* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The axilla
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
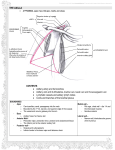
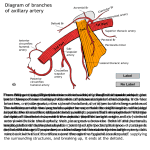
The axilla University Of Babylon College Of Medicine Department Of Human Anatomy And Histology Dr. Haythem Ali Alsayigh M.B.CH.B. - F.I.M.B.S. The axilla Walls Axillary sheath Axillary artery Axillary vein Scapular anastomosis The axilla Is the space between the medial part of the arm and the side of the chest The axilla forms an important passage for nerves and vessels from the neck to the upper limb The axilla It has the shape of a truncated 3-sided pyramid Apex of the axilla The apex is directed towards the root of the neck it is a narrow triangular gap which is bounded by the clavicle anteriorly, scapula posteriorly, and the first rib medially. Apex of the axilla The apex is also called the inlet since it allows the entrance to the axilla of nerves and vessels Base of the axilla The base faces inferiorly and is formed by fascia and skin, the fascia is supported by the suspensory ligament of the axilla which renders the base hollow Base of the axilla The base faces inferiorly and is formed by fascia and skin, the fascia is supported by the suspensory ligament of the axilla which renders the base hollow Anterior wall of the axilla Pectoralis minor Pectoralis major This is formed by the clavicle, pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, and the clavipectoral fascia Posterior wall of the axilla scapula subscapularis Latissimus dorsi Axillary folds The anterior and posterior walls of the axilla can be palpated by fingers and thumb thus forming the anterior and posterior axillary folds. The anterior axillary fold is formed by the lateral border of pectoralis major Axillary folds The posterior axillary fold is formed by teres major and latissimus dorsi teres major latissimus dorsi Medial wall of axilla The medial wall is formed by the upper ribs and intercostal muscles covered by serratus anterior muscle Lateral wall of axilla The lateral wall is narrow and is formed by the floor of the intertubercular groove of the humerus to which is attached the tendon of latissimus dorsi and in which runs the tendon of the long head of biceps Contents of the axilla axillary a. axillary v. Fat brachial axillary artery plexus axillary vein brachial plexus fat axillary nodes axillary lymph lymph nodes Axillary sheath The vessels and the brachial plexus are enclosed in a fascial sleeve (axillary sheeth) which is a downward prolongation of the pre-vertebral fascia in the neck Axillary sheath In the neck, the cervical vertebrae and the muscles attached to them are bound together by a dense fascial layer called prevertebral fascia Axillary sheath Among the muscles of the neck are scalenus anterior and scalenus medius, these are attached to the anterior and posterior tubercles of the transverse process of cervical vertebrae respectively Axillary sheath The roots of the brachial plexus lie between these muscles The subclavian artery passes behind scalenus anterior at the root of the neck Axillary sheath the brachial plexus and the axillary artery (the continuation of the subclavian artery), during their passage from the neck to the axilla have to pierce the prevertebral fascia and while doing so they take a prolongation of the fascia down with them in the form of a sleeve called the "axillary sheath" Axillary artery Begins at the outer border of the first rib as the continuation of the subclavian artery Axillary artery Ends by becoming the brachial artery at the lower border of teres major Axillary artery For descriptive purposes it is divided into three parts by pectoralis minor muscle Axillary artery The second part is located behind the muscle Axillary artery the axillary vein is medial to the artery Axillary artery Axillary v. Medial cord Axillary a. posterior cord lateral cord the cords of the brachial plexus are arranged according to their names around the second part of the axillary artery Axillary artery the medial cord is thus between the artery and vein Branches of the axillary artery 1 from the 1st part 2 from the 2nd part 3 from the 3rd part Branches of the 1st part of the axillary artery Superior thoracic artery Branches of the 2nd part of the axillary artery Thoraco-acromial artery Thoraco-acromial artery This artery is short and wide, it pierces the clavipectoral fascia and is divided then into four branches (acromial, deltoid, pectoral, and clavicular) Branches of the 2nd part of the axillary artery Thoraco-acromial artery lateral thoracic artery Lateral thoracic artery The lateral thoracic artery follows the lower border of pectoralis minor muscle and is important for the blood supply of the female breast. Branches of the 3rd part of the axillary artery Anterior circumflex humeral artery posterior circumflex humeral artery Branches of the 3rd part of the axillary artery Anterior circumflex humeral artery posterior circumflex humeral artery subscapular artery Subscapular artery descends along the lateral border of the scapula and ends as the circumflex scapular and thoracodorsal arteries Circumflex scapular Thoraco-dorsal Subscapular artery the circumflex scapular artery passes around the lateral border of the scapula to supply muscles on the dorsal aspect of the scapula. The thoracodorsal artery is the continuation of the subscapular artery along the lateral border of the scapula Circumflex humeral arteries the posterior is the larger the circumflex humeral arteries pass around the surgical neck of the humerus to anastomose with each other Palpation of the axillary artery The third part of the axillary artery can be palpated in the lateral wall of the inferior part of the axilla and can be compressed against the humerus Axillary vein begins at the lower border of teres major as the continuation of the basilic vein It receives the venae comitantes of the brachial artery and tributaries that correspond to the branches of the axillary artery in addition to the cephalic vein. Axillary vein It becomes the subclavian vein at the outer border of the first rib Axillary vein It is located medial to the axillary artery but when the arm is abducted it lies anterior to the artery hiding it from vision Owing to the large size of the axillary vein and its exposed position, it is liable to be injured in wounds of the axilla Axillary vein Injury is dangerous not only because of severe hemorrhage but also because of the risk of air entering the vessel since the wall tends to be held apart by the fibrous expansions over the vessel from the clavipectoral fascia Axillary vein for this reason, the axillary vein is cleared away to avoid injuring it in subsequent dissection Scapular anastomosis Several vessels around the scapula form a network that provides collateral circulation for the upper limb during ligation of an injured axillary or subclavian artery Subclavian artery The subclavian artery is divided (for descriptive purposes) into three parts by scalenus anterior muscle Subclavian artery The first part lies medial to scalenus anterior one of its branches is the thyrocervical trunk Thyrocervical trunk From the thyrocervical trunk arises the transverse cervical and suprascapular arteries. Transverse cervical artery The transverse cervical has a descending branch that runs along the vertebral border of the scapula Suprascapular artery crosses over the transverse ligament of the scapular notch passes through supraspinous fossa then around the lateral border of the scapular spine (spino-glenoid notch) to supply the infraspinous fossa. Scapular anastomosis The subscapular artery from the third part of the axillary artery descends along the lateral border of the scapula and provides the circumflex scapular artery which enters the infraspinous fossa. Scapular anastomosis The subscapular, suprascapular, and descending branch of the circumflex scapular arteries anastomose, thus connecting the first part of the subclavian with the third part of the axillary artery Scapular anastomosis Thus the axillary artery may be ligated between the thyrocervical trunk and the subscapular artery i.e. between the first part of the subclavian artery and the third part of the axillary artery Scapular anastomosis in this case the circulation of blood in the subscapular artery is reversed