Arthropods: compare crayfish and grasshopper
... Arthropods - Part Two: Grasshoppers Grasshoppers are insects, the largest arthropod subgroup. There are more named insect species than in any other group of animals; whether there are more actual species is much more difficult to determine. Insects are considered a terrestrial, or land, group. Grass ...
... Arthropods - Part Two: Grasshoppers Grasshoppers are insects, the largest arthropod subgroup. There are more named insect species than in any other group of animals; whether there are more actual species is much more difficult to determine. Insects are considered a terrestrial, or land, group. Grass ...
Quiz Bowl Study Guide
... *The Hamstrings are sometimes referred to as the “NATURAL KNEE BRACE” *The KNEE is the largest joint in the body *The QUADRICEPS are the strongest muscle group in the body *Your quadriceps pull your leg into extension and flex your hip *The ACHILLES TENDON is the strongest tendon in the body *Contus ...
... *The Hamstrings are sometimes referred to as the “NATURAL KNEE BRACE” *The KNEE is the largest joint in the body *The QUADRICEPS are the strongest muscle group in the body *Your quadriceps pull your leg into extension and flex your hip *The ACHILLES TENDON is the strongest tendon in the body *Contus ...
Dissection of the Rat
... cavity is covered by a membrane called the peritoneum, which includes the visceral peritoneum (covers the internal organs), the mesenteries (attach the internal organs to the dorsal body wall) and the omentia (connect organ to organ). Locate the liver, which is a dark colored organ suspended just un ...
... cavity is covered by a membrane called the peritoneum, which includes the visceral peritoneum (covers the internal organs), the mesenteries (attach the internal organs to the dorsal body wall) and the omentia (connect organ to organ). Locate the liver, which is a dark colored organ suspended just un ...
Oncorhynchus mykiss
... Eyes: The pupils have a slight triangle shape which helps the trout see above, in front and below its body. Mouth: Trout use their mouths to grab food and feel things. Operculum: This is a hard plate that covers the delicate gills ...
... Eyes: The pupils have a slight triangle shape which helps the trout see above, in front and below its body. Mouth: Trout use their mouths to grab food and feel things. Operculum: This is a hard plate that covers the delicate gills ...
Lampry presentation
... • The latter portion of the intestine digests bacteria, reabsorbs water and forms feces. • The last section of the intestine narrows to form an exit called the anus. The resulting solid wastes leave the body at this point. ...
... • The latter portion of the intestine digests bacteria, reabsorbs water and forms feces. • The last section of the intestine narrows to form an exit called the anus. The resulting solid wastes leave the body at this point. ...
Animal Evolution –The Invertebrates
... A newer system puts all animals with a threelayer embryo into protostomes or deuterostomes • Protostomes are divided into animals that molt (Ecdysozoa) and don’t molt (Lophotrochozoa) ...
... A newer system puts all animals with a threelayer embryo into protostomes or deuterostomes • Protostomes are divided into animals that molt (Ecdysozoa) and don’t molt (Lophotrochozoa) ...
chapter25_part1 - OCC
... A newer system puts all animals with a threelayer embryo into protostomes or deuterostomes • Protostomes are divided into animals that molt (Ecdysozoa) and don’t molt (Lophotrochozoa) ...
... A newer system puts all animals with a threelayer embryo into protostomes or deuterostomes • Protostomes are divided into animals that molt (Ecdysozoa) and don’t molt (Lophotrochozoa) ...
2 Skeletal muscle contractions - delano
... Muscles contract weaker and weaker, and their contractions become less and less effective **Oxygen Debt must be paid back—Cause of rapid, deep breathes Deep Breathes Continue until Oxygen rids the muscles of Lactic Acid and ATP/CP reserves are replenished ...
... Muscles contract weaker and weaker, and their contractions become less and less effective **Oxygen Debt must be paid back—Cause of rapid, deep breathes Deep Breathes Continue until Oxygen rids the muscles of Lactic Acid and ATP/CP reserves are replenished ...
The Skeletal and Muscular Systems
... • Fact: the body of a newborn baby has about 300 bones, but the average adult has only 206 bones. • This is because as a child grows, some bones fuse together. ...
... • Fact: the body of a newborn baby has about 300 bones, but the average adult has only 206 bones. • This is because as a child grows, some bones fuse together. ...
PPT 1 MB embryology skeletal system
... remains between the diaphyseal epiphyseal ossification centers. The epiphyseals plate plays an important role in growth and length of the bones of the embryo. When the bones has acquired its full length, the epiphyseal plates disappear and the epiphyses then unite with the shaft of the bone. In long ...
... remains between the diaphyseal epiphyseal ossification centers. The epiphyseals plate plays an important role in growth and length of the bones of the embryo. When the bones has acquired its full length, the epiphyseal plates disappear and the epiphyses then unite with the shaft of the bone. In long ...
Invertebrate Zoology Lecture 2, March 31, 1999
... NOTE: Cannot move its gut independently of its body wall D. Feeding/digestive system: ...
... NOTE: Cannot move its gut independently of its body wall D. Feeding/digestive system: ...
Bio11 Animals Lower Invertebrates Part 2
... freshwater, and damp terrestrial environments. Platyhelminthes can be divided into four classes: ...
... freshwater, and damp terrestrial environments. Platyhelminthes can be divided into four classes: ...
Anatomie en Fysiologie Vinyasa 300 TT deel 1
... • Metabolism and homeostasis • Catabolism / Anabolism • Maintain a constant internal environment ...
... • Metabolism and homeostasis • Catabolism / Anabolism • Maintain a constant internal environment ...
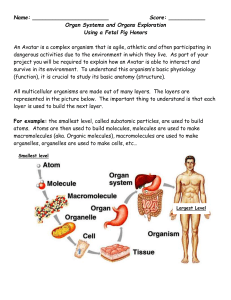
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet
... Using a Fetal Pig Honors An Avatar is a complex organism that is agile, athletic and often participating in dangerous activities due to the environment in which they live. As part of your project you will be required to explain how an Avatar is able to interact and survive in its environment. To und ...
... Using a Fetal Pig Honors An Avatar is a complex organism that is agile, athletic and often participating in dangerous activities due to the environment in which they live. As part of your project you will be required to explain how an Avatar is able to interact and survive in its environment. To und ...
Rat External Anatomy
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: Cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hair ...
... The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: Cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hair ...
Neuro Anatomy Lec.8 د.عبد الجبار الحبي طي The lateral ventricle
... III- Lateral boundary on each side by superior cerebellar peduncle above & inferior cerebellar peduncle below and on each side. ...
... III- Lateral boundary on each side by superior cerebellar peduncle above & inferior cerebellar peduncle below and on each side. ...
echinoderms and
... Amniotic Egg - An egg that is protected from the environment by a more or less impervious shell during its development, requiring only oxygen from outside Ampullae - The 'bulbs' of the water vascular system that lie above each of the podia (or tube feet) of the echinoderms. Water is forced from them ...
... Amniotic Egg - An egg that is protected from the environment by a more or less impervious shell during its development, requiring only oxygen from outside Ampullae - The 'bulbs' of the water vascular system that lie above each of the podia (or tube feet) of the echinoderms. Water is forced from them ...
Nervous System Pathology
... Axons of cerebral nerves that connect with distal neurons in the anterior horn of the SC ...
... Axons of cerebral nerves that connect with distal neurons in the anterior horn of the SC ...
Notes: Human Systems, Homeostasis and Feedback Inhibition
... • The broadest levels of organization within multicellular organisms are cells, tissues, organ, and organ systems ...
... • The broadest levels of organization within multicellular organisms are cells, tissues, organ, and organ systems ...
ANIMAL BIOLOGY (1604) LABORATORY Week of
... • Recognize and distinguish between the three cnidarian classes. • Understand the differences between the polyp and medusa forms. Exercise 5-2: Sponge Anatomy Phylum Porifera (sponges) • Sedentary aquatic (mostly marine) animals • Lack true tissue, organs, and body symmetry • Body perforated by nume ...
... • Recognize and distinguish between the three cnidarian classes. • Understand the differences between the polyp and medusa forms. Exercise 5-2: Sponge Anatomy Phylum Porifera (sponges) • Sedentary aquatic (mostly marine) animals • Lack true tissue, organs, and body symmetry • Body perforated by nume ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... Most don’t have a brain (except Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
... Most don’t have a brain (except Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
academic affairs - Springfield Technical Community College
... Define anatomy and physiology. Describe levels of organization and major characteristics of life. Discuss importance of energy sources and needs. Define homeostasis, discuss its importance to life, and feedback mechanisms of control. Describe location of body cavities, membranes associated with each ...
... Define anatomy and physiology. Describe levels of organization and major characteristics of life. Discuss importance of energy sources and needs. Define homeostasis, discuss its importance to life, and feedback mechanisms of control. Describe location of body cavities, membranes associated with each ...
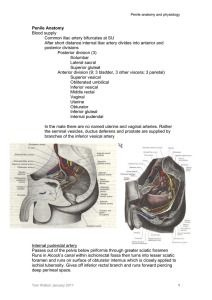
Penile Anatomy Blood supply Common iliac artery bifurcates
... cGMP from GTP. Most important mechanism. Re-inforced by eNOS stimulated production of more nitric oxide Cyclic GMP stimulated production of protein kinase G which opens potassium channels and closes calcium channels Degradation of cGMP by phosphodiesterase limits effect Reduced circulating calcium l ...
... cGMP from GTP. Most important mechanism. Re-inforced by eNOS stimulated production of more nitric oxide Cyclic GMP stimulated production of protein kinase G which opens potassium channels and closes calcium channels Degradation of cGMP by phosphodiesterase limits effect Reduced circulating calcium l ...
The Notes
... The student will demonstrate an understanding of structures, processes, and responses in animals that allow them to survive and reproduce. (Life Science) ...
... The student will demonstrate an understanding of structures, processes, and responses in animals that allow them to survive and reproduce. (Life Science) ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.