nipple innervation
... it has always been recognized as the most important nerve for the innervation of the nipple1–5,8,9 (its course, however, has been described controversially). We found that in 93 percent of the breasts it took a subglandular course within the pectoral fascia and reached the nipple from its posterior ...
... it has always been recognized as the most important nerve for the innervation of the nipple1–5,8,9 (its course, however, has been described controversially). We found that in 93 percent of the breasts it took a subglandular course within the pectoral fascia and reached the nipple from its posterior ...
Myelopathy - Cloudfront.net
... • Intrathecal contrast then X-ray • Assess space occupying lesions by changes in contour – Dural sac – Nerve roots – Spinal cord ...
... • Intrathecal contrast then X-ray • Assess space occupying lesions by changes in contour – Dural sac – Nerve roots – Spinal cord ...
Abdomen - Kalam Books
... ♦ The head contains the elongated flattened nucleus with condensed, deeply staining chromatin and the acrosomal cap anteriorly, which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, correspon ...
... ♦ The head contains the elongated flattened nucleus with condensed, deeply staining chromatin and the acrosomal cap anteriorly, which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, correspon ...
Study of Abnormal Foramen Over the Posterior Arch of
... complete canal for vertebral artery in labourers compared to that of nonlabourers, reveling chances of protective mechanism of the bony canal. He also noted the higher incidence of canal in the 5-44 years of age group. Taitz & Nathan (1986) proposed a hypothesis that carrying heavy objects on head a ...
... complete canal for vertebral artery in labourers compared to that of nonlabourers, reveling chances of protective mechanism of the bony canal. He also noted the higher incidence of canal in the 5-44 years of age group. Taitz & Nathan (1986) proposed a hypothesis that carrying heavy objects on head a ...
the anatomical study and clinical importance of the axillary arch
... and branches of brachial plexus, lymph nodes, loose areolar tissue with fat and tail of breast [1]. The Pectoralis major muscle having accessory muscle slips from ribs and costal cartilages, one may extend to latissmusdorsi in posterior axillary fold crossing axillary vessels and nerves calling it a ...
... and branches of brachial plexus, lymph nodes, loose areolar tissue with fat and tail of breast [1]. The Pectoralis major muscle having accessory muscle slips from ribs and costal cartilages, one may extend to latissmusdorsi in posterior axillary fold crossing axillary vessels and nerves calling it a ...
Femoral triangle
... Femoral a. and its branches Femoral vein and its tributaries. Femoral canal Deep inguinal lymph nodes Fatty tissue ...
... Femoral a. and its branches Femoral vein and its tributaries. Femoral canal Deep inguinal lymph nodes Fatty tissue ...
Subperitoneal compartment
... The superior hypogastric plexus is a continuation of the aortic plexus that divides into left and right hypogastric nerves as it enters the pelvis. The hypogastric and pelvic splanchnic nerves merge to form the inferior hypogastric plexuses thus contain both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers. ...
... The superior hypogastric plexus is a continuation of the aortic plexus that divides into left and right hypogastric nerves as it enters the pelvis. The hypogastric and pelvic splanchnic nerves merge to form the inferior hypogastric plexuses thus contain both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers. ...
ANATOMICAL ASPECT OF SHOULDER JOINT
... Shoulder joint is the most common dislocated joint at our body. This joint has freedom movement and it is anatomically unstable, therefore active and passive mechanism is needed to strengthen joint stability. Passive mechanisms are ligaments, articular capsule, glenoid labrum, coracoid process, and ...
... Shoulder joint is the most common dislocated joint at our body. This joint has freedom movement and it is anatomically unstable, therefore active and passive mechanism is needed to strengthen joint stability. Passive mechanisms are ligaments, articular capsule, glenoid labrum, coracoid process, and ...
Musculoskeletal System
... œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • œ Understand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • œ Recognize common eponyms and acronyms • œ Identify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II codes or modifiers are a ...
... œnderstand the most common pathologies affecting these organs • œ Understand orthopedic surgeries and how they relate to pathologies • œ Recognize common eponyms and acronyms • œ Identify when other sections of CPT® or ICD-9-CM should be accessed • œ Know when HCPCS Level II codes or modifiers are a ...
Slide 1 - SchoolRack
... worm invertebrates [as] they have tissues and internal organs [as well as] the three embryonic differentiated cells: Ecto/meso/endoderm ...
... worm invertebrates [as] they have tissues and internal organs [as well as] the three embryonic differentiated cells: Ecto/meso/endoderm ...
An anomalous muscle in the forearm extensor compartment
... 1941 cited by Tan and Smith, 1999).5 Comparative anatomy studies have suggested that the superficial portion exhibits ...
... 1941 cited by Tan and Smith, 1999).5 Comparative anatomy studies have suggested that the superficial portion exhibits ...
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
... Supplies infundibulum & forms a capillary network from which vessels pass downward & form sinusoids into the anterior lobe of pituitary gland (hypophyseal portal ...
... Supplies infundibulum & forms a capillary network from which vessels pass downward & form sinusoids into the anterior lobe of pituitary gland (hypophyseal portal ...
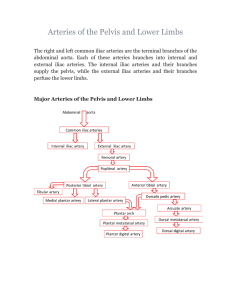
Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs
... front of the legs, ankle joints; branches supply feet and toes ...
... front of the legs, ankle joints; branches supply feet and toes ...
Localisation of hypogastric nerves and pelvic plexus in relation to
... the upper, lower, anterior and posterior borders of the pelvic plexuses. An AP X-ray of the pelvis was performed to demonstrate the position of the pelvic plexuses in the bony skeleton. The midpoints of the pelvic plexuses were plotted on the X-rays by finding the point of transection of lines drawn ...
... the upper, lower, anterior and posterior borders of the pelvic plexuses. An AP X-ray of the pelvis was performed to demonstrate the position of the pelvic plexuses in the bony skeleton. The midpoints of the pelvic plexuses were plotted on the X-rays by finding the point of transection of lines drawn ...
Penetration of cranial nerves by intracranial arteries and veins: a
... arteries originate from medial or dorsal surface of the initial segment of the posterior cerebral artery; their sizes range between 0.3–0.7 mm. Branches of the interpeduncular perforating posterior cerebral arteries account for 31% of vessels; their diameter are considerably thinner (0.1–0.5 mm). Bo ...
... arteries originate from medial or dorsal surface of the initial segment of the posterior cerebral artery; their sizes range between 0.3–0.7 mm. Branches of the interpeduncular perforating posterior cerebral arteries account for 31% of vessels; their diameter are considerably thinner (0.1–0.5 mm). Bo ...
Course of the Ophtmalmic Nerve Both in the Cavernous Sinus and
... bone were removed by a dental drill for the intraorbital part to be studied. All the ophthalmic by a Leica M3 camera. ...
... bone were removed by a dental drill for the intraorbital part to be studied. All the ophthalmic by a Leica M3 camera. ...
Iliac spine
... This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Ilium. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the. ATP (ā′tē′pē′) n. A nucleotide, C10H16N5O13P3, that is composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups and releases energy when hydrol ...
... This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Ilium. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the. ATP (ā′tē′pē′) n. A nucleotide, C10H16N5O13P3, that is composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups and releases energy when hydrol ...
Squid Lab Outreach Teacher Booklet Sept 2004.qxd
... cuttlefish have small shells that are located inside of the body, rather than outside. The octopus, on the other hand, has lost its shell completely. All of the cephalopods are marine animals and all are carnivores. While cephalopods appear to be very different from other classes of molluscs, they h ...
... cuttlefish have small shells that are located inside of the body, rather than outside. The octopus, on the other hand, has lost its shell completely. All of the cephalopods are marine animals and all are carnivores. While cephalopods appear to be very different from other classes of molluscs, they h ...
7-Pelvis nd Sacrum2017-01-17 10:393.2 MB
... # Primary: The skeleton of the pelvis is a basin-shaped ring of bones with holes in its wall connecting the vertebral column to both femora. Its primary functions are: bear the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing; transfer that weight from the axial skeleton to the lower appendicu ...
... # Primary: The skeleton of the pelvis is a basin-shaped ring of bones with holes in its wall connecting the vertebral column to both femora. Its primary functions are: bear the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing; transfer that weight from the axial skeleton to the lower appendicu ...
Anatomical Study of the Superior Gluteal Artery
... artery was classified into four types, the vertical, the horizontal, the descending, and the penetrating main branches. The average external diameter of the pedicle and the main perforator of the horizontal main branches were the largest (2.7 + 0.6 mm and 1.2 + 0.2 mm, respectively). These perforato ...
... artery was classified into four types, the vertical, the horizontal, the descending, and the penetrating main branches. The average external diameter of the pedicle and the main perforator of the horizontal main branches were the largest (2.7 + 0.6 mm and 1.2 + 0.2 mm, respectively). These perforato ...
Radial secondary growth and formation of successive cambia and
... discontinuous cambial segments, the internal phloem, the formation of secondary xylem and phloem from the internal cambium, and differentiation of cork in the pith. After primary growth, the first ring of cambium arises between the external primary phloem and primary xylem, producing secondary phloe ...
... discontinuous cambial segments, the internal phloem, the formation of secondary xylem and phloem from the internal cambium, and differentiation of cork in the pith. After primary growth, the first ring of cambium arises between the external primary phloem and primary xylem, producing secondary phloe ...
Acland`s DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 3
... There are marked differences between vertebrae of different regions, but they all have some basic features in common. We’ll look at a typical thoracic vertebra to see what these features are. ...
... There are marked differences between vertebrae of different regions, but they all have some basic features in common. We’ll look at a typical thoracic vertebra to see what these features are. ...
FREE Sample Here
... PTS: 1 15. ____________________ are drugs that prevent rejection of transplanted tissues. ANS: immunosuppressive drugs PTS: 1 16. The ____________________ system is the transport system of the body. ANS: circulatory PTS: 1 17. The ____________________ system eliminates waste products other than carb ...
... PTS: 1 15. ____________________ are drugs that prevent rejection of transplanted tissues. ANS: immunosuppressive drugs PTS: 1 16. The ____________________ system is the transport system of the body. ANS: circulatory PTS: 1 17. The ____________________ system eliminates waste products other than carb ...
Laparoscopic anatomy of the female pelvis, from the
... The lateral ligaments carry the terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. Concerning the sagittal ligaments, these contain autonomic nervous ...
... The lateral ligaments carry the terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. Concerning the sagittal ligaments, these contain autonomic nervous ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.