124 - Library of 19th Century Science
... preserved and increase in development, as during this forward movement they form a In the same way those right and a left centre for the reception of outward stimuli. of the radially-arranged stems of the Polyclada that are parallel to the longitudinal body-axis, and mark out right and left, are mor ...
... preserved and increase in development, as during this forward movement they form a In the same way those right and a left centre for the reception of outward stimuli. of the radially-arranged stems of the Polyclada that are parallel to the longitudinal body-axis, and mark out right and left, are mor ...
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb
... • Pelvic girdle - bony articulation of the lower limb • Arm - upper aspect of upper limb (versus forearm) • Leg - lower portion of the lower limb (versus thigh) ...
... • Pelvic girdle - bony articulation of the lower limb • Arm - upper aspect of upper limb (versus forearm) • Leg - lower portion of the lower limb (versus thigh) ...
Body Organization and
... 4. Is the following sentence true or false? An organ is made up of just one kind of tissue. 5. Circle the letter of an example of an organ system. a. heart b. circulatory system c. blood vessels 6. Draw a line from each term to its meaning. Term ...
... 4. Is the following sentence true or false? An organ is made up of just one kind of tissue. 5. Circle the letter of an example of an organ system. a. heart b. circulatory system c. blood vessels 6. Draw a line from each term to its meaning. Term ...
Chapters 12-13 Practice Quiz/Questions
... 24) Ventral spinal cord roots contain ________ fibers, while the dorsal roots contain ...
... 24) Ventral spinal cord roots contain ________ fibers, while the dorsal roots contain ...
Animilia - Paxon Biology
... - Move rapidly by jet propulsion using their siphon/ - Closed circulatory system with two types of hearts: - Arterial heart: pumps blood throughout the body. - Systematic hearts: receive blood from the body and pump it to the gills. - May have an external shell (nautilus), internal shell (squid and ...
... - Move rapidly by jet propulsion using their siphon/ - Closed circulatory system with two types of hearts: - Arterial heart: pumps blood throughout the body. - Systematic hearts: receive blood from the body and pump it to the gills. - May have an external shell (nautilus), internal shell (squid and ...
Horizontal Disposition of the Peritoneum
... In males it is close cavity but in females there is a communication with the exterior through uterine tubes, the uterus and the vagina. ...
... In males it is close cavity but in females there is a communication with the exterior through uterine tubes, the uterus and the vagina. ...
Grip and Pinch
... A low median nerve paralysis affects the thenar muscles of the thumb and the lateral 2 lumbricals. The thumb loses motion and coordination, which will hinder the formation of opposition pinch and have a deleterous affect on grasp. Types of pinch 1. Tip pinch 2. Pulp pinch 3. Key pinch 4. Chuck or tr ...
... A low median nerve paralysis affects the thenar muscles of the thumb and the lateral 2 lumbricals. The thumb loses motion and coordination, which will hinder the formation of opposition pinch and have a deleterous affect on grasp. Types of pinch 1. Tip pinch 2. Pulp pinch 3. Key pinch 4. Chuck or tr ...
Shin Splints - Therapy In Motion
... The lower leg consists of one large bone called the Tibia and a small bone on the outside of the leg known as the Fibula. The tibia is the large bone in the front of the lower leg and is the common area of pain from individuals suffering from shin splints. Muscles of the lower leg affected by shin s ...
... The lower leg consists of one large bone called the Tibia and a small bone on the outside of the leg known as the Fibula. The tibia is the large bone in the front of the lower leg and is the common area of pain from individuals suffering from shin splints. Muscles of the lower leg affected by shin s ...
D2-1 UNIT 2. DISSECTION: SUPERFICIAL MUSCLES OF THE
... plates 174, 177; G plate 4.31). Pass your hand deep to the inferior and lateral border of the muscle. You are separating the trapezius from other muscles. Starting inferiorly, cut the muscle from its origin all the way to the external occipital protuberance. Now detach the upper fibers of the trapez ...
... plates 174, 177; G plate 4.31). Pass your hand deep to the inferior and lateral border of the muscle. You are separating the trapezius from other muscles. Starting inferiorly, cut the muscle from its origin all the way to the external occipital protuberance. Now detach the upper fibers of the trapez ...
Pelvic Floor DisorDers DvD-roM
... View clear, detailed and accurate 3D modeling of the key anatomy of the pelvis and pelvic floor. Choose from highly detailed and labeled views of the pelvis, muscles of the pelvic floor, reproductive system, urinary and digestive systems, bone regions, surface markings, neurology including the lumba ...
... View clear, detailed and accurate 3D modeling of the key anatomy of the pelvis and pelvic floor. Choose from highly detailed and labeled views of the pelvis, muscles of the pelvic floor, reproductive system, urinary and digestive systems, bone regions, surface markings, neurology including the lumba ...
Document
... anterior, and subclavius • Posterior: latissimus dorsi, trapezius muscles, levator scapulae, and rhomboids • These muscles are involved with the movements of the scapula including elevation, depression, rotation, and lateral and medial movements ...
... anterior, and subclavius • Posterior: latissimus dorsi, trapezius muscles, levator scapulae, and rhomboids • These muscles are involved with the movements of the scapula including elevation, depression, rotation, and lateral and medial movements ...
Phylum Annelida - University of Evansville
... within blood vessels that run the length of the body and branch to every segment • Several hearts (5 in earthworms) are used to pump blood through the closed circuit ...
... within blood vessels that run the length of the body and branch to every segment • Several hearts (5 in earthworms) are used to pump blood through the closed circuit ...
Document
... 1. The muscles of the anterior abdominal wall flex and rotate the vertebral column. 2. Contraction of the abdominal muscles when the vertebral column is fixed decreases the volume of the abdominal and thoracic cavities and increases the intra-abdominal pressure which aids in defecation, urination an ...
... 1. The muscles of the anterior abdominal wall flex and rotate the vertebral column. 2. Contraction of the abdominal muscles when the vertebral column is fixed decreases the volume of the abdominal and thoracic cavities and increases the intra-abdominal pressure which aids in defecation, urination an ...
Joint - Fisiokinesiterapia
... • Attaches upper extremity to the body • Scapula and clavicle • Clavicle attaches medially to the sternum and laterally to the scapula • Scapula articulates with the humerus ...
... • Attaches upper extremity to the body • Scapula and clavicle • Clavicle attaches medially to the sternum and laterally to the scapula • Scapula articulates with the humerus ...
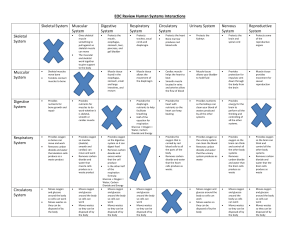
EOC Review Human Systems Interactions Skeletal System Muscular
... Muscle tissue found in the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and rectum ...
... Muscle tissue found in the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and rectum ...
Axial Skeleton - El Camino College
... 9. The Orbits are sockets for eye balls. Each orbit is formed of 7 bones. Superior – frontal; lateral – zygomatic; inferior – zygomatic, maxilla, palatine; medial – lacrimal, sphenoid, ethmoid. Optic canal is part of ethmoid. Fig 7.9. The lacrimal glands are lodged superolateral to eye balls. Fig 15 ...
... 9. The Orbits are sockets for eye balls. Each orbit is formed of 7 bones. Superior – frontal; lateral – zygomatic; inferior – zygomatic, maxilla, palatine; medial – lacrimal, sphenoid, ethmoid. Optic canal is part of ethmoid. Fig 7.9. The lacrimal glands are lodged superolateral to eye balls. Fig 15 ...
The Pharnyx and Larynx - California Health Information Association
... b. Vocal cords or voice box, which is located at the top of the trachea. It is composed of ligaments that vibrate to produce sound as air passes over them. The more air passes over them, the louder the sound that is produced. Change in pitch occurs through the use of small muscles that pull on the v ...
... b. Vocal cords or voice box, which is located at the top of the trachea. It is composed of ligaments that vibrate to produce sound as air passes over them. The more air passes over them, the louder the sound that is produced. Change in pitch occurs through the use of small muscles that pull on the v ...
The_Thigh_and_Hip_notes - ProvidencePanthersSportsMedicine
... The thigh is continually exposed to traumatic injuries; contusions and strains occur most frequently. Because of its bony, ligamentous, and muscular arrangements, the hip joint is considered by many to be the strongest articulation in the body. Though seldom injured, it is subject to muscular strain ...
... The thigh is continually exposed to traumatic injuries; contusions and strains occur most frequently. Because of its bony, ligamentous, and muscular arrangements, the hip joint is considered by many to be the strongest articulation in the body. Though seldom injured, it is subject to muscular strain ...
PP 6 - FA Joints_Pal_ROM - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Heads of the Metatarsals • Metatarsals • Navicular Tuberosity • Styloid process of fifth metatarsal • Sinus Tarsi - soft tissue depression just anterior to the lateral malleolus. • Medial and Lateral Malleoli • Head of the Talus • Calcaneous ...
... • Heads of the Metatarsals • Metatarsals • Navicular Tuberosity • Styloid process of fifth metatarsal • Sinus Tarsi - soft tissue depression just anterior to the lateral malleolus. • Medial and Lateral Malleoli • Head of the Talus • Calcaneous ...
Lec
... 3- The trachea, that lies ventral to the esophagus and is supported by partially ossified rings. In the thorax, it divides into two bronchi, to the two lungs. 4- The syrinx, or vocal organ, is formed by the posterior end of the trachea and the adjacent portions of the two bronchi 5- The air-sacs, wh ...
... 3- The trachea, that lies ventral to the esophagus and is supported by partially ossified rings. In the thorax, it divides into two bronchi, to the two lungs. 4- The syrinx, or vocal organ, is formed by the posterior end of the trachea and the adjacent portions of the two bronchi 5- The air-sacs, wh ...
Back_joints
... • Concentric lamellae of fibrocartilage – Fibers run at an angle – Fibers in one lamellae are perpendicular to fibers in the next lamellae – Lamellae are thinner and less numerous posteriorly than anteriorly or laterally ...
... • Concentric lamellae of fibrocartilage – Fibers run at an angle – Fibers in one lamellae are perpendicular to fibers in the next lamellae – Lamellae are thinner and less numerous posteriorly than anteriorly or laterally ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... and largest bone of the arm, extending from the elbow to the shoulder. • Ulna (UL-nuh). Inner and larger bone of the forearm (lower arm), attached to the wrist and located on the side of the little finger. • Radius (RAY-dee-us). Smaller bone in the forearm (lower arem) on the same side as the thumb. ...
... and largest bone of the arm, extending from the elbow to the shoulder. • Ulna (UL-nuh). Inner and larger bone of the forearm (lower arm), attached to the wrist and located on the side of the little finger. • Radius (RAY-dee-us). Smaller bone in the forearm (lower arem) on the same side as the thumb. ...
The Skeleton - Mr. Haan`s Science
... 4) Breaks outward b/c of curve 5) Secures scapula and muscles of arm, chest, and ...
... 4) Breaks outward b/c of curve 5) Secures scapula and muscles of arm, chest, and ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.