nervous system worksheet
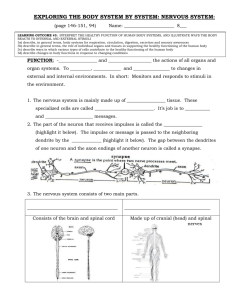
... organ systems. To _________, ____________ and ________________ to changes in external and internal environments. In short: Monitors and responds to stimuli in the environment. 1. The nervous system is mainly made up of _________________ tissue. These specialized cells are called ____________________ ...
... organ systems. To _________, ____________ and ________________ to changes in external and internal environments. In short: Monitors and responds to stimuli in the environment. 1. The nervous system is mainly made up of _________________ tissue. These specialized cells are called ____________________ ...
The Supraclavicularis Proprius Muscle
... 10% formalin fixed, we found it in one adult Caucasian male cadaver. In our experience, the frequency of occurrence of the supraclavicularis proprius muscle would be 0.64%. • This abnormal muscle consists of an anterior tendon inserting into the sternal aspect of the clavicle, lateral to the clavicu ...
... 10% formalin fixed, we found it in one adult Caucasian male cadaver. In our experience, the frequency of occurrence of the supraclavicularis proprius muscle would be 0.64%. • This abnormal muscle consists of an anterior tendon inserting into the sternal aspect of the clavicle, lateral to the clavicu ...
HISTOLOGY OF MUSCLES
... 6. Cells within each chain bifurcate or branch giving an appearance of syncytial network. 7. Unique character of cardiac muscle is presence of darkly stained transverse lines that cross the chain of cardiac cells, these bands often follow an irregular step like course and are known as Intercalated d ...
... 6. Cells within each chain bifurcate or branch giving an appearance of syncytial network. 7. Unique character of cardiac muscle is presence of darkly stained transverse lines that cross the chain of cardiac cells, these bands often follow an irregular step like course and are known as Intercalated d ...
skeletal system
... false ribs. Instead of attaching directly to the sternum, they all attach to the lowest true rib. The last two pairs of ribs are called floating ribs and attach only to the spine. ...
... false ribs. Instead of attaching directly to the sternum, they all attach to the lowest true rib. The last two pairs of ribs are called floating ribs and attach only to the spine. ...
Bones of Upper Limb
... Bones of Upper Limb • Should girdle clavicle,scapula • Bones of free upper limb – Humerus – Radius and ulna – Carpal bones, metacarpals and phalanges ...
... Bones of Upper Limb • Should girdle clavicle,scapula • Bones of free upper limb – Humerus – Radius and ulna – Carpal bones, metacarpals and phalanges ...
Body Systems
... Right Atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae. The superior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, arm and chest regions of the body to the right atrium. The inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body regions ...
... Right Atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae. The superior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, arm and chest regions of the body to the right atrium. The inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body regions ...
Mnstrviola`s Anatomy Practice Test- v 2.0
... 16. The ___________ valve allows materials to move from the ileum to the large intestine, but not back. 17. Mucus is produced by __________ cells. 18. The three longitudal strips of muscle that are on the outer walls of the colon are called ___________. 19. The large intestine is the main site of __ ...
... 16. The ___________ valve allows materials to move from the ileum to the large intestine, but not back. 17. Mucus is produced by __________ cells. 18. The three longitudal strips of muscle that are on the outer walls of the colon are called ___________. 19. The large intestine is the main site of __ ...
Anatomytest2012v24real
... 16. The ___________ valve allows materials to move from the ileum to the large intestine, but not back. 17. Mucus is produced by __________ cells. 18. The three longitudal strips of muscle that are on the outer walls of the colon are called ___________. 19. The large intestine is the main site of __ ...
... 16. The ___________ valve allows materials to move from the ileum to the large intestine, but not back. 17. Mucus is produced by __________ cells. 18. The three longitudal strips of muscle that are on the outer walls of the colon are called ___________. 19. The large intestine is the main site of __ ...
Sexual/asexual reproduction - Science
... • The average three-year-old has two pints of blood in their body; the average adult at least five times more! • A "heartbeat" is really the sound of the valves in the heart closing as they push blood through its chambers. Menu ...
... • The average three-year-old has two pints of blood in their body; the average adult at least five times more! • A "heartbeat" is really the sound of the valves in the heart closing as they push blood through its chambers. Menu ...
Joint Move Type
... returns joint from Flexion to Anatomical Position Extension beyond the Anatomical Position ...
... returns joint from Flexion to Anatomical Position Extension beyond the Anatomical Position ...
Posterior Triangle Dr. Hany Sonpo
... Beginning: Appear in the triangle at the lateral border of the scalnenus anterior between it and scalenus medius. Termination: it continues as the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. Relations: Posterior: related to the 8th cervical nerve which unit the 1st thoracic to form the l ...
... Beginning: Appear in the triangle at the lateral border of the scalnenus anterior between it and scalenus medius. Termination: it continues as the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. Relations: Posterior: related to the 8th cervical nerve which unit the 1st thoracic to form the l ...
(F).
... Why do we humans grow into the shape we do? Why do we stand rather than creep like animals? What enables us to move our heads, hands, and legs, and all the other parts of the body? The answer is the skeleton, the human framework. The skeleton is all the bones in our body put together. With it, all o ...
... Why do we humans grow into the shape we do? Why do we stand rather than creep like animals? What enables us to move our heads, hands, and legs, and all the other parts of the body? The answer is the skeleton, the human framework. The skeleton is all the bones in our body put together. With it, all o ...
Notes Key
... bloodstream to tell your kidneys to hold onto water. When you have too much water, the pituitary stops releasing the hormone, so that you can excrete the excess water (pee…) 8. Explain how a reflex works. What two systems work together to respond when you touch something that causes you pain, such a ...
... bloodstream to tell your kidneys to hold onto water. When you have too much water, the pituitary stops releasing the hormone, so that you can excrete the excess water (pee…) 8. Explain how a reflex works. What two systems work together to respond when you touch something that causes you pain, such a ...
Animals PPT
... – Fight-or-flight response gets body ready for greater activity • Automatic response (controlled by hormones and nervous system) ...
... – Fight-or-flight response gets body ready for greater activity • Automatic response (controlled by hormones and nervous system) ...
4-Thoracolumbar Spine-2015
... oblique muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall. • In the lumbar region: • Flexion is produced by the rectus abdominis and the psoas muscles. • Extension is produced by the postvertebral muscles. • Lateral flexion is produced by the postvertebral muscles, the quadratus lumborum, and the oblique ...
... oblique muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall. • In the lumbar region: • Flexion is produced by the rectus abdominis and the psoas muscles. • Extension is produced by the postvertebral muscles. • Lateral flexion is produced by the postvertebral muscles, the quadratus lumborum, and the oblique ...
2.Humangasexchange1
... As deoxygenated blood from the body tissues flows through the network of capillaries surrounding each alveolus, oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveolus; oxygenated blood travels from the lungs to the left of the heart for delivery to the body tissu ...
... As deoxygenated blood from the body tissues flows through the network of capillaries surrounding each alveolus, oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveolus; oxygenated blood travels from the lungs to the left of the heart for delivery to the body tissu ...
small intestine
... You have already seen how the esophagus leads from the pharynx through the neck region. Using a probe, trace follow the esophagus to thestomach. Identify the small intestine and large intestine. Find the posterior part of the large intestine called the rectum and observe that it leads to the anus. ...
... You have already seen how the esophagus leads from the pharynx through the neck region. Using a probe, trace follow the esophagus to thestomach. Identify the small intestine and large intestine. Find the posterior part of the large intestine called the rectum and observe that it leads to the anus. ...
ORTHOPAEDIC SCREWS
... Transverse (also called horizontal) planes divide the body into upper and lower parts. ...
... Transverse (also called horizontal) planes divide the body into upper and lower parts. ...
ornithischian pars preacetabularis has swung medially, fused with
... In both great groups of dinosaurs and in birds are found anterior prolongations of the ilium not present in primitive reptiles. The posession of a preacetabular part of the ilium is often used as a diagnostic character of the Dinosauria, but, when considered in connection with the related musculatur ...
... In both great groups of dinosaurs and in birds are found anterior prolongations of the ilium not present in primitive reptiles. The posession of a preacetabular part of the ilium is often used as a diagnostic character of the Dinosauria, but, when considered in connection with the related musculatur ...
My bone/Muscle project
... tube that runs from the mouth to the anus plus a few other organs that produce or store digestive chemicals. The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the chemical. After being chewed and swallowed, the food enters the esophagus. The esoph ...
... tube that runs from the mouth to the anus plus a few other organs that produce or store digestive chemicals. The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the chemical. After being chewed and swallowed, the food enters the esophagus. The esoph ...
Morphologically description of body shape
... 6. Metamerism , the body wall shows metameric segmentation , being made of blocks of muscles called ( myotomes or myomeres ), there are about 62 of these on each side . These myotomes are < shaped. ...
... 6. Metamerism , the body wall shows metameric segmentation , being made of blocks of muscles called ( myotomes or myomeres ), there are about 62 of these on each side . These myotomes are < shaped. ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Pectoral girdle is highly mobile, stabilized primarily by muscles Pelvic girdle is more massive, stronger, and less mobile ...
... Pectoral girdle is highly mobile, stabilized primarily by muscles Pelvic girdle is more massive, stronger, and less mobile ...
Pelvis & Perineum - Indiana University
... Postoperatively, the patient did quite well. Motor strength on the right was only slightly less than that on the left, in spite of the fact that the C6 nerve was sacrificed. The patient's arm pain was improved. At time of discharge, the patient was afebrile and vital signs were stable. She had some ...
... Postoperatively, the patient did quite well. Motor strength on the right was only slightly less than that on the left, in spite of the fact that the C6 nerve was sacrificed. The patient's arm pain was improved. At time of discharge, the patient was afebrile and vital signs were stable. She had some ...
Presentation Package
... • Exchange of Air – The amount and movement of air and expired gases in and out of the lungs are controlled by expansion and recoil of the lungs. ...
... • Exchange of Air – The amount and movement of air and expired gases in and out of the lungs are controlled by expansion and recoil of the lungs. ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Pectoral girdle is highly mobile, stabilized primarily by muscles Pelvic girdle is more massive, stronger, and less mobile ...
... Pectoral girdle is highly mobile, stabilized primarily by muscles Pelvic girdle is more massive, stronger, and less mobile ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.























