gcse pe easter revision 2016
... Power = Strength x Speed The ability to use two or more body parts together The time between the presentation of a stimulus and the onset of movement The ability to change the position of the body quickly and to control the movement of the whole body The ability to retain the centre of mass (gravity ...
... Power = Strength x Speed The ability to use two or more body parts together The time between the presentation of a stimulus and the onset of movement The ability to change the position of the body quickly and to control the movement of the whole body The ability to retain the centre of mass (gravity ...
PERITONEUM and TORSION of GUT TUBE
... Genitofemoral nerve (L1-2.): Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
... Genitofemoral nerve (L1-2.): Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
HEALTH SCIENCES 365
... pelvis; either the left pelvis rotates downward or the right pelvis rotates upward; (left lateral tilt); accomplished by left hip abduction, right hip adduction, and/or right lumbar lateral flexion Left Transverse Pelvic Rotation: in a horizontal plane of motion, rotation of the pelvis to the body’s ...
... pelvis; either the left pelvis rotates downward or the right pelvis rotates upward; (left lateral tilt); accomplished by left hip abduction, right hip adduction, and/or right lumbar lateral flexion Left Transverse Pelvic Rotation: in a horizontal plane of motion, rotation of the pelvis to the body’s ...
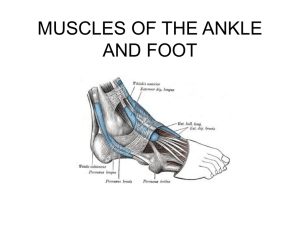
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
... Peroneus longus muscle • Origin: head and upper 2/3 of the outer surface of the fibula • Insertion: undersurfaces of the 1st cuneiform and first metatarsal bones • Note: passes posterior to lateral malleolus. • Actions: – Eversion – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral ...
... Peroneus longus muscle • Origin: head and upper 2/3 of the outer surface of the fibula • Insertion: undersurfaces of the 1st cuneiform and first metatarsal bones • Note: passes posterior to lateral malleolus. • Actions: – Eversion – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral ...
Chapter 14 - Kinesiology - Delmar
... Directional Terms Medial is toward the midline; lateral is away from the midline Proximal refers to nearest to the trunk; distal is farthest away from the trunk Inferior means below; superior means above ...
... Directional Terms Medial is toward the midline; lateral is away from the midline Proximal refers to nearest to the trunk; distal is farthest away from the trunk Inferior means below; superior means above ...
PERITONEUM and TORSION of GUT TUBE
... Genitofemoral nerve (L1-2.): Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
... Genitofemoral nerve (L1-2.): Travels through psoas major. Divides into genital and femoral branches. ...
Dissection Instructions of the Superficial Nerves of the Neck, Arm
... c. The accessory is blocked by placing the needle and giving local into the upper part (junction of the upper and middle third) of the SCM. This helps to disallow the patient from strongly turning their head towards the surgical field and helps prevent the patient from lifting their shoulder. Bot of ...
... c. The accessory is blocked by placing the needle and giving local into the upper part (junction of the upper and middle third) of the SCM. This helps to disallow the patient from strongly turning their head towards the surgical field and helps prevent the patient from lifting their shoulder. Bot of ...
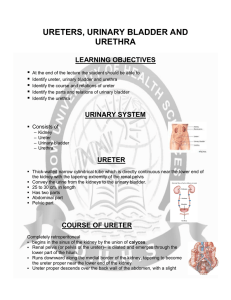
Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
... lateral to the inferior mesenteric vein. Its pelvis is more exposed than that of the right After it escapes from behind the renal vessels, it is covered only by the peritoneum. Ureter proper, as on the right side, is separated at intervals from the peritoneum by vessels – Upper left colic ar ...
... lateral to the inferior mesenteric vein. Its pelvis is more exposed than that of the right After it escapes from behind the renal vessels, it is covered only by the peritoneum. Ureter proper, as on the right side, is separated at intervals from the peritoneum by vessels – Upper left colic ar ...
Mouth and Mastication
... All supplied by the mandibular division of the Trigeminal nerve Temporalis: Temporal fossa to Coronoid process => elevate & retract Masseter: Angle of the mandible to the zygomatic arch => elevator Medial pterygoid: Inside angle of mandible to medial side of lateral pterygoid ...
... All supplied by the mandibular division of the Trigeminal nerve Temporalis: Temporal fossa to Coronoid process => elevate & retract Masseter: Angle of the mandible to the zygomatic arch => elevator Medial pterygoid: Inside angle of mandible to medial side of lateral pterygoid ...
Axillary Artery
... -Impaired movement of the 1st, 4th, and 5th digits-resulting in poor grasp.(CLAW HAND) -Inability to abduct or adduct medial four digits due to loss of interosseous muscles. -Loss of sensation to 5th and ½ of 4th digit on palm side. -Loss of sensation to 5th, 4th(minus the tip), 3rd(minus the tip). ...
... -Impaired movement of the 1st, 4th, and 5th digits-resulting in poor grasp.(CLAW HAND) -Inability to abduct or adduct medial four digits due to loss of interosseous muscles. -Loss of sensation to 5th and ½ of 4th digit on palm side. -Loss of sensation to 5th, 4th(minus the tip), 3rd(minus the tip). ...
CASEPRESENTATION ON FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURE
... is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera. ...
... is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera. ...
Flexor retinaculum
... wrist and is continuous with the deep fascia of the forearm. The lower border is attached to the palmar aponeurosis ...
... wrist and is continuous with the deep fascia of the forearm. The lower border is attached to the palmar aponeurosis ...
Gastro06-AbWallPeritonealCavityPt2
... 4. This liquid will NOT EXTEND IN THE THIGH because of the attachment of the Scarpa’s fascia to the fascia lata a few inches below the inguinal ligament. Description of the Inguinal Canal and Spermatic Cord (Moore 130-132, N242-245) 1. As the testes descend during development, they must push through ...
... 4. This liquid will NOT EXTEND IN THE THIGH because of the attachment of the Scarpa’s fascia to the fascia lata a few inches below the inguinal ligament. Description of the Inguinal Canal and Spermatic Cord (Moore 130-132, N242-245) 1. As the testes descend during development, they must push through ...
The Cranial Nerves
... The fibers emerge from the anterior surface of the medulla oblongata through the sulcus between the pyramid and the olive. Foramen of exit from skull: Hypoglossal canal ...
... The fibers emerge from the anterior surface of the medulla oblongata through the sulcus between the pyramid and the olive. Foramen of exit from skull: Hypoglossal canal ...
Leg
... Regio cruris - Leg o between knee & ankle joint o includes most of tibia & fibula Distally, structures pass between the leg & foot mainly through tarsal tunnel on the posteromedial side of the ankle, Except anterior tibial artery & ends of the deep and superficial fibular nerves ...
... Regio cruris - Leg o between knee & ankle joint o includes most of tibia & fibula Distally, structures pass between the leg & foot mainly through tarsal tunnel on the posteromedial side of the ankle, Except anterior tibial artery & ends of the deep and superficial fibular nerves ...
4. Cardiovascular System - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... posterior to the sternoclavicular (SC) joints. ...
... posterior to the sternoclavicular (SC) joints. ...
Flexor Digitorum Profondus Flexor Pollicis Longus Pronator
... Median nerve, Tendons of Flexor digitorum superficialis, Tendons of Flexor digitorum profondus, Tendons of Flexor pollicis longus, Ulnar bursa, Radial bursa ** The tendon of Flexor carpi radialis lies between the retinaculm and its deep slip, in the groove of trapezium** ...
... Median nerve, Tendons of Flexor digitorum superficialis, Tendons of Flexor digitorum profondus, Tendons of Flexor pollicis longus, Ulnar bursa, Radial bursa ** The tendon of Flexor carpi radialis lies between the retinaculm and its deep slip, in the groove of trapezium** ...
1. The gastroesophageal junction occurs at - NYCC SP-01
... 59. The ligament that anchors the uterus to the lateral wall of the pelvis is: a) suspensory ligament b) Broad ligament c) Ovarian ligament d) Round ligament 60. A surge of which female hormone is the primary cause of ovulation: a) Estrogen b)FSH c)LH d)Human Chorionic gonadotrphin 61. Spermatogenes ...
... 59. The ligament that anchors the uterus to the lateral wall of the pelvis is: a) suspensory ligament b) Broad ligament c) Ovarian ligament d) Round ligament 60. A surge of which female hormone is the primary cause of ovulation: a) Estrogen b)FSH c)LH d)Human Chorionic gonadotrphin 61. Spermatogenes ...
An anomalous muscle in the forearm extensor compartment
... abductor pollicis longus, which has a similar orientation. Interestingly, this anomalous muscle also has an anomalous insertion site, located proximal to the styloid process of the radius. Although many anomalous muscles from the extensor compartment of the forearm have been reported,5 the present v ...
... abductor pollicis longus, which has a similar orientation. Interestingly, this anomalous muscle also has an anomalous insertion site, located proximal to the styloid process of the radius. Although many anomalous muscles from the extensor compartment of the forearm have been reported,5 the present v ...
AP Biology
... Bilaterally symmetrical animals have A dorsal (top) side and a ventral (bottom) side A right and left side Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends ...
... Bilaterally symmetrical animals have A dorsal (top) side and a ventral (bottom) side A right and left side Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends ...
Critical Content/Concept Web
... 1. The structure of a neuron and how it functions. 2. The difference between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. 3. The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord. 4. The CNS is the control center for the body. 5. The anatomical structure of the spinal cord. 6. The major regions of the brain and ...
... 1. The structure of a neuron and how it functions. 2. The difference between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. 3. The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord. 4. The CNS is the control center for the body. 5. The anatomical structure of the spinal cord. 6. The major regions of the brain and ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.