The axilla
... and is formed by the floor of the intertubercular groove of the humerus to which is attached the tendon of latissimus dorsi and in which runs the tendon of the long head of biceps ...
... and is formed by the floor of the intertubercular groove of the humerus to which is attached the tendon of latissimus dorsi and in which runs the tendon of the long head of biceps ...
Effectiveness of a Shoulder Strengthening
... the glenohumeral joint must be intact. Any pathology to the glenoid labrum, the ligaments or the joint capsule, or the rotator cuff muscles will affect the joint kinematics and the stability of the glenohumeral joint. The soft tissue structures surrounding the glenohumeral joint provide static and d ...
... the glenohumeral joint must be intact. Any pathology to the glenoid labrum, the ligaments or the joint capsule, or the rotator cuff muscles will affect the joint kinematics and the stability of the glenohumeral joint. The soft tissue structures surrounding the glenohumeral joint provide static and d ...
Report No. 5, Institute for Historical Biology, 12 May 2011
... clavicles, scapulae, humeri, ulnae, and radii, exhibit hypertrophic attachment points for their muscles and ligaments. In addition, the costal tuberosity of the right clavicle, exhibited a lesion associated with costoclavicular syndesmosis, which is a condition involving stress of the pectoral girdl ...
... clavicles, scapulae, humeri, ulnae, and radii, exhibit hypertrophic attachment points for their muscles and ligaments. In addition, the costal tuberosity of the right clavicle, exhibited a lesion associated with costoclavicular syndesmosis, which is a condition involving stress of the pectoral girdl ...
Nerve Injury
... - common sites of injury: 1- supratrochlear above the trochlea of humerus (which means in the elbow). 2- in front of the rest joint. - Muscles supplied and its function: Injury in median nerve causes the ape hand. Ape hand means: thumb adducted, extension at rest joint and ulnar deviation. The muscl ...
... - common sites of injury: 1- supratrochlear above the trochlea of humerus (which means in the elbow). 2- in front of the rest joint. - Muscles supplied and its function: Injury in median nerve causes the ape hand. Ape hand means: thumb adducted, extension at rest joint and ulnar deviation. The muscl ...
Chapter 10
... • The thoracic vertebrae, their corresponding ribs, and the sternum form a strong thoracic cage which helps to protect internal organs such as the * • Because of the union with the ribs and costal cartilage, the thoracic spine is much less mobile than the cervical or lumbar regions • The limited mov ...
... • The thoracic vertebrae, their corresponding ribs, and the sternum form a strong thoracic cage which helps to protect internal organs such as the * • Because of the union with the ribs and costal cartilage, the thoracic spine is much less mobile than the cervical or lumbar regions • The limited mov ...
Transcripts/2_26 8
... i. Red represents fibers of the pharyngeal branch of V2 that innervates this area of the pharynx just superior to the Eustachian tube orifice ii. Blue represents the pharyngeal branches of the IX n. which supplies sensory fibers to most of the pharynx iii. Auburn represents the innervation overlap b ...
... i. Red represents fibers of the pharyngeal branch of V2 that innervates this area of the pharynx just superior to the Eustachian tube orifice ii. Blue represents the pharyngeal branches of the IX n. which supplies sensory fibers to most of the pharynx iii. Auburn represents the innervation overlap b ...
Multiple accessory structures in the upper limb of
... The classical description of attachments of the biceps brachii muscle include: the short head arising from the tip of the coracoid process of the scapula and the long head arising from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula and from the glenoidal labrum. Distally, the two bellies unite to form a c ...
... The classical description of attachments of the biceps brachii muscle include: the short head arising from the tip of the coracoid process of the scapula and the long head arising from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula and from the glenoidal labrum. Distally, the two bellies unite to form a c ...
cubital fossa
... BOUNDARIES OF CUBITAL FOSSA: It is bounded: Superiorly by an imaginary line connecting the medial and ...
... BOUNDARIES OF CUBITAL FOSSA: It is bounded: Superiorly by an imaginary line connecting the medial and ...
posterior compartment of the forearm
... division ( superficial & deep only) , but Snell (the required book ) divide it into 3 groups as we mentioned . Some of posterior muscles shared the ( Origin …NS…Action ) CEO Radial.N Extention *see figure 4 * ...
... division ( superficial & deep only) , but Snell (the required book ) divide it into 3 groups as we mentioned . Some of posterior muscles shared the ( Origin …NS…Action ) CEO Radial.N Extention *see figure 4 * ...
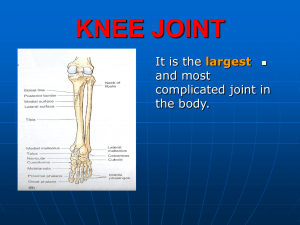
21-KNEE JOINT
... 1. Deepen the tibial articular surfaces. 2. Act as cushions between the two bones. ...
... 1. Deepen the tibial articular surfaces. 2. Act as cushions between the two bones. ...
Membranes of the Larynx: Extrinsic membranes connect the
... movement at the joint is described as a rocking-gliding motion. The net result of the complex movement is that the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages swing downward and inward, or upward and outward. A thickening in the posterior joint capsule, the posterior cricoarytenoid ligament limits t ...
... movement at the joint is described as a rocking-gliding motion. The net result of the complex movement is that the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages swing downward and inward, or upward and outward. A thickening in the posterior joint capsule, the posterior cricoarytenoid ligament limits t ...
Elbow Trauma
... occult supracondylar fracture or radial head/neck fracture in children. Fat pad sign is valid only in a true lateral view with elbow in 90 degree flexion. *Raised fat pads usually indicate radial head fracture in an adult or supracondylar fracture in a child ...
... occult supracondylar fracture or radial head/neck fracture in children. Fat pad sign is valid only in a true lateral view with elbow in 90 degree flexion. *Raised fat pads usually indicate radial head fracture in an adult or supracondylar fracture in a child ...
Pharynx
... Naso- pharyngeal tonsil • Aggregation of lymphoid tissue below mucous membrane • Projects down & forward as conical mass • Usually more prominent in children • Called Adenoids when enlarged in infection • Obstruct nasal respiration (Mouth breathing) ...
... Naso- pharyngeal tonsil • Aggregation of lymphoid tissue below mucous membrane • Projects down & forward as conical mass • Usually more prominent in children • Called Adenoids when enlarged in infection • Obstruct nasal respiration (Mouth breathing) ...
Head and Neck ROM Assessments
... the head and neck. They are likely to limit flexion by invoking their referral to the back of the head and neck along with a band of pain around the head. A pull may be felt into the upper back. Suboccipitals are likely to limit flexion of the head at the neck. Their pain tends to spread laterally a ...
... the head and neck. They are likely to limit flexion by invoking their referral to the back of the head and neck along with a band of pain around the head. A pull may be felt into the upper back. Suboccipitals are likely to limit flexion of the head at the neck. Their pain tends to spread laterally a ...
TSM97 - The Knee Joint
... Arise from the tibia (area of origin determines name) and cross over Insert onto the lateral and medial femoral condyles respectively Anterior ligament is tensed in extension; posterior is tensed in flexion Posterior ligament is much thicker and stronger The femoral condyles are rounded wher ...
... Arise from the tibia (area of origin determines name) and cross over Insert onto the lateral and medial femoral condyles respectively Anterior ligament is tensed in extension; posterior is tensed in flexion Posterior ligament is much thicker and stronger The femoral condyles are rounded wher ...
neck topography_engl.2011
... - a. suprascapularis - a. cervicalis superficialis - n. phrenicus (C3-5) - ndd. lymphaticae, around - v. jugularis interna - a. transversa cervicis ...
... - a. suprascapularis - a. cervicalis superficialis - n. phrenicus (C3-5) - ndd. lymphaticae, around - v. jugularis interna - a. transversa cervicis ...
Chapter 11
... SPINAE GROUP – LATERAL COLUMN Iliocostalis Lumborum Origin – Anterior surface of a broad and thick tendon which originates from the sacrum, spinous processes of the lumbar and 11 th and 12 th thoracic vertebrae, and from the medial lip of the iliac crest. Insertion – Inferior borders of the an ...
... SPINAE GROUP – LATERAL COLUMN Iliocostalis Lumborum Origin – Anterior surface of a broad and thick tendon which originates from the sacrum, spinous processes of the lumbar and 11 th and 12 th thoracic vertebrae, and from the medial lip of the iliac crest. Insertion – Inferior borders of the an ...
nerves of upper limb and their injuries
... Winging of scapula vertebral border and inferior angle of scapula unduly prominent ...
... Winging of scapula vertebral border and inferior angle of scapula unduly prominent ...
Joints of the Human Body
... * There are 6 types of synovial joints in the human skeleton (refer to our skeletal system #1 notes for more information) ...
... * There are 6 types of synovial joints in the human skeleton (refer to our skeletal system #1 notes for more information) ...
Brochure
... replacement procedure. A bone graft serves as a type of scaffolding in an area where bone is missing. This scaffolding is composed of material that encourages the growth of new cells and bone where your existing bone is depleted or weakened. There are four main reasons bone grafts are used: • Bone g ...
... replacement procedure. A bone graft serves as a type of scaffolding in an area where bone is missing. This scaffolding is composed of material that encourages the growth of new cells and bone where your existing bone is depleted or weakened. There are four main reasons bone grafts are used: • Bone g ...
Biology 3B Laboratory Muscles of Vertebrate Animals: Shark
... on the linea alba and insert on the humerus. Flexion of the forearm is achieved by the humero-antebrachialis, which originates on the humerus and inserts on the radius and the coracobranchialis, which originates on the coracoid process and inserts on the humerus. Muscles of the pelvic girdle The pel ...
... on the linea alba and insert on the humerus. Flexion of the forearm is achieved by the humero-antebrachialis, which originates on the humerus and inserts on the radius and the coracobranchialis, which originates on the coracoid process and inserts on the humerus. Muscles of the pelvic girdle The pel ...
bones
... fracture due to tensile loading is usually an avulsion撕裂 other injuries include sprains, strains, inflammation, bony deposits when the tibial tuberosity experiences excessive loads from quadriceps muscle group develop condition known as Osgood-Schlatter’s disease ...
... fracture due to tensile loading is usually an avulsion撕裂 other injuries include sprains, strains, inflammation, bony deposits when the tibial tuberosity experiences excessive loads from quadriceps muscle group develop condition known as Osgood-Schlatter’s disease ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.