upper limb vessels
... Commences lower border of teres major axillary vein on medial side median nerve lateral to it proximally but then crosses in front of it to lie medial ulnar nerve is posterior to it proximally but leaves it as it slopes downward thru the medial IM septum Branches o Muscular branches o Nutr ...
... Commences lower border of teres major axillary vein on medial side median nerve lateral to it proximally but then crosses in front of it to lie medial ulnar nerve is posterior to it proximally but leaves it as it slopes downward thru the medial IM septum Branches o Muscular branches o Nutr ...
Variation of Nerve to Flexor Hallucis Brevis
... in 40 of 45 patients with complete division of the median or ulnar nerves. Falconer and Spinner2 performed high magnification dissections of ten specimens and found the RicheCannieu anastomosis in three. While the purpose of this study was to determine the presence of Hallopeau’s nerve, we can not c ...
... in 40 of 45 patients with complete division of the median or ulnar nerves. Falconer and Spinner2 performed high magnification dissections of ten specimens and found the RicheCannieu anastomosis in three. While the purpose of this study was to determine the presence of Hallopeau’s nerve, we can not c ...
Anatomic study of infrapopliteal vessels
... arteries (92.2%); (IB) the AT, PR, and PT arise within 0.5 cm (2%); the PT is the first branch followed by the anterior tibioperoneal trunk that bifurcates into the PR and AT (1.2%). In type II, the popliteal artery has a high division; (IIA) when the AT arises above the knee joint (3.7%); (IIB) whe ...
... arteries (92.2%); (IB) the AT, PR, and PT arise within 0.5 cm (2%); the PT is the first branch followed by the anterior tibioperoneal trunk that bifurcates into the PR and AT (1.2%). In type II, the popliteal artery has a high division; (IIA) when the AT arises above the knee joint (3.7%); (IIB) whe ...
The Cranial Bones
... Are areas of fibrous connective tissue (soft spots) Cover unfused sutures in the infant skull Allow the skull to flex during birth ...
... Are areas of fibrous connective tissue (soft spots) Cover unfused sutures in the infant skull Allow the skull to flex during birth ...
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
... feet of large intestine, or colon, which ends in the rectum. Just above the rectum is the sigmoid (s-shaped) part of the colon where diverticulosis usually occurs. About two gallons of liquid stool enters the right colon each day where excess water is purified and recycled back into the blood stream ...
... feet of large intestine, or colon, which ends in the rectum. Just above the rectum is the sigmoid (s-shaped) part of the colon where diverticulosis usually occurs. About two gallons of liquid stool enters the right colon each day where excess water is purified and recycled back into the blood stream ...
The Skeleton - Sinoe Medical Association
... Forms a protective cage around the heart, lungs, and great blood vessels Supports the shoulder girdles and upper limbs Provides attachment for many neck, back, chest, and shoulder muscles Uses intercostal muscles to lift and depress the thorax during breathing ...
... Forms a protective cage around the heart, lungs, and great blood vessels Supports the shoulder girdles and upper limbs Provides attachment for many neck, back, chest, and shoulder muscles Uses intercostal muscles to lift and depress the thorax during breathing ...
CHAPTER 5
... If the reader is unfamiliar with the basic structure of the innominate bone, he or she should refer to Chapter 12. ...
... If the reader is unfamiliar with the basic structure of the innominate bone, he or she should refer to Chapter 12. ...
Gross 2 notes C
... Anterior ethmoidal artery, anterior septal branch, anterolateral nasal branch Posterior ethmoidal branches – septal and lateral nasal branches some form anterior some from posterior External carotid terminates as maxillary and superficial temporal Posterior septal branch, posterior lateral nasal bra ...
... Anterior ethmoidal artery, anterior septal branch, anterolateral nasal branch Posterior ethmoidal branches – septal and lateral nasal branches some form anterior some from posterior External carotid terminates as maxillary and superficial temporal Posterior septal branch, posterior lateral nasal bra ...
TMJ
... Danlos syndrome, etc. can be the predisposing factors. The use of antipsychotic drugs may cause extrapyramidal reactions and dislocation. Clinical picture o f acute dislocation Dislocation is a dramatic event. It maybe unilateral or bilateral. 1 listory of the patient may be diagnostic. Unilateral ...
... Danlos syndrome, etc. can be the predisposing factors. The use of antipsychotic drugs may cause extrapyramidal reactions and dislocation. Clinical picture o f acute dislocation Dislocation is a dramatic event. It maybe unilateral or bilateral. 1 listory of the patient may be diagnostic. Unilateral ...
11. Axial Muscles
... describes the muscle’s action, location, number of heads, orientation of muscle fibers, shape, or size. Refer to figure 10.14 for examples of how some muscles are named. ...
... describes the muscle’s action, location, number of heads, orientation of muscle fibers, shape, or size. Refer to figure 10.14 for examples of how some muscles are named. ...
Lecture 6- sacral plexus femoral and sciatic nerves
... rami of L1,2,3 and most of L4, in the substance of psoas major muscle. The sacral plexus is formed by ventral (anterior) rami of a part of L4 & whole L5 (lumbosacral trunk) + S1,2,3 and most of S4, in front of piriformis msucle. The femoral nerve, a branch of lumbar plexus (L2,3,4). Its injury l ...
... rami of L1,2,3 and most of L4, in the substance of psoas major muscle. The sacral plexus is formed by ventral (anterior) rami of a part of L4 & whole L5 (lumbosacral trunk) + S1,2,3 and most of S4, in front of piriformis msucle. The femoral nerve, a branch of lumbar plexus (L2,3,4). Its injury l ...
( arrows ). - Rackcdn.com
... Supplies the muscles of the lower lip and chin: Quadratus labii inferioris muscle Lower part of the orbicularis oris muscle ...
... Supplies the muscles of the lower lip and chin: Quadratus labii inferioris muscle Lower part of the orbicularis oris muscle ...
Identifying pericardial recesses on computed tomography : is it
... lymphadenopathy or vice versa can have important clinical ramifications especially in onco-imaging. Occasional prominence of one or more recess in comparison to others increases the probability of misinterpretation ...
... lymphadenopathy or vice versa can have important clinical ramifications especially in onco-imaging. Occasional prominence of one or more recess in comparison to others increases the probability of misinterpretation ...
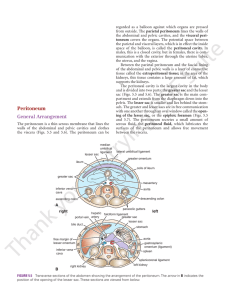
Peritoneum
... Movement of Peritoneal Fluid The peritoneal cavity is divided into an upper part within the abdomen and a lower part in the pelvis. The abdominal part is further subdivided by the many peritoneal reflections into important recesses and spaces, which, in turn, are continued into the paracolic gutters ...
... Movement of Peritoneal Fluid The peritoneal cavity is divided into an upper part within the abdomen and a lower part in the pelvis. The abdominal part is further subdivided by the many peritoneal reflections into important recesses and spaces, which, in turn, are continued into the paracolic gutters ...
Body in Balance - Science4Inquiry.com
... screen” so that the web page advertisements located on the right-hand side and underneath the video will not be seen. In addition, please be on the lookout for “pop up” ads while the video is playing 2. Teacher will ask students to THINK about the following question: a. What is one word you would us ...
... screen” so that the web page advertisements located on the right-hand side and underneath the video will not be seen. In addition, please be on the lookout for “pop up” ads while the video is playing 2. Teacher will ask students to THINK about the following question: a. What is one word you would us ...
Document
... Remember when we discussed the abdominal muscles, we said that the external oblique muscle will reflect on itself, and extends from the anterior superior iliac spine to the symphysis tubercle and form what is known as the inguinal ligament. This muscle extends all the way medially to the pubic symph ...
... Remember when we discussed the abdominal muscles, we said that the external oblique muscle will reflect on itself, and extends from the anterior superior iliac spine to the symphysis tubercle and form what is known as the inguinal ligament. This muscle extends all the way medially to the pubic symph ...
Bones of the Upper Limb Bone Structure Description Notes clavicle an
... the capitate is the largest carpal bone; it is named for its rounded head; forces generated in the hand (as during a punching blow with the fist) are transmitted through the third metacarpal bone to the capitate and proximally through the lunate to the radius the hamulus (hook) of the hamate is its ...
... the capitate is the largest carpal bone; it is named for its rounded head; forces generated in the hand (as during a punching blow with the fist) are transmitted through the third metacarpal bone to the capitate and proximally through the lunate to the radius the hamulus (hook) of the hamate is its ...
ORAL REGION ORAL CAVITY Mouth consists of ORAL VESTIBULE
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
shouldergirdle chp 8
... weeks and then exercise Grade three immobilize 5 weeks and then exercise ...
... weeks and then exercise Grade three immobilize 5 weeks and then exercise ...
Movement
... MOVEMENT OF TORSION BY THE VAULT During the phase of expansion, to carry out a movement of right torsion, the therapitist carries out a movement of inflection to which he adds a component of flexion in the following ...
... MOVEMENT OF TORSION BY THE VAULT During the phase of expansion, to carry out a movement of right torsion, the therapitist carries out a movement of inflection to which he adds a component of flexion in the following ...
Movement
... MOVEMENT OF TORSION BY THE VAULT During the phase of expansion, to carry out a movement of right torsion, the therapitist carries out a movement of inflection to which he adds a component of flexion in the following ...
... MOVEMENT OF TORSION BY THE VAULT During the phase of expansion, to carry out a movement of right torsion, the therapitist carries out a movement of inflection to which he adds a component of flexion in the following ...
Morphological and Topographical Study of the Degree of Angulation
... Susruta in the sixth century BC correctly described the hip bone. In the fifth century BC Hippocrates wrote on the articulation of the hip joint. In the late nineteenth century, Eadweard Muybridge photographed human motion in rapid sequence to examine the action of various levers of the body. Recent ...
... Susruta in the sixth century BC correctly described the hip bone. In the fifth century BC Hippocrates wrote on the articulation of the hip joint. In the late nineteenth century, Eadweard Muybridge photographed human motion in rapid sequence to examine the action of various levers of the body. Recent ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.