in upper aspect of arm in deep fascia. Joins venae comitantes to form axillary ...
... Medial continuation of dorsal venous arch. Ascends in superficial fascia along lateral aspect of forearm and arm to middle of arm. Pierces deep fascia and ascends in upper aspect of arm in deep fascia. Joins venae comitantes to form axillary ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 7. The maxillary sinuses extend from the floor of the orbits to the roots of the upper teeth. 8. During development, portions of the maxillary bones called palatine processes grow together and form the anterior section of the hard palate. 9. The alveolar arch is a horseshoe shaped collection of alv ...
... 7. The maxillary sinuses extend from the floor of the orbits to the roots of the upper teeth. 8. During development, portions of the maxillary bones called palatine processes grow together and form the anterior section of the hard palate. 9. The alveolar arch is a horseshoe shaped collection of alv ...
Systemic Exam III Review (From Class)
... c. Aka semilunar notch Trapezius m insert directly sup to what muscle? a. Inserts directly above deltoid muscle origin b. Lateral clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Axons carry info away from soma. Dendrites carry info twd soma. What info to bipolar neurons carry? a. Special b. E.g. sight, sound, ...
... c. Aka semilunar notch Trapezius m insert directly sup to what muscle? a. Inserts directly above deltoid muscle origin b. Lateral clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Axons carry info away from soma. Dendrites carry info twd soma. What info to bipolar neurons carry? a. Special b. E.g. sight, sound, ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSRJDMS)
... Abstract: An unusual origin of sub scapulo suprascapular arterial trunk was observed in one of the nearly old male embalmed cadaver during routine dissection classes for MBBS students. The sub scapulo supra scapular arterial trunk was seen to emerge from the 1st part of axillary artery on the right ...
... Abstract: An unusual origin of sub scapulo suprascapular arterial trunk was observed in one of the nearly old male embalmed cadaver during routine dissection classes for MBBS students. The sub scapulo supra scapular arterial trunk was seen to emerge from the 1st part of axillary artery on the right ...
a student`s guide to anatomy of the camel
... It may be divided into cranial, orbital and pre-orbital regions. The cranial region presents the teIllPoral fossa, the zygomatic arch and the outer part of the petrous temporal bone. The temporal fossa is bounded medially by the parietal and frontal crests, behind by the nuchal crest, and laterally ...
... It may be divided into cranial, orbital and pre-orbital regions. The cranial region presents the teIllPoral fossa, the zygomatic arch and the outer part of the petrous temporal bone. The temporal fossa is bounded medially by the parietal and frontal crests, behind by the nuchal crest, and laterally ...
Knee Anatomy PowerPoint
... Largest sesmoid bone in the body Embedded in the patellar tendon Gives Quadriceps a mechanical advantage by providing a fulcrum ...
... Largest sesmoid bone in the body Embedded in the patellar tendon Gives Quadriceps a mechanical advantage by providing a fulcrum ...
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
... 3. Eventually the cartilage decomposes. 4. As the cartilage decomposes, a periosteum forms from connective tissue that encircles the developing structure. 5. Blood vessels and undifferentiated connective tissue cells invade the disintegrating tissue. 6. Some of the cells differentiate into osteobla ...
... 3. Eventually the cartilage decomposes. 4. As the cartilage decomposes, a periosteum forms from connective tissue that encircles the developing structure. 5. Blood vessels and undifferentiated connective tissue cells invade the disintegrating tissue. 6. Some of the cells differentiate into osteobla ...
a variation in the origin and course of the posterior circumflex
... branch of the brachial artery at the distal border of the subscapularis muscle. It runs through the quadrangular space which is bounded by subscapularis muscle, the capsule of the shoulder joint and teres minor muscle above, teres major muscle below, the long head of triceps brachii muscle medially ...
... branch of the brachial artery at the distal border of the subscapularis muscle. It runs through the quadrangular space which is bounded by subscapularis muscle, the capsule of the shoulder joint and teres minor muscle above, teres major muscle below, the long head of triceps brachii muscle medially ...
Female pelvis and fetal skull
... iliopubic eminence and form about 1/5 of the acetabulum. Major markings include superior and inferior rami, the pubic crest, pubic tubercle, pubic arch, pubic symphysis, and obturator foramen (along with ilium and ischium) Sacrum: Compose of 5 fused vertebrae. It is triangular in shape with anterior ...
... iliopubic eminence and form about 1/5 of the acetabulum. Major markings include superior and inferior rami, the pubic crest, pubic tubercle, pubic arch, pubic symphysis, and obturator foramen (along with ilium and ischium) Sacrum: Compose of 5 fused vertebrae. It is triangular in shape with anterior ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.