BODY PLANES, DIRECTIONS, CAVITIES
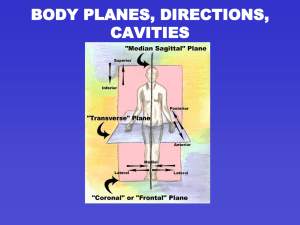
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
APBiology 12
... Faced with environmental fluctuations, animals must manage their internal environments. Animals may be regulators or conformers for a particular environmental variable. ...
... Faced with environmental fluctuations, animals must manage their internal environments. Animals may be regulators or conformers for a particular environmental variable. ...
Chapter 2 b ~ General Plan of Chordate Organisation
... 1) Blood vessels of amphioxus show the basic plan on the circulation of all chordates. 2) Slow contraction of the body drives blood forward in ventral vessels; backwards in dorsal. 3) Blood is collected into sinous venousus (a large sac) located behind the pharynx. Ventral aorta extend from sinous v ...
... 1) Blood vessels of amphioxus show the basic plan on the circulation of all chordates. 2) Slow contraction of the body drives blood forward in ventral vessels; backwards in dorsal. 3) Blood is collected into sinous venousus (a large sac) located behind the pharynx. Ventral aorta extend from sinous v ...
Human Body
... STANDARD 7.L.1.4 Summarize the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestion, respiration, reproduction, circulation, and excretion) and ways that these systems interact with each other to sustain life. ...
... STANDARD 7.L.1.4 Summarize the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestion, respiration, reproduction, circulation, and excretion) and ways that these systems interact with each other to sustain life. ...
Anatomy of the Cervical Spine - All About Back and Neck Pain
... occurs at occiput-C1 • Approximately 50% of rotation occurs at C1-C2 • Lesser amounts of flexionextension, rotation, and lateral bending occur segmentally between C2-C7 ...
... occurs at occiput-C1 • Approximately 50% of rotation occurs at C1-C2 • Lesser amounts of flexionextension, rotation, and lateral bending occur segmentally between C2-C7 ...
Superficial Muscles of the Back
... necessitate the insertion of a chest tube. Generally, the optimal puncture site in a sitting patient is at the level of the 7th or 8th intercostal space on the posterior axillary line. The drain should always be introduced at the upper margin of a rib to avoid injuring the intercostal vein, artery, ...
... necessitate the insertion of a chest tube. Generally, the optimal puncture site in a sitting patient is at the level of the 7th or 8th intercostal space on the posterior axillary line. The drain should always be introduced at the upper margin of a rib to avoid injuring the intercostal vein, artery, ...
Name: Period:_____ Virtual Lab: Virtual Frog Dissection In this
... The last portion of this activity involves an examination of the internal anatomy of a frog. To do this, click the “Internal Anatomy” button on the opening page of the laboratory. Read through, watch and listen to all of the information presented in these segments and actively participate where requ ...
... The last portion of this activity involves an examination of the internal anatomy of a frog. To do this, click the “Internal Anatomy” button on the opening page of the laboratory. Read through, watch and listen to all of the information presented in these segments and actively participate where requ ...
Structural Organization in Animals
... (a) Simple Epithelium Simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells and functions as a lining for body cavities, ducts, and tubes. (b) Compound Epithelium. The compound epithelium consists of two or more cell layers and has protective function as it does in our skin. They cover the dry su ...
... (a) Simple Epithelium Simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells and functions as a lining for body cavities, ducts, and tubes. (b) Compound Epithelium. The compound epithelium consists of two or more cell layers and has protective function as it does in our skin. They cover the dry su ...
extra review
... 2. Esophagus: Food is sent to the esophagus (the Trachea is protected by the epiglottis) where it is squeezed into the stomach (peristalsis) 3. The stomach digests food chemically and mechanically 4. Food moves into the small intestine where chemical digestion continues (villi) 5. The large intestin ...
... 2. Esophagus: Food is sent to the esophagus (the Trachea is protected by the epiglottis) where it is squeezed into the stomach (peristalsis) 3. The stomach digests food chemically and mechanically 4. Food moves into the small intestine where chemical digestion continues (villi) 5. The large intestin ...
Flatworms, Nematodes, and Arthropods
... used to expel digestive system wastes. Some species also have an anal opening. The gut may be a simple sac or highly branched. Digestion is extracellular, with enzymes secreted into the space by cells lining the tract, and digested materials taken into the same cells by phagocytosis. One group, the ...
... used to expel digestive system wastes. Some species also have an anal opening. The gut may be a simple sac or highly branched. Digestion is extracellular, with enzymes secreted into the space by cells lining the tract, and digested materials taken into the same cells by phagocytosis. One group, the ...
Title - Iowa State University
... c. Dinoflagellates, photosynthetic protists that live in the coral’s tissues. d. A and C 22. Some cnidarians go through both a motile and sessile (attached) stage during their life cycle. The attached stage is called a(n) __________. a. Embryo b. Medusa c. Larva d. Polyp ...
... c. Dinoflagellates, photosynthetic protists that live in the coral’s tissues. d. A and C 22. Some cnidarians go through both a motile and sessile (attached) stage during their life cycle. The attached stage is called a(n) __________. a. Embryo b. Medusa c. Larva d. Polyp ...
Document
... of metabolic energy. A large mammal uses more oxygen than a small mammal, but the cost of maintaining its body temperature is less per gram of weight for a large mammal than for a small one. Large animals also can move at less energy cost than can small animals. A large mammal uses more oxygen in ru ...
... of metabolic energy. A large mammal uses more oxygen than a small mammal, but the cost of maintaining its body temperature is less per gram of weight for a large mammal than for a small one. Large animals also can move at less energy cost than can small animals. A large mammal uses more oxygen in ru ...
origin of the long head of triceps - Axis: The Online Journal of CAHId
... passes downwards interposed between teres minor (posterior) and teres major (anterior), running superficial to the medial head of triceps. It forms the medial border of both the quadrilateral and lower triangular spaces. The long and lateral heads descend to join the medial head, with the lateral he ...
... passes downwards interposed between teres minor (posterior) and teres major (anterior), running superficial to the medial head of triceps. It forms the medial border of both the quadrilateral and lower triangular spaces. The long and lateral heads descend to join the medial head, with the lateral he ...
Introduction to Vertebrates _Notes - Extra Notes
... The subphylum Vertebrata consists of about 43,700 species of animals with backbones. Vertebrates exhibit all three of the chordate characteristics at some point during their lives. The embryonic notochord is replaced by a vertebral column in the adult. The vertebral column is made of individual hard ...
... The subphylum Vertebrata consists of about 43,700 species of animals with backbones. Vertebrates exhibit all three of the chordate characteristics at some point during their lives. The embryonic notochord is replaced by a vertebral column in the adult. The vertebral column is made of individual hard ...
Basic Human Anatomy - The Brookside Associates
... paces (vestibules). Guard hairs in the nostrils filter inflowing air. b. Nasal Chambers (Internal Nose). Behind each vestibule of the external nose is a nasal chamber. The two nasal chambers together form the internal nose. These chambers too are separated by the nasal septum. (1) Mucoperiosteum. Th ...
... paces (vestibules). Guard hairs in the nostrils filter inflowing air. b. Nasal Chambers (Internal Nose). Behind each vestibule of the external nose is a nasal chamber. The two nasal chambers together form the internal nose. These chambers too are separated by the nasal septum. (1) Mucoperiosteum. Th ...
An Overview of Body Systems
... (a) Flow between arteries and veins 2) The heart is a 4-chambered pump. 3) The left side of the heart pumps blood through the arteries to the capillaries. 4) At the capillaries, the blood releases nutrients, oxygen, and other necessary molecules into the body tissues. 5) Also at the capillaries, the ...
... (a) Flow between arteries and veins 2) The heart is a 4-chambered pump. 3) The left side of the heart pumps blood through the arteries to the capillaries. 4) At the capillaries, the blood releases nutrients, oxygen, and other necessary molecules into the body tissues. 5) Also at the capillaries, the ...
Evolutionary Evidence - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • I can analyze vestigial structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze homologous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze analogous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common anc ...
... • I can analyze vestigial structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze homologous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze analogous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common anc ...
sponge - Closter Public Schools
... ex. lobsters, shrimp, crabs, barnacles, krill, and copepods. - complex body systems that include a circulatory system. ...
... ex. lobsters, shrimp, crabs, barnacles, krill, and copepods. - complex body systems that include a circulatory system. ...
The Skeletal and Muscular Systems
... adult has only bones. • This is because as a child grows, some bones fuse together. ...
... adult has only bones. • This is because as a child grows, some bones fuse together. ...
CHAPTER 4 copy - WordPress.com
... Habitat – ectoparasites on some fishes. Body shape – elongated body Respiration – 6-15 pairs of gill slits. Mouth – Cyclostomes have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws. Scales and paired fins are absent. Cranium and vertebral column are cartilaginous. Circulation is of closed type. Marine but ...
... Habitat – ectoparasites on some fishes. Body shape – elongated body Respiration – 6-15 pairs of gill slits. Mouth – Cyclostomes have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws. Scales and paired fins are absent. Cranium and vertebral column are cartilaginous. Circulation is of closed type. Marine but ...
Body Planes, Directions, and Cavities
... One long continuous cavity that is located on the back of the body, divided into two sections ...
... One long continuous cavity that is located on the back of the body, divided into two sections ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.























