Nerve Supply
... Muscular branches to the surrounding muscles. Anterior ulnar recurrent (anastomosis around elbow). Posterior ulnar recurrent (anastomosis around elbow). Common interosseus artery arises near the origin of the ulnar artery, and divides into: A. Anterior interosseus artery supplies the deep flexor mus ...
... Muscular branches to the surrounding muscles. Anterior ulnar recurrent (anastomosis around elbow). Posterior ulnar recurrent (anastomosis around elbow). Common interosseus artery arises near the origin of the ulnar artery, and divides into: A. Anterior interosseus artery supplies the deep flexor mus ...
Surgical Anatomy of the FaceImplications for Modern Face
... followed in a superolateral direction over the mandible, it continues as the SMAS into the face. It becomes obvious that the SMAS and platysma represent an anatomically homogeneous unit that maintains its muscular consistency and direction of fibers as it crosses the mandible. The mandibulocutaneous ...
... followed in a superolateral direction over the mandible, it continues as the SMAS into the face. It becomes obvious that the SMAS and platysma represent an anatomically homogeneous unit that maintains its muscular consistency and direction of fibers as it crosses the mandible. The mandibulocutaneous ...
Surgical Anatomy of the Face Implications for Modern Face-lift Techniques
... followed in a superolateral direction over the mandible, it continues as the SMAS into the face. It becomes obvious that the SMAS and platysma represent an anatomically homogeneous unit that maintains its muscular consistency and direction of fibers as it crosses the mandible. The mandibulocutaneous ...
... followed in a superolateral direction over the mandible, it continues as the SMAS into the face. It becomes obvious that the SMAS and platysma represent an anatomically homogeneous unit that maintains its muscular consistency and direction of fibers as it crosses the mandible. The mandibulocutaneous ...
231 - Bossier Parish Community College
... 87. Trace the pathways of vessels from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left ventricle. (B) 88. List the major arteries that carry blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the major areas of the body. (B) 89. Name the major veins that return blood from the systemic circulation t ...
... 87. Trace the pathways of vessels from the right ventricle to the lungs and back to the left ventricle. (B) 88. List the major arteries that carry blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the major areas of the body. (B) 89. Name the major veins that return blood from the systemic circulation t ...
Microanatomy and Surgical Approaches to the
... pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid venous plexus, the otic ganglion, the chorda tympani nerve and the mandibular nerve. In this study, we describe the microsurgical anatomy of the ITF, as viewed by step-by-step anatomical dissection and also through the perspective of three latera ...
... pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid venous plexus, the otic ganglion, the chorda tympani nerve and the mandibular nerve. In this study, we describe the microsurgical anatomy of the ITF, as viewed by step-by-step anatomical dissection and also through the perspective of three latera ...
45-sole of the foot
... hallucis longus, from which it receives a strong slip. • It is here that it receives on its lateral border the insertion of the quadratus plantae muscle. ...
... hallucis longus, from which it receives a strong slip. • It is here that it receives on its lateral border the insertion of the quadratus plantae muscle. ...
Lymphatic System
... Posterior lymph nodes are located along the back of the neck. Deep cervical lymph nodes are associated with their positions adjacent to the internal jugular vein, which runs near the sides of the neck. They are known as the lateral jugular, anterior jugular, and jugulo-digastric lymph nodes. ...
... Posterior lymph nodes are located along the back of the neck. Deep cervical lymph nodes are associated with their positions adjacent to the internal jugular vein, which runs near the sides of the neck. They are known as the lateral jugular, anterior jugular, and jugulo-digastric lymph nodes. ...
19-Gluteal region2009-05-16 11:384.9 MB
... passes through GSF, above piriformis, then divides into superficial branch between gluteus maximus & medius and deep branch between gluteus medius & minimus INFERIOR GLUTEAL Course: ...
... passes through GSF, above piriformis, then divides into superficial branch between gluteus maximus & medius and deep branch between gluteus medius & minimus INFERIOR GLUTEAL Course: ...
Inglês
... is removed from the same area. This flap has been used so far in reconstructive surgery including oral and maxillofacial surgery (Wang et al.). The PSDA is a branch of the PCHA. The artey arises from the third section of the axillar artery which is placed between the bottom edge of the minor pectora ...
... is removed from the same area. This flap has been used so far in reconstructive surgery including oral and maxillofacial surgery (Wang et al.). The PSDA is a branch of the PCHA. The artey arises from the third section of the axillar artery which is placed between the bottom edge of the minor pectora ...
Location and Stability of Rectus Muscle Pulleys
... extraocular muscles in primary gaze. Muscle paths in primary position were highly uniform across normal subjects. In secondary gaze positions, rectus muscle paths at the level of the pulleys exhibited small but consistent shifts, relative to the orbit, opposite the direction of gaze, consistent with ...
... extraocular muscles in primary gaze. Muscle paths in primary position were highly uniform across normal subjects. In secondary gaze positions, rectus muscle paths at the level of the pulleys exhibited small but consistent shifts, relative to the orbit, opposite the direction of gaze, consistent with ...
Synovial Joints - Anatomy and Physiology
... • Elevation (lifting a body part superiorly) • Depression (moving a body part inferiorly) ...
... • Elevation (lifting a body part superiorly) • Depression (moving a body part inferiorly) ...
Anatomy of Deltoid Flap Based on Posterior Subcutaneous Deltoid
... is removed from the same area. This flap has been used so far in reconstructive surgery including oral and maxillofacial surgery (Wang et al.). The PSDA is a branch of the PCHA. The artey arises from the third section of the axillar artery which is placed between the bottom edge of the minor pectora ...
... is removed from the same area. This flap has been used so far in reconstructive surgery including oral and maxillofacial surgery (Wang et al.). The PSDA is a branch of the PCHA. The artey arises from the third section of the axillar artery which is placed between the bottom edge of the minor pectora ...
variations in the arterial branching pattern of the coeliac trunk
... T11 –L1. A high origin of coeliac artery may give rise to coeliac axis compression syndrome leading to severe post-prandial epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting. In our study we did not find any case of high origin of the coeliac trunk. Variability of the level of origin of coeliac trunk is importan ...
... T11 –L1. A high origin of coeliac artery may give rise to coeliac axis compression syndrome leading to severe post-prandial epigastric pain, nausea and vomiting. In our study we did not find any case of high origin of the coeliac trunk. Variability of the level of origin of coeliac trunk is importan ...
Contributions to the Cranial Osteology of the Fishes. No. IV
... constituted as in Pagrosornus; it differs therefrom in being markedly inflated, so that the two together produce a cordiform prominence on the base of the skull. The basisphenoid is a much smaller bone in this form than in Pagrosmnu8, the three arms, being little more than spicules of bone. The deve ...
... constituted as in Pagrosornus; it differs therefrom in being markedly inflated, so that the two together produce a cordiform prominence on the base of the skull. The basisphenoid is a much smaller bone in this form than in Pagrosmnu8, the three arms, being little more than spicules of bone. The deve ...
A posterior approach to the elbow joint
... osteoperiosteal flaps from the olecranon. Van Gorder created an inverted ‘V’-shaped flap of the triceps mechanism to expose the distal humerus. In all of these approaches there is considerable mobilisation of the ulnar nerve. Petalling of the olecranon, described in the Gschwend approach, can be dif ...
... osteoperiosteal flaps from the olecranon. Van Gorder created an inverted ‘V’-shaped flap of the triceps mechanism to expose the distal humerus. In all of these approaches there is considerable mobilisation of the ulnar nerve. Petalling of the olecranon, described in the Gschwend approach, can be dif ...
Topographical mapping of the posterior interosseous nerve in
... extensor digitorum, the extensor digiti minimi and the extensor carpi ulnaris muscles, together with two long branches: a medial branch to the extensor pollicis longus and extensor indicis muscles, and a lateral branch to the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis muscles (Gray and Ca ...
... extensor digitorum, the extensor digiti minimi and the extensor carpi ulnaris muscles, together with two long branches: a medial branch to the extensor pollicis longus and extensor indicis muscles, and a lateral branch to the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis muscles (Gray and Ca ...
Scapular_region_true_false_with_explanation
... 15. False. The upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm is a continuation of the axillary nerve. The dorsal scapular terminates in muscular branches to rhomboids and levator scapulae. “The upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm can be used to test the intergrity of the dorsal scapular nerve.” 16. ...
... 15. False. The upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm is a continuation of the axillary nerve. The dorsal scapular terminates in muscular branches to rhomboids and levator scapulae. “The upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm can be used to test the intergrity of the dorsal scapular nerve.” 16. ...
for each numbered word or phrase, select the one lettered
... (A) If choices 1, 2 and 3 are correct (B) if choices 1 and 3 are correct (C) If choices 2 and 4 are correct (D) If only choice 4 is correct (E) If all choices are correct 41. Structures embedded in the parotid gland include (1) retromandibular vein (2) auriculotemporal nerve (3) facial nerve (4) lin ...
... (A) If choices 1, 2 and 3 are correct (B) if choices 1 and 3 are correct (C) If choices 2 and 4 are correct (D) If only choice 4 is correct (E) If all choices are correct 41. Structures embedded in the parotid gland include (1) retromandibular vein (2) auriculotemporal nerve (3) facial nerve (4) lin ...
dr.mohamed farouk Cervical cancer
... The cervix is attached to the lateral pelvic wall by a pair of ligaments at the base of the broad ligament referred to as the cardinal ligaments This ligament contains the uterine arteries and veins. The uterine arteries pass over the ureters on each side in close proximity to the cervix Most cervic ...
... The cervix is attached to the lateral pelvic wall by a pair of ligaments at the base of the broad ligament referred to as the cardinal ligaments This ligament contains the uterine arteries and veins. The uterine arteries pass over the ureters on each side in close proximity to the cervix Most cervic ...
Your Body Systems
... Each cell does a specialized job. Nerve cells, for example, carry messages to and from your brain. Skin cells, on the other hand, are flat and rectangular. This allows them to spread out and cover the surface of your body. Groups of similar cells that do the same kind of work are called tissues. For ...
... Each cell does a specialized job. Nerve cells, for example, carry messages to and from your brain. Skin cells, on the other hand, are flat and rectangular. This allows them to spread out and cover the surface of your body. Groups of similar cells that do the same kind of work are called tissues. For ...
Fracture proximal humerus
... do counter traction, flexion of the elbow 90` and held close to the body , no traction , slow lateral rotation of the arm then adduction and medial rotation . 2-Hippocratic’s method . Traction on the line of the limb with counter traction . 3-stimson’s technique (gravity) .patient prone the arm hang ...
... do counter traction, flexion of the elbow 90` and held close to the body , no traction , slow lateral rotation of the arm then adduction and medial rotation . 2-Hippocratic’s method . Traction on the line of the limb with counter traction . 3-stimson’s technique (gravity) .patient prone the arm hang ...
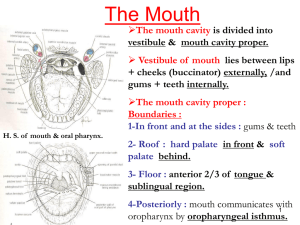
19. oral cavity+pharynx2010-10-01 03:411.2 MB
... foramen coecum ( is an embryologic remnant of upper end of thyroglossal duct). --The mucous membrane of oral part (anterior 2/3) contains vallate papillae. --The mucous membrane of pharyngeal part (post.1/3) devoid of papillae, but it has a nodular irrigular5 ...
... foramen coecum ( is an embryologic remnant of upper end of thyroglossal duct). --The mucous membrane of oral part (anterior 2/3) contains vallate papillae. --The mucous membrane of pharyngeal part (post.1/3) devoid of papillae, but it has a nodular irrigular5 ...
Larynx
... Vocal ligaments extend from the deep surface of the thyroid angle to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage ...
... Vocal ligaments extend from the deep surface of the thyroid angle to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage ...
Shoulder
... INDICATION: Shoulder pain and limited range of motion. TECHNIQUE: Axial gradient echo, proton density fat-suppressed, coronal proton density, T2 fatsuppressed, axial T2, and sagittal proton density fat-suppressed images of the right shoulder were performed on the 1.5 Tesla magnet. FINDINGS: Moderate ...
... INDICATION: Shoulder pain and limited range of motion. TECHNIQUE: Axial gradient echo, proton density fat-suppressed, coronal proton density, T2 fatsuppressed, axial T2, and sagittal proton density fat-suppressed images of the right shoulder were performed on the 1.5 Tesla magnet. FINDINGS: Moderate ...
Larynx
... {forms Epiglottis} and laterally by ventral folds of 6th brachial arches) Arytenoid swellings develop on each side of tracheobroncheal groove, enlarge to come close to each other and to hypo brachial eminence (caudal portion). This converts the Vertical slit like cavity into a T shaped one Initially ...
... {forms Epiglottis} and laterally by ventral folds of 6th brachial arches) Arytenoid swellings develop on each side of tracheobroncheal groove, enlarge to come close to each other and to hypo brachial eminence (caudal portion). This converts the Vertical slit like cavity into a T shaped one Initially ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.