* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CUBITAL FOSSA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
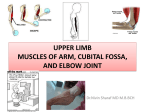
Cubital Fossa Learning Objectives: At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: o Study the boundaries, contents and relationship among structures of cubital fossa. o Surface anatomy of the cubital fossa. o Clinical importance of the cubital fossa. Cubital Fossa Lecture Outline: INTRODUCTION: The cubital fossa is a triangular hollow area that lies in front of the elbow joint. BOUNDARIES OF CUBITAL FOSSA: It is bounded: Superiorly by an imaginary line connecting the medial and lateral epicondyles. Medially by the pronator teres muscle. Laterally by the brachioradialis muscle. Floor: o Its floor is formed of the brachialis and supinator muscles overlying the capsule of the elbow joint. Roof: o The deep fascia of the forearm forms its roof, which is strengthened by fibres of the bicipital aponeurosis. o Lying on the roof in the superficial fascia are the anterior branches of the medial and lateral cutaneous nerves of the forearm and the median cubital vein, which joins the cephalic and basilic veins. CONTENTS OF CUBITAL FOSSA The contents of the fossa from medial to lateral are: • Median nerve • Brachial artery and its terminal branches, the radial and ulnar arteries • Biceps tendon and bicipital aponeurosis (which separates the median cubital vein from the brachial artery) • Radial and posterior interosseous nerves, which are often overlapped by the fibres of brachioradialis Surface Anatomy Of Cubital Fossa: Quick Review Of Cubital Fossa CLINICAL ASPECT OF CUBITAL FOSSA The cephalic, basilic and median cubital veins are usually easily seen and palpated in the roof of the fossa, and this is therefore a common site for venepuncture. It is worth noting that variations in venous anatomy at this site are common . The use of the cubital fossa for intravenous fluid therapy is not recommended because movement of the elbow joint disturbs the cannula and irritates the vein wall with the consequence that thrombosis of the vein quickly occurs. The sphygmomanometer cuff is applied proximal to the base of it and the diaphragm of the stethoscope is placed over it to meassure the blood pressure of the individual. THANK YOU