ULNA BONE:
... 2. Has hook-like projection (trochlear notch), concavity of which faces forward. 3. Lower end has small head. 4. Thin sharp crest like interosseous border of shaft lies laterally. 5. Styloid process projects downwards from posteriomedial aspect of head. ...
... 2. Has hook-like projection (trochlear notch), concavity of which faces forward. 3. Lower end has small head. 4. Thin sharp crest like interosseous border of shaft lies laterally. 5. Styloid process projects downwards from posteriomedial aspect of head. ...
Anatomy 2011.2
... Run just inside the tips of transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae, on surface of psoas Over SI joint lying on bifurcation of common iliac To ischial spine and thence into bladder at VUJ Enters abdo at T12, Left of midline, Bifurcation at L4 just below umbilici=us ...
... Run just inside the tips of transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae, on surface of psoas Over SI joint lying on bifurcation of common iliac To ischial spine and thence into bladder at VUJ Enters abdo at T12, Left of midline, Bifurcation at L4 just below umbilici=us ...
The Musculi Suboccipitales of the Formosan Monkey
... M. rectus capitis posterior minor, but during its course branches are given off to these muscles. On the other hand, the branch of the A. vertebralis which emerges from the space formed between the base of the skull and the first transverse process, in other words, by the M. obliquus capitis superio ...
... M. rectus capitis posterior minor, but during its course branches are given off to these muscles. On the other hand, the branch of the A. vertebralis which emerges from the space formed between the base of the skull and the first transverse process, in other words, by the M. obliquus capitis superio ...
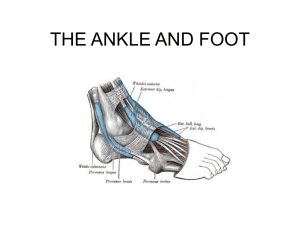
ankle_muscle
... • Insertion: top of the distal phalanx of the great toe • Note: passes anterior • Actions: – Extension of big toe – Dorsiflexion – Weak inversion of the foot Anterior ...
... • Insertion: top of the distal phalanx of the great toe • Note: passes anterior • Actions: – Extension of big toe – Dorsiflexion – Weak inversion of the foot Anterior ...
Body Systems
... • What is the function of arteries? (pg 526) • What is the function of veins (pg 526) • What is the function of capillaries? (pg 526) ...
... • What is the function of arteries? (pg 526) • What is the function of veins (pg 526) • What is the function of capillaries? (pg 526) ...
Earthworm Dissection
... storing sperm made before being discharged from the body. In segments 9 and 10 you may see ...
... storing sperm made before being discharged from the body. In segments 9 and 10 you may see ...
Nervous System: Cranial nerves
... function of the cranial nerves 2. List and define disorders of the nervous tissue 3. Define nerve and associated definitions 4. Be able to identify and know functions of structures shown on sagittal section of the central nervous system ...
... function of the cranial nerves 2. List and define disorders of the nervous tissue 3. Define nerve and associated definitions 4. Be able to identify and know functions of structures shown on sagittal section of the central nervous system ...
Intramuscular Tenderness and Muscle Fiber Orientation
... Ten of each beef round, top untrimmed (IMPS #168; NAMP, 2007), beef round, outside round (IMPS #171B; NAMP, 2007), and beef round, eye of round (IMPS #171C; NAMP, 2007) were purchased as USDA Choice boxed beef subprimals and aged for 14 days from boxed date. The BF, ST, SM, and AF were fabricated fr ...
... Ten of each beef round, top untrimmed (IMPS #168; NAMP, 2007), beef round, outside round (IMPS #171B; NAMP, 2007), and beef round, eye of round (IMPS #171C; NAMP, 2007) were purchased as USDA Choice boxed beef subprimals and aged for 14 days from boxed date. The BF, ST, SM, and AF were fabricated fr ...
Anatomy of thoracic wall
... Intercostal nerves 4 to 6 are "typical” in that they supply only the thoracic wall and its associated muscles (intercostal, subcostal, serratus posterior superior, and transversus thoracis). Each passes inferior to the neck of the corresponding rib and enters the costal groove. At the anterior end o ...
... Intercostal nerves 4 to 6 are "typical” in that they supply only the thoracic wall and its associated muscles (intercostal, subcostal, serratus posterior superior, and transversus thoracis). Each passes inferior to the neck of the corresponding rib and enters the costal groove. At the anterior end o ...
A rehabilitation programme after C1
... 4) The ligamentum nuchae across the posterior surface of the spinous canal and between the arches of neighbouring ...
... 4) The ligamentum nuchae across the posterior surface of the spinous canal and between the arches of neighbouring ...
PALMAR APONEUROSIS
... Deep fascia of wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis ...
... Deep fascia of wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... • Fovea Capitas- attachment of a small ligament that secures the bone into the socket – looks like a small pit on the top center of the head • Neck –weakest area prone to fracture (broken hip) ...
... • Fovea Capitas- attachment of a small ligament that secures the bone into the socket – looks like a small pit on the top center of the head • Neck –weakest area prone to fracture (broken hip) ...
43-Hip Joint
... and reflex spasm of muscles) Deformity i.e. flexion, adduction & external rotation (due to muscle spasm & later on muscle contractures) ...
... and reflex spasm of muscles) Deformity i.e. flexion, adduction & external rotation (due to muscle spasm & later on muscle contractures) ...
Kinematics analysis of children gait carrying knapsack with different
... The behavior of the angle of the hip, characterized by the maximum extension in the contact of the opposite foot and for a maximum flexion in the terminal swinging phase according to Sutherland et al (1998), presented a larger flexion degree, a significant statistical difference (p <0,05),when compa ...
... The behavior of the angle of the hip, characterized by the maximum extension in the contact of the opposite foot and for a maximum flexion in the terminal swinging phase according to Sutherland et al (1998), presented a larger flexion degree, a significant statistical difference (p <0,05),when compa ...
inferior transverse axis
... – The coccyx inferiorly – Two pelvic( innominate bones )through the “L” shaped sacroiliac articulation ...
... – The coccyx inferiorly – Two pelvic( innominate bones )through the “L” shaped sacroiliac articulation ...
Biomechanical Principles
... Mechanical advantage—the ratio of the movement arm through which an applied force acts to that through which a resistive force acts (e.g., a pliers with 9” handles with 1.5” jaws has a mechanical advantage of 9/1.5 = 6; a 10 pound squeeze on the handle generates a 6 x 10 pound = 60 pound squeeze at ...
... Mechanical advantage—the ratio of the movement arm through which an applied force acts to that through which a resistive force acts (e.g., a pliers with 9” handles with 1.5” jaws has a mechanical advantage of 9/1.5 = 6; a 10 pound squeeze on the handle generates a 6 x 10 pound = 60 pound squeeze at ...
Diapositiva 1
... Extraction: pulling or stripping out or off a portion of body part the use of force • 3rd character D • Includes: c-sections, forceps and internal version Delivery: assisting the passage of POC from the genital canal • 3rd character is E • Always an external approach • No device or qualifier ...
... Extraction: pulling or stripping out or off a portion of body part the use of force • 3rd character D • Includes: c-sections, forceps and internal version Delivery: assisting the passage of POC from the genital canal • 3rd character is E • Always an external approach • No device or qualifier ...
Tibial nerve
... The posterior tibial artery Branches in the leg: 1- peroneal artery : a-muscular bNutrient branch to the fibula. c- Perforating artery dThe peroneal artery ends by giving posterior lateral malleollar ...
... The posterior tibial artery Branches in the leg: 1- peroneal artery : a-muscular bNutrient branch to the fibula. c- Perforating artery dThe peroneal artery ends by giving posterior lateral malleollar ...
Labs 7, 8, 9 Skeletal tissue
... C. Be able to identify and describe the location of the following bones and markings on articulated skeletons and disarticulated bones. Be able to tell the left from the right bone where indicated by an asterisk (*) and know how many of each bone are found in the body. ...
... C. Be able to identify and describe the location of the following bones and markings on articulated skeletons and disarticulated bones. Be able to tell the left from the right bone where indicated by an asterisk (*) and know how many of each bone are found in the body. ...
- An International Journal of Experimental and Clinical
... O’Neill and Folan-Curran reported the direct connection of muscle fibers between the sternalis and pectoralis major muscles.13 Additionally, Kida et al. reported the partial absence of the sternocostal portion of the pectoralis major muscle.26 They suggested that the close relation of both muscles m ...
... O’Neill and Folan-Curran reported the direct connection of muscle fibers between the sternalis and pectoralis major muscles.13 Additionally, Kida et al. reported the partial absence of the sternocostal portion of the pectoralis major muscle.26 They suggested that the close relation of both muscles m ...
Modeling Control of Eye Orientation in three Dimensions. I. Role of
... Human Visual System…. • The brain sends a neuronal control signal to each muscle to direct the muscle to perform its work. • A neuronal control signal is anatomically implemented as a neuronal discharge that is sent through a nerve to a designated muscle from the brain. • The neuronal control signa ...
... Human Visual System…. • The brain sends a neuronal control signal to each muscle to direct the muscle to perform its work. • A neuronal control signal is anatomically implemented as a neuronal discharge that is sent through a nerve to a designated muscle from the brain. • The neuronal control signa ...
respiratory
... 1 This is the toxic gas that is released when we breathe out? (6, 7) 2 When these contract and relax they move the rib-cage out and in? (3, 7) 3 The name for the minute air sacs that are covered with blood vessels? (7) 4 The area of the body where the lungs are found? (6) 5 A protective structure su ...
... 1 This is the toxic gas that is released when we breathe out? (6, 7) 2 When these contract and relax they move the rib-cage out and in? (3, 7) 3 The name for the minute air sacs that are covered with blood vessels? (7) 4 The area of the body where the lungs are found? (6) 5 A protective structure su ...
animal form and function
... filaments draw respiratory water currents into the mantle cavity on either side. The two currents filter through the ctenidial filaments, meet dorsally, and pass backward as an exhalent stream out of the mantle cavity. Gland cells on the filaments secrete mucus, and particles brought into the mantle ...
... filaments draw respiratory water currents into the mantle cavity on either side. The two currents filter through the ctenidial filaments, meet dorsally, and pass backward as an exhalent stream out of the mantle cavity. Gland cells on the filaments secrete mucus, and particles brought into the mantle ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.