• Mouthparts 1 • Mouthparts 2 • Thorax and abdomen 1 • Thorax and
... eyes have thousands of more or less equivalent sensory cartridges called ommatidia. Each ommatidium has a hexagonal lens (hundreds in focus in this picture) and six to eight light-sensitive cells. Single homologous sensory cells from numerous adjacent ommatidia respond to light in their limited fiel ...
... eyes have thousands of more or less equivalent sensory cartridges called ommatidia. Each ommatidium has a hexagonal lens (hundreds in focus in this picture) and six to eight light-sensitive cells. Single homologous sensory cells from numerous adjacent ommatidia respond to light in their limited fiel ...
spaces at the scapular region (posterior aspect )
... note: when you look at the dorsal aspect of your hand is blue colors vein which is a network of vein called dorsal venous arc cephalic vein : start from lateral side of the dorsal venous arch then pass on the lateral side of the forearm then pass anterior to the elbow ( which called cubital fossa a ...
... note: when you look at the dorsal aspect of your hand is blue colors vein which is a network of vein called dorsal venous arc cephalic vein : start from lateral side of the dorsal venous arch then pass on the lateral side of the forearm then pass anterior to the elbow ( which called cubital fossa a ...
PDF - World Wide Journals
... Introduction: Fibula is one of our lateral leg bone which does not take part in weight transmission of the body1. Usually it is supplied by one nutrient artery that is peroneal artery branch of popliteal artery2. This artery enters in to bone through an opening present in diaphysis of long bone call ...
... Introduction: Fibula is one of our lateral leg bone which does not take part in weight transmission of the body1. Usually it is supplied by one nutrient artery that is peroneal artery branch of popliteal artery2. This artery enters in to bone through an opening present in diaphysis of long bone call ...
Anterior mediastinal masses
... recurrent laryngeal Posterior mediastinum: Oesophagus, descending aorta, azygos & hemiazygos veins, thoracic duct, vagus and splanchnic nerves, lymph nodes, fat Paraspinal structures ...
... recurrent laryngeal Posterior mediastinum: Oesophagus, descending aorta, azygos & hemiazygos veins, thoracic duct, vagus and splanchnic nerves, lymph nodes, fat Paraspinal structures ...
The Knee
... Purely mechanical event, occurs with passive or active knee extension and can not be produced voluntarily In closed chain motion, such as rising from sitting, terminal rotation is seen as internal rotation of the femur on fixed tibia ...
... Purely mechanical event, occurs with passive or active knee extension and can not be produced voluntarily In closed chain motion, such as rising from sitting, terminal rotation is seen as internal rotation of the femur on fixed tibia ...
The Knee
... Purely mechanical event, occurs with passive or active knee extension and can not be produced voluntarily In closed chain motion, such as rising from sitting, terminal rotation is seen as internal rotation of the femur on fixed tibia ...
... Purely mechanical event, occurs with passive or active knee extension and can not be produced voluntarily In closed chain motion, such as rising from sitting, terminal rotation is seen as internal rotation of the femur on fixed tibia ...
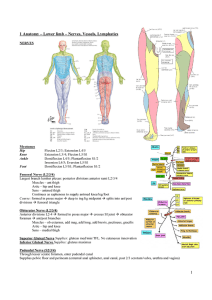
1 1 Anatomy – Lower limb – Nerves, Vessels, Lymphatics
... Cutaneous innervation: Medial plantar nerve → medial sole foot; Lateral plantar nerve → lateral sole foot Also calcaneal branches Loss of flexion toes and inversion foot ARTERIES Blood Supply to Hip Trochanteric anastomosis (greater trochanter): main supply head of femur – sup/inf gluteal, med/lat c ...
... Cutaneous innervation: Medial plantar nerve → medial sole foot; Lateral plantar nerve → lateral sole foot Also calcaneal branches Loss of flexion toes and inversion foot ARTERIES Blood Supply to Hip Trochanteric anastomosis (greater trochanter): main supply head of femur – sup/inf gluteal, med/lat c ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Inferior view (b) Right clavicle, superior and inferior views Figure 5.23b ...
... Inferior view (b) Right clavicle, superior and inferior views Figure 5.23b ...
оперативная хирургия и топографическая анатомия operative
... All items of discipline are well presented in this testbook from topographic anatomy and operative surgery. Test control is a component of subject examination. It is recomenned for students of medical universities with the English language of studies. ...
... All items of discipline are well presented in this testbook from topographic anatomy and operative surgery. Test control is a component of subject examination. It is recomenned for students of medical universities with the English language of studies. ...
parotid gland and duct
... • A portion of fascia extending from the styloid process to the angle of mandible is called stylomandibular ligament. It separates the parotid gland from the submandibular gland. • Arterial supply : external carotid artery & its terminal branches • Venous drainage : into the retro-mandibular vein . ...
... • A portion of fascia extending from the styloid process to the angle of mandible is called stylomandibular ligament. It separates the parotid gland from the submandibular gland. • Arterial supply : external carotid artery & its terminal branches • Venous drainage : into the retro-mandibular vein . ...
18-Medial side of thigh2009-05-21 07:183.0 MB
... In the thigh, it divides into medial & lateral branches running along the outer surface of obturator membrane, deep to obturator externus. Branches: Muscular to: adductors & obturator externus. Articular to: hip joint. ...
... In the thigh, it divides into medial & lateral branches running along the outer surface of obturator membrane, deep to obturator externus. Branches: Muscular to: adductors & obturator externus. Articular to: hip joint. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... ---somatic motor fibers arising from the nucleus ambiguus. ---visceral motor fibers arising from the dorsal nucleus of vagus n. ---somatic sensory fibers arising from the superior ganglion of vagus n. and stop to the spinal nucleus of trigeminal n. ...
... ---somatic motor fibers arising from the nucleus ambiguus. ---visceral motor fibers arising from the dorsal nucleus of vagus n. ---somatic sensory fibers arising from the superior ganglion of vagus n. and stop to the spinal nucleus of trigeminal n. ...
Embryology Lec5 Dr.Ban The branchial apparatus =The branchial
... Develops into the external auditory meatus(the corresponding 1st pharyngeal pouch develops into the auditory or eustacian tube, and the intervening membrane develops into the typanic membrane). Defects in the development of pharyngeal cleft1 can result in preauricularcysts and/or fistulas(in front ...
... Develops into the external auditory meatus(the corresponding 1st pharyngeal pouch develops into the auditory or eustacian tube, and the intervening membrane develops into the typanic membrane). Defects in the development of pharyngeal cleft1 can result in preauricularcysts and/or fistulas(in front ...
External Anatomy of Insects: The Exoskeleton, Head
... The insect thorax consists of three segments, each of which bears a pair of legs. The legs are segmental appendages. Two of the thoracic segments may bear paired wings, which are complex folds of the body wall not segmental appendages. The three thoracic segments are, in order from anterior to poste ...
... The insect thorax consists of three segments, each of which bears a pair of legs. The legs are segmental appendages. Two of the thoracic segments may bear paired wings, which are complex folds of the body wall not segmental appendages. The three thoracic segments are, in order from anterior to poste ...
The Development of the Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine
... (Hapa et al., 2013). In Pan and Gorilla, the relative position of the origin of rectus femoris appears intermediate between the reflected origin and the direct origin in humans. At a glance, the rectus femoris positioning in hominids would seem to offer a biomechanical advantage to the bipedal gait ...
... (Hapa et al., 2013). In Pan and Gorilla, the relative position of the origin of rectus femoris appears intermediate between the reflected origin and the direct origin in humans. At a glance, the rectus femoris positioning in hominids would seem to offer a biomechanical advantage to the bipedal gait ...
Pelvic and thigh musculature in frogs (Anura) and origin of anuran
... externus on the iliac shaft are isolated from each other by a thin dorsal crista, which is moderately declined medially, part of the iliacus externus extends dorsally such that both muscles meet and completely cover the iliac shaft. The iliacus internus originates on the inner surface of the ilium, ...
... externus on the iliac shaft are isolated from each other by a thin dorsal crista, which is moderately declined medially, part of the iliacus externus extends dorsally such that both muscles meet and completely cover the iliac shaft. The iliacus internus originates on the inner surface of the ilium, ...
MariebThe AppendicularSkeleton
... sacroiliac joint. Alae - winglike portions of the ilia. Iliac crest – upper edge of alae that ends anteriorly in the anterior superior iliac spine & posteriorly in the posterior superior iliac spine w/ small inferior spines located below these. ...
... sacroiliac joint. Alae - winglike portions of the ilia. Iliac crest – upper edge of alae that ends anteriorly in the anterior superior iliac spine & posteriorly in the posterior superior iliac spine w/ small inferior spines located below these. ...
Arthrography and Myelography
... indicates probable irritation within the spinal canal, which can be aggravated by the contrast medium. •Arachnoiditis (inflammation of the arachnoid membrane): Myelography is contraindicated in the case of arachnoiditis because the contrast medium may increase the severity of the inflammation. •Incr ...
... indicates probable irritation within the spinal canal, which can be aggravated by the contrast medium. •Arachnoiditis (inflammation of the arachnoid membrane): Myelography is contraindicated in the case of arachnoiditis because the contrast medium may increase the severity of the inflammation. •Incr ...
üst ekstremi̇te kiriklari
... 2. Should be able to explain the term of stability of pelvis fractures and also classify the pelvic fractures by stability 3. Should be able to tell the X-rays to be investigated for pelvis fractures and also evaluate X-rays 4. Should be able to list emergency attempts for haemodynamic instability 5 ...
... 2. Should be able to explain the term of stability of pelvis fractures and also classify the pelvic fractures by stability 3. Should be able to tell the X-rays to be investigated for pelvis fractures and also evaluate X-rays 4. Should be able to list emergency attempts for haemodynamic instability 5 ...
. Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
... through the elbow's center locus of rotation; thus, little change is seen in this ligament's uniform length from 0° to 120° offlexion. The three fiber groups functionally are anterior, middle, and posterior (8). The middle fibers are taut through a full range of motion while the anterior fibers are ...
... through the elbow's center locus of rotation; thus, little change is seen in this ligament's uniform length from 0° to 120° offlexion. The three fiber groups functionally are anterior, middle, and posterior (8). The middle fibers are taut through a full range of motion while the anterior fibers are ...
THE SKIN - Aromalyne
... provide large areas of bone to which the muscles of the arm, back and chest are attached. The shoulder joint is held in position by these muscles. The scapula is able to move by sliding over the ribs. The function of the clavicle is to support the shoulder joint. ...
... provide large areas of bone to which the muscles of the arm, back and chest are attached. The shoulder joint is held in position by these muscles. The scapula is able to move by sliding over the ribs. The function of the clavicle is to support the shoulder joint. ...
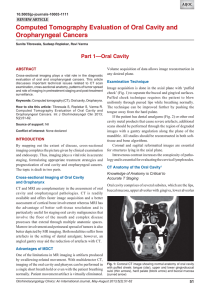
Computed Tomography Evaluation of Oral Cavity
... cheek’ (Fig. 1) to separate the buccal and gingival surfaces. Puffed cheek technique requires the patient to blow uniformly through pursed lips while breathing normally. The technique can be improved further by pushing the tongue away from the hard palate. If the patient has dental amalgams (Fig. 2) ...
... cheek’ (Fig. 1) to separate the buccal and gingival surfaces. Puffed cheek technique requires the patient to blow uniformly through pursed lips while breathing normally. The technique can be improved further by pushing the tongue away from the hard palate. If the patient has dental amalgams (Fig. 2) ...
The Reproductive System
... Secrete part of seminal fluid Located on posterior surface of bladder, lateral to ampulla ductus deferentis ...
... Secrete part of seminal fluid Located on posterior surface of bladder, lateral to ampulla ductus deferentis ...
Thigh and Knee
... Trace the posterior cutaneous nerve of the calf (the medial sural cutaneous nerve) proximally to its origin from the tibial nerve, because the contents of the fossa can be dissected accurately and safely once this nerve is located. Trace the tibial nerve distally and expose its branches to the heads ...
... Trace the posterior cutaneous nerve of the calf (the medial sural cutaneous nerve) proximally to its origin from the tibial nerve, because the contents of the fossa can be dissected accurately and safely once this nerve is located. Trace the tibial nerve distally and expose its branches to the heads ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.