* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download compression of the axillary artery and vein and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
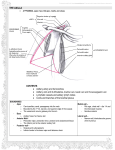
COMPRESSION OF THE AXILLARY ARTERY AND VEIN AND CORDS OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS AXILLARY ARTERY • The continuation of the subclavian artery • Begins at the lateral border of the first rib and ends at the teres major • Divided into 3 parts by the pectoralis minor muscle • Cords of the brachial plexus are named according to their position relative to the axillary artery Compression of the axillary artery • The axillary artery can be palpated in the inferior part of the lateral wall of the axilla. • Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus may be necessary when profuse bleeding occurs[e.g resulting from a stab or bullet wound in the axilla] • If compression is required at a more proximal site,the axillary artery can be compressed at its origin[as the subclavian artery crosses the first rib] by extending downward pressure in the angle between the clavicle and the inferior attachment of the sternocladomastoid joint COMPRESSION OF THE AXILLARY ARTERY COMPRESSION OF THE THIRD PORTION OF AXILLARY ARTERY AXILLARY VEIN • Begins at the lower border of the teres major muscle • Anterior and medial to the artery • Continuation of the brachial vein • Formed from the union of the brachial veins and basilic vein • Ends at the lateral border of 1st rib-the subclavian COMPRESSION OF THE AXILLARY VEIN • It is well recognised that after unaccoustomed use of the arm the axillary vein may thrombose • The vein intima is thought to be damaged by excessive movement between the clavicle and first rib • Thrombosis produces painful congestion and oedema of the arm which subside as the collateral veinous circulation develops • The serious sequale of veinous thrombosis[e.g pulmonary embolism] are common following the axillary vein thrombosis Compression of the axillary vein cont’d • A case reported of effort thrombosis of the axillary vein caused by violent abduction of the arm raising a 40kg weight above the head • The close relationship between the axillary vessels and surrounding anatomical structures may during violent effort and in a particular position,cause compression of the vein with damage to the intima and clot formation PRE & POST AXILLARY VEIN COMPRESSION PHLEBOGRAPHY SHOWING COMPLETE COMPRESSION OF THE LEFT AXILLARY VEIN HEAD OF THE HUMERUS MAY COMPRESS THE AXILLARY VEIN COMPRESSION OF THE AXILLARY VEIN BRACHIAL PLEXUS • The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibres,running from the spine,formed by ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots[C5-C8,T1] • It proceeds through the neck,the axilla[armpit region],and into the arm • It is a network of nerves passing through the cervico-axillary canal to reach axilla and supplies brachium,antebrachium and hand. COMPRESSION OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS • It may result from prolong hyperabduction of the arm during performance of manual task over the head such as painting a ceiling • The cords are inpinged or compressed between the coracoid process of the scapula and the pectoralis minor tendon • Common neurologic symptoms are pain radiating down the arm,numbness,paresthesia[tingling],erythema[re dness of the skin caused by capillary dilation] and weakness of the hands • Compression of the axillary artery and vein causes Ischema of the upper limbs and distension of the superficial veins • The 3 spaces where the brachial plexus can be compressed in the thoracic outlet are:Costoclavicular space,interscalene space,and the retro pectoralis minor space Thoracic outlet syndrome as a result of compression of the brachial plexus T1 weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan The 3 spaces where the brachial plexus can be compressed in the thoracic outlet