31-Aorta& IVC
... upward and medially along the medial margin of the deep inguinal ring and enters the rectus sheath behind the rectus abdominis muscle. The deep circumflex iliac artery arises close to the inferior epigastric artery. It ascends laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine and iliac crest supplying ...
... upward and medially along the medial margin of the deep inguinal ring and enters the rectus sheath behind the rectus abdominis muscle. The deep circumflex iliac artery arises close to the inferior epigastric artery. It ascends laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine and iliac crest supplying ...
HISTOLOGY
... Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and diffusion. The ...
... Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, and diffusion. The ...
1 Anatomy – Thorax
... Vagus nerve → right and left vagus → right or left recurrent laryngeal nerves Oesophagus, Thoracic duct (duck between 2 gooses – ayzGOUS and oesophaGOUS) Anterior mediastinum potential space between pericardium and sternum Contents - Thymus, Sternopericardial ligaments, Lymph nodes, Branches of the ...
... Vagus nerve → right and left vagus → right or left recurrent laryngeal nerves Oesophagus, Thoracic duct (duck between 2 gooses – ayzGOUS and oesophaGOUS) Anterior mediastinum potential space between pericardium and sternum Contents - Thymus, Sternopericardial ligaments, Lymph nodes, Branches of the ...
LECTURE 17 Arthropods I Phylum Arthropoda (arthros – jointed
... 4. One set of vertical muscles attach to the dorsal and ventral sides of the thorax. These vertical muscles force the wings up by pulling down on the top of the thorax (tergum). 5. The wings are forced back down by the relaxation of these vertical muscles. a. A second set of longitudinal muscles con ...
... 4. One set of vertical muscles attach to the dorsal and ventral sides of the thorax. These vertical muscles force the wings up by pulling down on the top of the thorax (tergum). 5. The wings are forced back down by the relaxation of these vertical muscles. a. A second set of longitudinal muscles con ...
Transcripts/1_29_09_8
... IX. Muscular Triangle Contents [S27,28] a. Named because of the strap muscles/infrahyoid muscles. b. [S29] The lower parts of the anterior jugular veins are in this triangle. These two veins are united in the midline above the manubrium by a jugular venous arch. The anterior jugular vein passes late ...
... IX. Muscular Triangle Contents [S27,28] a. Named because of the strap muscles/infrahyoid muscles. b. [S29] The lower parts of the anterior jugular veins are in this triangle. These two veins are united in the midline above the manubrium by a jugular venous arch. The anterior jugular vein passes late ...
Introduction Shoulder girdle is a complex structure
... Scapula is a triangular flat bone that lies on the posterior – lateral surface of the thorax between second and seventh rib. It is important to remember that it is not parallel to frontal plane. The scapular body forms 30–45 degree angle with frontal plane. Anatomically it has three borders – medial ...
... Scapula is a triangular flat bone that lies on the posterior – lateral surface of the thorax between second and seventh rib. It is important to remember that it is not parallel to frontal plane. The scapular body forms 30–45 degree angle with frontal plane. Anatomically it has three borders – medial ...
LOWER LIMB 2
... entrapment sites 15. Tibial nerve: origin, course in the popliteal fossa and the leg, topography, branches, area of innervation, signs of palsy, entrapment sites 16. Superficial and deep veins of the popliteal fossa and the leg: origin, course, topography, tributaries, perforating veins, area of dra ...
... entrapment sites 15. Tibial nerve: origin, course in the popliteal fossa and the leg, topography, branches, area of innervation, signs of palsy, entrapment sites 16. Superficial and deep veins of the popliteal fossa and the leg: origin, course, topography, tributaries, perforating veins, area of dra ...
Sprains and Strains and Fractures… Oh My
... - production blood cells/storage of ions/endocrine regulation ...
... - production blood cells/storage of ions/endocrine regulation ...
Word format
... find the bones. * E. Identify the bones of the posterior leg in a photograph. F. Compare the leg of the frog to the leg of a human. How are they different? Internal Anatomy 6. Still with the ventral side up and the head away from you, insert your scissors under the skin and cut along the mid-line to ...
... find the bones. * E. Identify the bones of the posterior leg in a photograph. F. Compare the leg of the frog to the leg of a human. How are they different? Internal Anatomy 6. Still with the ventral side up and the head away from you, insert your scissors under the skin and cut along the mid-line to ...
Lecture 3 – Treatment and Evaluation of the Pelvis ADductors à
... Two pelvic( innominate bones )through the “L” shaped sacroiliac articulation ...
... Two pelvic( innominate bones )through the “L” shaped sacroiliac articulation ...
Blocks at the Wrist
... Blocks at the Wrist Indication: Surgery of the hand, rescue blocks Position: The arm is placed with the palm facing up. ...
... Blocks at the Wrist Indication: Surgery of the hand, rescue blocks Position: The arm is placed with the palm facing up. ...
SO_Cyprus_med_14-15_urinarybladder_32
... - however can tolerate 500ml. of urine. • Location in Adult; when empty: entirely within lesser pelvis; when distended: expands into abdominal cavity • Location in child: even when empty in lesser pelvis +abdominal cavity ...
... - however can tolerate 500ml. of urine. • Location in Adult; when empty: entirely within lesser pelvis; when distended: expands into abdominal cavity • Location in child: even when empty in lesser pelvis +abdominal cavity ...
Dissection 14: Abdominopelvic Cavity
... abdominal muscles near the anterior superior internal and external oblique muscles to supply the skin of the suprapubic and inguinal regions and nervous supply to abdominal musculature. 5. Genitofemoral nerve (L1, L2): pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major and runs inferiorly on it deep to ...
... abdominal muscles near the anterior superior internal and external oblique muscles to supply the skin of the suprapubic and inguinal regions and nervous supply to abdominal musculature. 5. Genitofemoral nerve (L1, L2): pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major and runs inferiorly on it deep to ...
Answers to animal label me handouts
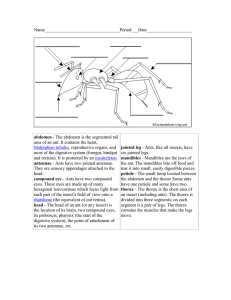
... simple eye - small, primitive organs that distinguish dark from light spiracles - a series of holes located along both sides of the abdomen; they are used for breathing thorax - the middle area of the cricket's body - where the legs and wings are attached walking legs - the four, short front legs th ...
... simple eye - small, primitive organs that distinguish dark from light spiracles - a series of holes located along both sides of the abdomen; they are used for breathing thorax - the middle area of the cricket's body - where the legs and wings are attached walking legs - the four, short front legs th ...
14 The Ankle Is A Bone: Fact Or Fiction?
... Ankle movement is accomplished by a combination of three bones and soft tissue structures that work together to produce a very stable joint. This stability is created by the anatomical arrangement of these bones, which form a carpenter’s mortiseand-tendon joint (see Fig. 14-1). A mortise is created ...
... Ankle movement is accomplished by a combination of three bones and soft tissue structures that work together to produce a very stable joint. This stability is created by the anatomical arrangement of these bones, which form a carpenter’s mortiseand-tendon joint (see Fig. 14-1). A mortise is created ...
Anatomy of Fat
... measures 1.5 to 2 cm in diameter and lies anatomically within the midline at the level of the superior iliac crests, midway between xiphoid and pubis. umbilicus is formed as a result of contraction of four fibrous cords. These consist of the obliterated left umbilical vein, which runs superiorly in ...
... measures 1.5 to 2 cm in diameter and lies anatomically within the midline at the level of the superior iliac crests, midway between xiphoid and pubis. umbilicus is formed as a result of contraction of four fibrous cords. These consist of the obliterated left umbilical vein, which runs superiorly in ...
Lysbilde 1 - Legeforeningen
... cancer based on anatomy and lymphatic spread. Werner Hohenberger The Japanese approach to colon cancer resections based on the vascular anatomy of the colon and rectosigmoid. Kenichi Sugihara Turnbull’s good results in view of today’s concept of mesocolon and the central tie. Defining surgical appro ...
... cancer based on anatomy and lymphatic spread. Werner Hohenberger The Japanese approach to colon cancer resections based on the vascular anatomy of the colon and rectosigmoid. Kenichi Sugihara Turnbull’s good results in view of today’s concept of mesocolon and the central tie. Defining surgical appro ...
Earthworms
... cuticle to provide anchoring points when the earthworm moves or burrows. Food is brought in by a muscular pharynx ...
... cuticle to provide anchoring points when the earthworm moves or burrows. Food is brought in by a muscular pharynx ...
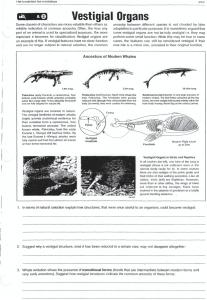
Vestigial Organs
... In all snakes (far left), one lobe of the lung is vestigial (there is not sufficient room in the narrow body cavity for it). In some snakes there are also vestiges of the pelvic girdle and hind limbs of their walking ancestors. Like all ratites, kiwis (left) are flightless. However, more than in oth ...
... In all snakes (far left), one lobe of the lung is vestigial (there is not sufficient room in the narrow body cavity for it). In some snakes there are also vestiges of the pelvic girdle and hind limbs of their walking ancestors. Like all ratites, kiwis (left) are flightless. However, more than in oth ...
nasal cavity
... the nasal cavity and to dribble outward through the nostrils. This is why you have a “runny” nose on a cold day. ...
... the nasal cavity and to dribble outward through the nostrils. This is why you have a “runny” nose on a cold day. ...
Respiratory system
... • The walls of the alveoli which are ONLY about one cell thick, which are the respiratory surface. • They are thin, moist, and are surrounded by several numbers of capillaries. • It is the site of gas exchange. ...
... • The walls of the alveoli which are ONLY about one cell thick, which are the respiratory surface. • They are thin, moist, and are surrounded by several numbers of capillaries. • It is the site of gas exchange. ...
Chapter 5
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Carefully read each statement. Choose the word or phrase that correctly completes the meaning and write the corresponding letter in the blank provided. 1. All substances are made from subatomic particles that form ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Carefully read each statement. Choose the word or phrase that correctly completes the meaning and write the corresponding letter in the blank provided. 1. All substances are made from subatomic particles that form ...
Palpebrae (Eyelids)
... The lens separates the internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments ...
... The lens separates the internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.