Nasal Cavity - Dr. Meredith
... thru lateral nasal wall; also the sphenopalatine foramen that transmits the sphenopalatine n. & a. with posterior superior lateral nasal branches to the lateral nasal wall. 6. Lacrimal 7. Inferior concha B. Nasal Conchae (Turbinates): These are projections of the lateral nasal wall into the nasal ca ...
... thru lateral nasal wall; also the sphenopalatine foramen that transmits the sphenopalatine n. & a. with posterior superior lateral nasal branches to the lateral nasal wall. 6. Lacrimal 7. Inferior concha B. Nasal Conchae (Turbinates): These are projections of the lateral nasal wall into the nasal ca ...
Front & Lateral Compartment of the leg Dorsum of the foot
... tibia & fibula. It binds the two bones and provides attachment for muscles. ...
... tibia & fibula. It binds the two bones and provides attachment for muscles. ...
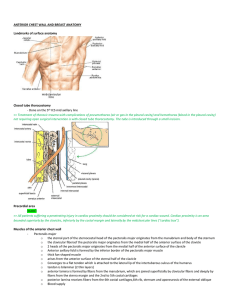
compression of the axillary artery and vein and
... • Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus may be necessary when profuse bleeding occurs[e.g resulting from a stab or bullet wound in the axilla] • If compression is required at a more proximal site,the axillary artery can be compressed at its origin[as the subclavian artery ...
... • Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus may be necessary when profuse bleeding occurs[e.g resulting from a stab or bullet wound in the axilla] • If compression is required at a more proximal site,the axillary artery can be compressed at its origin[as the subclavian artery ...
Cervical Plexus
... cisterna chyli. It enters the thorax through the aortic opening in the diaphragm and ascends through the posterior mediastinum, inclining gradually to the left. On reaching the superior mediastinum, it is found passing upward along the left margin of the esophagus. At the root of the neck, it contin ...
... cisterna chyli. It enters the thorax through the aortic opening in the diaphragm and ascends through the posterior mediastinum, inclining gradually to the left. On reaching the superior mediastinum, it is found passing upward along the left margin of the esophagus. At the root of the neck, it contin ...
Neck - Lectures - gblnetto
... 10. The prevertebral fat space is located between the prevertebral fascia anteriorly and the prevertebral muscles (longus cervicis muscle and longus capitis muscle) that is behind the prevertebral fascia. Pus arising from the tuberculosis of the upper cervical vertebrae is limited in front by the pr ...
... 10. The prevertebral fat space is located between the prevertebral fascia anteriorly and the prevertebral muscles (longus cervicis muscle and longus capitis muscle) that is behind the prevertebral fascia. Pus arising from the tuberculosis of the upper cervical vertebrae is limited in front by the pr ...
Brachial Plexus block 2 of 2
... the "chimney" effect as local anesthetic is forced to spread up between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, unable to go down because the first rib is in the way. ...
... the "chimney" effect as local anesthetic is forced to spread up between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, unable to go down because the first rib is in the way. ...
Neck(1)
... 10. The prevertebral fat space is located between the prevertebral fascia anteriorly and the prevertebral muscles (longus cervicis muscle and longus capitis muscle) that is behind the prevertebral fascia. Pus arising from the tuberculosis of the upper cervical vertebrae is limited in front by the pr ...
... 10. The prevertebral fat space is located between the prevertebral fascia anteriorly and the prevertebral muscles (longus cervicis muscle and longus capitis muscle) that is behind the prevertebral fascia. Pus arising from the tuberculosis of the upper cervical vertebrae is limited in front by the pr ...
Blood vessels and nerves of thoracic wall 胸壁的血管和神经The
... abdomen, consists of a peripheral muscular part and a central tendon ...
... abdomen, consists of a peripheral muscular part and a central tendon ...
fetal pig dissection - lab # 3
... insertion = proximal end of humerus 15. latissimus dorsi = This muscle is posterior to the spinotrapezius. It is broad and extends out from under the forelimb. It covers a large portion of the dorsal, lateral and ventral sides of the thoracic region. The muscle is also included on DIAGRAM #4. origin ...
... insertion = proximal end of humerus 15. latissimus dorsi = This muscle is posterior to the spinotrapezius. It is broad and extends out from under the forelimb. It covers a large portion of the dorsal, lateral and ventral sides of the thoracic region. The muscle is also included on DIAGRAM #4. origin ...
Foot and Ankle - Doral Academy High School
... • Medial arch is higher than the lateral longitudinal arch. It is made up by ...
... • Medial arch is higher than the lateral longitudinal arch. It is made up by ...
The Nasal Cavity
... - There are two cavities in the nose, each with a floor and a roof. A septum lies between them and forms the medial wall for each. - The septum is made of hyaline cartilage anteriorly, the vertical plate of ethmoidal bone (or the perpendicular plate of ethmoid) superiorly, and the vomer posteriorly. ...
... - There are two cavities in the nose, each with a floor and a roof. A septum lies between them and forms the medial wall for each. - The septum is made of hyaline cartilage anteriorly, the vertical plate of ethmoidal bone (or the perpendicular plate of ethmoid) superiorly, and the vomer posteriorly. ...
Nerve Supply
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
Location
... Location : In the region of the scapula, acupoint is located in the depresssion in the center of the sub-scapular fossa (at the junction of the upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 on the line between the lower border of the scapular spine and the inferior angle of the scapular) at the level with spinous process ...
... Location : In the region of the scapula, acupoint is located in the depresssion in the center of the sub-scapular fossa (at the junction of the upper 1/3 and lower 2/3 on the line between the lower border of the scapular spine and the inferior angle of the scapular) at the level with spinous process ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 4 of 17
... o Bilateral costal facets (demifacets) on bodies: usually inferior and superior pairs, articulate with rib heads Facets are arranged in pairs with superior and inferior vertebrae, to form a single socket for a rib head e.g. head of rib 6 forms socket with superior costal facet of T6 and inferior ...
... o Bilateral costal facets (demifacets) on bodies: usually inferior and superior pairs, articulate with rib heads Facets are arranged in pairs with superior and inferior vertebrae, to form a single socket for a rib head e.g. head of rib 6 forms socket with superior costal facet of T6 and inferior ...
ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... open. The arytenoid cartilages are abducted. The rima glottidis is triangular shaped. During forced inspiration, the arytenoid cartilages are rotated laterally. This occurs mainly by the action of the posterior crico-arytenoid muscles. As a result, the vocal folds are abducted, and the rima glottidi ...
... open. The arytenoid cartilages are abducted. The rima glottidis is triangular shaped. During forced inspiration, the arytenoid cartilages are rotated laterally. This occurs mainly by the action of the posterior crico-arytenoid muscles. As a result, the vocal folds are abducted, and the rima glottidi ...
ORAL CAVITY The oral cavity (O.C) and its accessory organs
... The oral cavity (O.C) and its accessory organs namely; the tongue, teeth, salivary glands are concerned with the prehension, mastication and in salivation of food i.e. they are involved in the conversion of food for palatability. The O.C. extends from the lips into the entrance of the pharynx. The o ...
... The oral cavity (O.C) and its accessory organs namely; the tongue, teeth, salivary glands are concerned with the prehension, mastication and in salivation of food i.e. they are involved in the conversion of food for palatability. The O.C. extends from the lips into the entrance of the pharynx. The o ...
study of variant heads of triceps muscle with its developmental basis.
... responsible for extension of the elbow joint. The plural form of triceps was tricipites, a form not in general use today; instead, triceps is both singular and plural. The triceps also make up approximately 2/3 of the muscle mass in the arm [1]. The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of ...
... responsible for extension of the elbow joint. The plural form of triceps was tricipites, a form not in general use today; instead, triceps is both singular and plural. The triceps also make up approximately 2/3 of the muscle mass in the arm [1]. The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of ...
PDF English - International Journal of Morphology
... A and B). In the present case, in addition to its normal sternal and clavicular heads, the right sternocleidomastoid muscle had an additional muscular head from the investing layer of cervical fascia near the lower part of roof of the subclavian triangle, close to the clavicle. The additional head w ...
... A and B). In the present case, in addition to its normal sternal and clavicular heads, the right sternocleidomastoid muscle had an additional muscular head from the investing layer of cervical fascia near the lower part of roof of the subclavian triangle, close to the clavicle. The additional head w ...
companion animal
... stretched. Two lines are drawn parallel to the humerus, from the elbow joint to the greater tubercle of the humerus. The flap is progressively tapered approaching the greater tubercle, where the two lines are connected, the length of the flap is defined by measuring from the pivot point. Incisions a ...
... stretched. Two lines are drawn parallel to the humerus, from the elbow joint to the greater tubercle of the humerus. The flap is progressively tapered approaching the greater tubercle, where the two lines are connected, the length of the flap is defined by measuring from the pivot point. Incisions a ...
the knee joint - Fisiokinesiterapia
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
OUTLINE
... Double layer of peritoneum (more limited than, or a…) ligament Double-layered sheet of peritoneum from stomach to Omentum another abdominal organ; Greater omentum (gastrocolic ligament) ...
... Double layer of peritoneum (more limited than, or a…) ligament Double-layered sheet of peritoneum from stomach to Omentum another abdominal organ; Greater omentum (gastrocolic ligament) ...
THE KNEE JOINT
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
questions
... D. A and B E. All of the above 6. ______ Which of the following statements is (are) true of the calvarium? A. The inner side of the calvarium is supplied by the meningeal arteries. B. The pterion is the junction of the sphenoid, temporal, parietal and frontal bones. C. The scalp overlying the poster ...
... D. A and B E. All of the above 6. ______ Which of the following statements is (are) true of the calvarium? A. The inner side of the calvarium is supplied by the meningeal arteries. B. The pterion is the junction of the sphenoid, temporal, parietal and frontal bones. C. The scalp overlying the poster ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.