Clinical head and neck
... At the medial border of scalenus anterior it joins the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein. ...
... At the medial border of scalenus anterior it joins the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein. ...
A.) Oral Phase - WordPress.com
... Note: Only going from my experience with my donor on this answer 1.) Anterior approach Reflect the masseter muscle, tendon of temporalis Remove the superior portion of the mandible, from the angle to the TMJ ...
... Note: Only going from my experience with my donor on this answer 1.) Anterior approach Reflect the masseter muscle, tendon of temporalis Remove the superior portion of the mandible, from the angle to the TMJ ...
6 and 7- Thoracic Spine Thorax Functions: Shield (vessels, lymph
... Ex: If found in extension and rotated left, then somatic dysfunction is E RLSL and the treatment position is F RRSR III. Initiation of motion in any one plane will modify motion in the other two planes. ...
... Ex: If found in extension and rotated left, then somatic dysfunction is E RLSL and the treatment position is F RRSR III. Initiation of motion in any one plane will modify motion in the other two planes. ...
Mollusks have a soft body and share several characteristics
... Mollusks have a muscular foot used for locomotion and anchorage that varies in shape and function, depending on the type of mollusk under study. In shelled mollusks, this foot is usually the same size as the opening of the shell. The foot is a retractable as well as an extendable organ. It is the ve ...
... Mollusks have a muscular foot used for locomotion and anchorage that varies in shape and function, depending on the type of mollusk under study. In shelled mollusks, this foot is usually the same size as the opening of the shell. The foot is a retractable as well as an extendable organ. It is the ve ...
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan
... catch dislodged emboli from veins of lower limb and pelvis. ...
... catch dislodged emboli from veins of lower limb and pelvis. ...
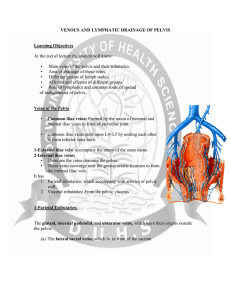
Anatomy - venous and lymphatic drainage of pelvis
... Surround internal iliac vessels. • Internal iliac and sacral lymph nodes receive afferents from all the pelvic viscera (e.g., cervix, prostate, and rectum) and from the perineum, buttock, and thigh they drain into the common iliac nodes. ...
... Surround internal iliac vessels. • Internal iliac and sacral lymph nodes receive afferents from all the pelvic viscera (e.g., cervix, prostate, and rectum) and from the perineum, buttock, and thigh they drain into the common iliac nodes. ...
Cat Dissection PreLab
... http://vanat.cvm.umn.edu/anatDirections/#directions 1. Use the link above to draw a cat and label the external anatomy of the cat. 2. Include the external anatomy, directional terms, and planes of division. (You will be referring to this as you dissect the cat, so make it nice and neat. http://www.n ...
... http://vanat.cvm.umn.edu/anatDirections/#directions 1. Use the link above to draw a cat and label the external anatomy of the cat. 2. Include the external anatomy, directional terms, and planes of division. (You will be referring to this as you dissect the cat, so make it nice and neat. http://www.n ...
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
... catch dislodged emboli from veins of lower limb and pelvis. ...
... catch dislodged emboli from veins of lower limb and pelvis. ...
Triangles of neck
... Internal carotid artery • It ascends upward within carotid sheath from its origin. • First; it is SF to ECA but then it becomes behind & deep to ECA. • At base of skull; it enters carotid canal to gain access to cranial cavity. • It gives no branches in the neck. ...
... Internal carotid artery • It ascends upward within carotid sheath from its origin. • First; it is SF to ECA but then it becomes behind & deep to ECA. • At base of skull; it enters carotid canal to gain access to cranial cavity. • It gives no branches in the neck. ...
Abdominal Cavity III
... Parietal branches of descending aorta • phrenic artery - at base of diaphragm - usually give off superior suprarenals • gonadal artery: either ovarian or testicular - at T12 or L1, • lumbar artery(4 pairs) to posterior wall structures • Middle sacral artery : single /unpaired vessel at bifurcation ...
... Parietal branches of descending aorta • phrenic artery - at base of diaphragm - usually give off superior suprarenals • gonadal artery: either ovarian or testicular - at T12 or L1, • lumbar artery(4 pairs) to posterior wall structures • Middle sacral artery : single /unpaired vessel at bifurcation ...
Anatomy of the heart
... as sinus 2 or left coronary aortic sinus). The branches of the coronary arteries are shown in Figure 1 and listed in Table 1. The third sinus is named the right posterior sinus or non-coronary sinus.6 Right coronary artery The right coronary artery passes anteriorly from its origin between the right ...
... as sinus 2 or left coronary aortic sinus). The branches of the coronary arteries are shown in Figure 1 and listed in Table 1. The third sinus is named the right posterior sinus or non-coronary sinus.6 Right coronary artery The right coronary artery passes anteriorly from its origin between the right ...
US Evaluation of Biceps Tendon
... extension and elbow pronation – Can abduct shoulder with arm externally rotated ...
... extension and elbow pronation – Can abduct shoulder with arm externally rotated ...
Lecture 1
... A muscular tube extending from the oropharynx to the stomach First lies between the trachea and the cervical muscles Soon deviates to the right throughout its entire course in the neck Ventral wall greatly expanded at the thoracic inlet forming the crop which bulges further to the right and lies aga ...
... A muscular tube extending from the oropharynx to the stomach First lies between the trachea and the cervical muscles Soon deviates to the right throughout its entire course in the neck Ventral wall greatly expanded at the thoracic inlet forming the crop which bulges further to the right and lies aga ...
Introduction to Human Osteology Chapter 5: Pelvis and Dentition
... Two parts make up the structure of teeth: a portion within the mouth called the crown, and a portion within the jaw called the root. The outer surface of the crown seen in the mouth is a hard white substance called enamel. Directly beneath the enamel is a softer material called dentine. The central ...
... Two parts make up the structure of teeth: a portion within the mouth called the crown, and a portion within the jaw called the root. The outer surface of the crown seen in the mouth is a hard white substance called enamel. Directly beneath the enamel is a softer material called dentine. The central ...
Shark and Perch
... To view this system you need to remove all of the digestive tract: 1. Remove the liver by cutting at its cranial end. 2. Cut through the esophagus where it enters the body cavity above the stomach. 3. Cut the colon at its caudal end. 4. Cut the membranes attaching the stomach, intestine, pancreas an ...
... To view this system you need to remove all of the digestive tract: 1. Remove the liver by cutting at its cranial end. 2. Cut through the esophagus where it enters the body cavity above the stomach. 3. Cut the colon at its caudal end. 4. Cut the membranes attaching the stomach, intestine, pancreas an ...
An Anatomical Study Of Indrabasti Marma
... and wrist (Prakoshta Madhya), slightly branches, radial artery and median nerve are towards the hand. Part of forearm which is also present. As Acharya Susruta mentioned, situated between elbow and wrist is called that injury to the Indrabasti marama causes Prakoshta. Normally the length of adult de ...
... and wrist (Prakoshta Madhya), slightly branches, radial artery and median nerve are towards the hand. Part of forearm which is also present. As Acharya Susruta mentioned, situated between elbow and wrist is called that injury to the Indrabasti marama causes Prakoshta. Normally the length of adult de ...
Lower Leg, Ankle, and Foot Conditions
... Lower leg provides – Support for the entire body – Propulsion through space – Adaptation to uneven terrain – Absorption of shock ...
... Lower leg provides – Support for the entire body – Propulsion through space – Adaptation to uneven terrain – Absorption of shock ...
35–1 Human Body Systems
... types of tissue in the human body: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle. Slide 4 of 33 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... types of tissue in the human body: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle. Slide 4 of 33 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Surgical Science Generic Examination Anatomy MCQ Sample Paper
... E. in resuscitation of the newborn, the length of the trachea approximates the distance from the tragus of the ear to the tip of the nose ...
... E. in resuscitation of the newborn, the length of the trachea approximates the distance from the tragus of the ear to the tip of the nose ...
Biology_218_Lecture_Outline_24_Respration
... b. internal portion, which consists of a large cavity surrounded by bones; - it is located inferior to the nasal bones and superior to the mouth - anteriorly, it merges with the external nose - posteriorly, it communicates with the pharynx via two internal nares (choanae) - its walls have openings f ...
... b. internal portion, which consists of a large cavity surrounded by bones; - it is located inferior to the nasal bones and superior to the mouth - anteriorly, it merges with the external nose - posteriorly, it communicates with the pharynx via two internal nares (choanae) - its walls have openings f ...
Introduction to spinal examination
... 4. Ask the patient to touch their toes – full lumbar flexion 5. Measure the distance between the two lines (started at 15cm) Normally the distance between the two marks should increase to >20cm. Reduced range of motion can indicate conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis. ...
... 4. Ask the patient to touch their toes – full lumbar flexion 5. Measure the distance between the two lines (started at 15cm) Normally the distance between the two marks should increase to >20cm. Reduced range of motion can indicate conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis. ...
1 Female Pelvis Uterus, Cervix, and Vagina Ashley Dobos Lynn Ta
... its lateral borders are the cornua, where the fallopian tubes enter the uterine cavity (Hagen-Ansert p. 860, 2/1/2), (Curry-Tempkin p. 278, Fig.16-38). The body or corpus of the uterus lies between the fundus and the cervix and is the largest portion of the uterus. It is also continuous with the u ...
... its lateral borders are the cornua, where the fallopian tubes enter the uterine cavity (Hagen-Ansert p. 860, 2/1/2), (Curry-Tempkin p. 278, Fig.16-38). The body or corpus of the uterus lies between the fundus and the cervix and is the largest portion of the uterus. It is also continuous with the u ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.