Anatomical landmarks for transnasal endoscopie skull - Serval
... image guidance systems during endoscopic endonasal procedures have provided increasing accuracy and safety for this approach, allowing improved, constant surgical orientation in an anatomically complex area. We present an anatomical dissection study to deWne application of extended endoscopic endona ...
... image guidance systems during endoscopic endonasal procedures have provided increasing accuracy and safety for this approach, allowing improved, constant surgical orientation in an anatomically complex area. We present an anatomical dissection study to deWne application of extended endoscopic endona ...
ChiroCredit.com™ / OnlineCE.com presents Soft Tissue Injuries 114
... This muscle attaches from the anterior of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th lateral masses of the sacrum and the sacrotuberous ligament to the upper border of the greater trochanter. It laterally rotates the thigh when the hip is extended and abducts the thigh when the hip is flexed. The piriformis exhibits inv ...
... This muscle attaches from the anterior of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th lateral masses of the sacrum and the sacrotuberous ligament to the upper border of the greater trochanter. It laterally rotates the thigh when the hip is extended and abducts the thigh when the hip is flexed. The piriformis exhibits inv ...
Bones
... Note: External/internal ridges often “superimposed” over each other radiographically; therefore difficult to differentiate between the two; external always superior to internal oblique ridge (mylohyoid muscle attachment); internal usually runs below roots of mandibular molars (see figure 27-41, 27-4 ...
... Note: External/internal ridges often “superimposed” over each other radiographically; therefore difficult to differentiate between the two; external always superior to internal oblique ridge (mylohyoid muscle attachment); internal usually runs below roots of mandibular molars (see figure 27-41, 27-4 ...
Semi-Quantitative Measurements of Normal Organs With Variable
... In most organs, FDG accumulation is often fairly homogeneous within the organ. However, in lungs, the lower lung field accumulates slightly more than the upper and middle lung fields. The distribution of FDG may not always be homogeneous in an organ, such as in the case of the liver. The liver often ...
... In most organs, FDG accumulation is often fairly homogeneous within the organ. However, in lungs, the lower lung field accumulates slightly more than the upper and middle lung fields. The distribution of FDG may not always be homogeneous in an organ, such as in the case of the liver. The liver often ...
The Trauma of Birth
... direction. The lesion is named from the position of the basisphenoid: lateral strain with the spheroid to the right, etc. (From Magoun, H. Osteopathy in the Cranial Field.) Bilateral condylar compression may cause a buckling type of strain of the cranial base, producing a vertical strain between the ...
... direction. The lesion is named from the position of the basisphenoid: lateral strain with the spheroid to the right, etc. (From Magoun, H. Osteopathy in the Cranial Field.) Bilateral condylar compression may cause a buckling type of strain of the cranial base, producing a vertical strain between the ...
05 lung & pleura2012-01
... up into the root of the neck. • 2-Costal pleura: It lines inner surface of ribs, costal cartilages, intercostal muscles and back of the sternum. • 3-Diaphragmatic pleura: It covers upper surface of the diaphragm. • 4-Mediastinal pleura: It covers mediastinal surface of the lung. ...
... up into the root of the neck. • 2-Costal pleura: It lines inner surface of ribs, costal cartilages, intercostal muscles and back of the sternum. • 3-Diaphragmatic pleura: It covers upper surface of the diaphragm. • 4-Mediastinal pleura: It covers mediastinal surface of the lung. ...
Lecture Lower limb I 2010
... Which artery serve as the most important source of blood for adult femoral head and neck? ...
... Which artery serve as the most important source of blood for adult femoral head and neck? ...
Antebrachium Flexors - WELCOME to the future website of
... from medial epicondyle of humrus, ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint, and deep antebrachial fascia – Origin from ulnar head: medial side of coronoid process – Origin from radial head: obique line of radius ...
... from medial epicondyle of humrus, ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint, and deep antebrachial fascia – Origin from ulnar head: medial side of coronoid process – Origin from radial head: obique line of radius ...
Chapter 9 *Lecture PowerPoint Joints FlexArt PowerPoint
... – Atlantoaxial joint (dens of axis and atlas) • Transverse ligament ...
... – Atlantoaxial joint (dens of axis and atlas) • Transverse ligament ...
The Deltoid to Triceps Nerve Transfer
... • “Donor distal, recipient proximal” • Coaptation within 2 inches of medial triceps msucle • Simultaneous Brachialis to AIN/FCR nerve transfer performed in the same extremity (left) ...
... • “Donor distal, recipient proximal” • Coaptation within 2 inches of medial triceps msucle • Simultaneous Brachialis to AIN/FCR nerve transfer performed in the same extremity (left) ...
Anatomy & Physiology Workbook For Dummies
... why Mommy couldn’t drive for every school field trip, attend every Cub Scout den meeting, or set up play dates every single day of the week. And especially from Pat to Jim for his love, enthusiastic support, assistance, and encouragement without which she could not have finished this workbook. ...
... why Mommy couldn’t drive for every school field trip, attend every Cub Scout den meeting, or set up play dates every single day of the week. And especially from Pat to Jim for his love, enthusiastic support, assistance, and encouragement without which she could not have finished this workbook. ...
SACRAL PLEXUS, SCIATIC NERVE AND FEMORAL
... MOTOR MANIFESTATION: 1-Wasting of quadriceps femoris. 2-Loss of extension of knee. 3-Weak flexion of hip (psoas major is intact). SENSORY EFFECT: Loss of sensation of the areas supplied by femoral nerve. SENSORY MANIFESTATION : loss of sensation over areas supplied (antero-medial) aspect of th ...
... MOTOR MANIFESTATION: 1-Wasting of quadriceps femoris. 2-Loss of extension of knee. 3-Weak flexion of hip (psoas major is intact). SENSORY EFFECT: Loss of sensation of the areas supplied by femoral nerve. SENSORY MANIFESTATION : loss of sensation over areas supplied (antero-medial) aspect of th ...
The Dissection of a Fetal Pig
... systems are arranged within your own body. Dissection involves the careful and systematic examination of the internal structures of an organism. A good dissection will reveal not only the location and structure of individual organs, but also how different organs relate to one another in the various ...
... systems are arranged within your own body. Dissection involves the careful and systematic examination of the internal structures of an organism. A good dissection will reveal not only the location and structure of individual organs, but also how different organs relate to one another in the various ...
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
... Ventral rami, on the other hand often combine and branch extensively in a nerve plexus, which is a braided interweaving of different ventral rami from the spinal nerves. Emerging from these plexuses comes various named peripheral nerves, many of which we will be learning in lab. There are four perip ...
... Ventral rami, on the other hand often combine and branch extensively in a nerve plexus, which is a braided interweaving of different ventral rami from the spinal nerves. Emerging from these plexuses comes various named peripheral nerves, many of which we will be learning in lab. There are four perip ...
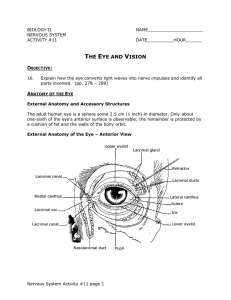
the eye and vision
... Hold the Blind Spot Card about 18 inches from your eyes. Close your left eye, and focus your right eye on the X, which should be positioned so that it is directly in line with your right eye. Move the figure slowly toward your face, keeping your right eye focused on the X. When the dot focuses on th ...
... Hold the Blind Spot Card about 18 inches from your eyes. Close your left eye, and focus your right eye on the X, which should be positioned so that it is directly in line with your right eye. Move the figure slowly toward your face, keeping your right eye focused on the X. When the dot focuses on th ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
... nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will • It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature • Walter Cannon coined the terms “homeostasis” and the “flight-or-fight” – He dedicated his career to the study of the ANS – Found that animals without AN ...
... nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will • It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature • Walter Cannon coined the terms “homeostasis” and the “flight-or-fight” – He dedicated his career to the study of the ANS – Found that animals without AN ...
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton
... thoracic vertebrae and the ribs, and between the ribs and sternum. ...
... thoracic vertebrae and the ribs, and between the ribs and sternum. ...
autonomic nervous system
... nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will • It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature • Walter Cannon coined the terms “homeostasis” and the “flight-or-fight” – He dedicated his career to the study of the ANS – Found that animals without AN ...
... nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will • It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature • Walter Cannon coined the terms “homeostasis” and the “flight-or-fight” – He dedicated his career to the study of the ANS – Found that animals without AN ...
Chapter 7 skeleton part I
... a. Identify the facial bones. b. Quincy suffers a hit to the skull that fractures the right superior lateral surface of his cranium. Which bone is fractured? c. Identify the following bones as either a facial bone or a cranial bone: vomer, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal, and inferior nasal conchae. © 2 ...
... a. Identify the facial bones. b. Quincy suffers a hit to the skull that fractures the right superior lateral surface of his cranium. Which bone is fractured? c. Identify the following bones as either a facial bone or a cranial bone: vomer, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal, and inferior nasal conchae. © 2 ...
Chapter 10 - Axial Skeleton: Muscle and Joint Interactions
... sagittal, frontal, and horizontal planes. Within each plane, the maximal internal torque potential is equal to the product of (1) the muscle force generated parallel to a given plane, and (2) the length of the internal moment arm available to the muscle (Figure 10-3). The spatial orientation of a mu ...
... sagittal, frontal, and horizontal planes. Within each plane, the maximal internal torque potential is equal to the product of (1) the muscle force generated parallel to a given plane, and (2) the length of the internal moment arm available to the muscle (Figure 10-3). The spatial orientation of a mu ...
Sciatica: Low back and Leg Pain Diagnosis and
... • Compression of the spinal nerves in the back which can lead to symptoms of leg pain, numbness and weakness along the different nerves as they travel down the leg and into the foot • Also known as Radiculopathy ...
... • Compression of the spinal nerves in the back which can lead to symptoms of leg pain, numbness and weakness along the different nerves as they travel down the leg and into the foot • Also known as Radiculopathy ...
Lateral Stabilizing Structures of the Knee: Functional Anatomy and
... area is essential for detection and understanding of the injuries associated with lateral instability. In this article, we present the functional anatomy and injuries of the lateral compartment as seen at MR imaging. The article is based on the MR images of 10 asymptomatic volunteers and 20 patients ...
... area is essential for detection and understanding of the injuries associated with lateral instability. In this article, we present the functional anatomy and injuries of the lateral compartment as seen at MR imaging. The article is based on the MR images of 10 asymptomatic volunteers and 20 patients ...
Buccal fat pad flap - Vula
... may be used to fill small-to-medium sized soft tissue and bony defects in the palate, superior and inferior alveoli and buccal mucosa. It is often encountered as it bulges into the surgical field during surgery in the pterygomandibular region. Relevant Anatomy Buccal fat pad The buccal fat pad (Figu ...
... may be used to fill small-to-medium sized soft tissue and bony defects in the palate, superior and inferior alveoli and buccal mucosa. It is often encountered as it bulges into the surgical field during surgery in the pterygomandibular region. Relevant Anatomy Buccal fat pad The buccal fat pad (Figu ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.